Notes from Walmart’s 2018 Investment Community Meeting
Walmart hosted its 2018 Investment Community Meeting in Bentonville, Arkansas on October 16. The event included presentations from CEO Doug McMillon; EVP and CFO Brett Biggs; Walmart International President and CEO Judith McKenna; and Sam’s Club President and CEO John Furner.
Also present were Walmart E-Commerce US President and CEO Marc Lore; Walmart US President and CEO Greg Foran; Walmart US Chief Merchandising Officer Steve Bratspies; Walmart US EVP, Realty & Central Operations, Mark Ibbotson; and Walmart US EVP and Chief Customer Officer, Janey Whiteside.
McMillon’s Thoughts on Execution, Momentum, Unique Assets and Thoughtful Investing
McMillon began his presentation with the slide shown below, which illustrates Walmart’s strong execution, including 16 consecutive quarters of positive comps for Walmart US, 36% e-commerce growth in the first half of the year, 10 consecutive quarters of positive comps for Sam’s Club, and key investments, such as acquisition of Flipkart in India.
 Walmart’s strong execution (Note: Results are for the first half of 2018.)
Source: Company presentation
Walmart’s strong execution (Note: Results are for the first half of 2018.)
Source: Company presentation
McMillon said that innovation is what drives the company and he presented examples of unsuccessful experiments (such as grocery delivery with Uber and Lyft) as well as successful programs, including:
- Walmart’s US grocery pickup service—that began in 2014 and has more than 2,000 locations today—which serves 70% of the US population;
- The company’s investment in last-mile delivery company JD Daojia, China, which grew from 16 stores two years ago to 200 Walmart stores in 30 cities currently; and
- The implementation of 500 software automation bots that use machine learning to complete manual and repetitive tasks in areas such as accounts payable, payroll, benefits, logistics and transportation, achieving $30 million in annual savings.
Walmart’s innovation, McMillon continued, is aimed at achieving several holistic goals:
- Making every day easier for busy families;
- Sharpening its focus and becoming more digital;
- Delivering strong and efficient growth; and
- Building trust with its customers.
At the same time, Walmart has, organically and through acquisition, built a portfolio of unique assets in shopping, social media and loyalty, financial services, health and wellness, digital entertainment, advertising, logistics and home and personal services.
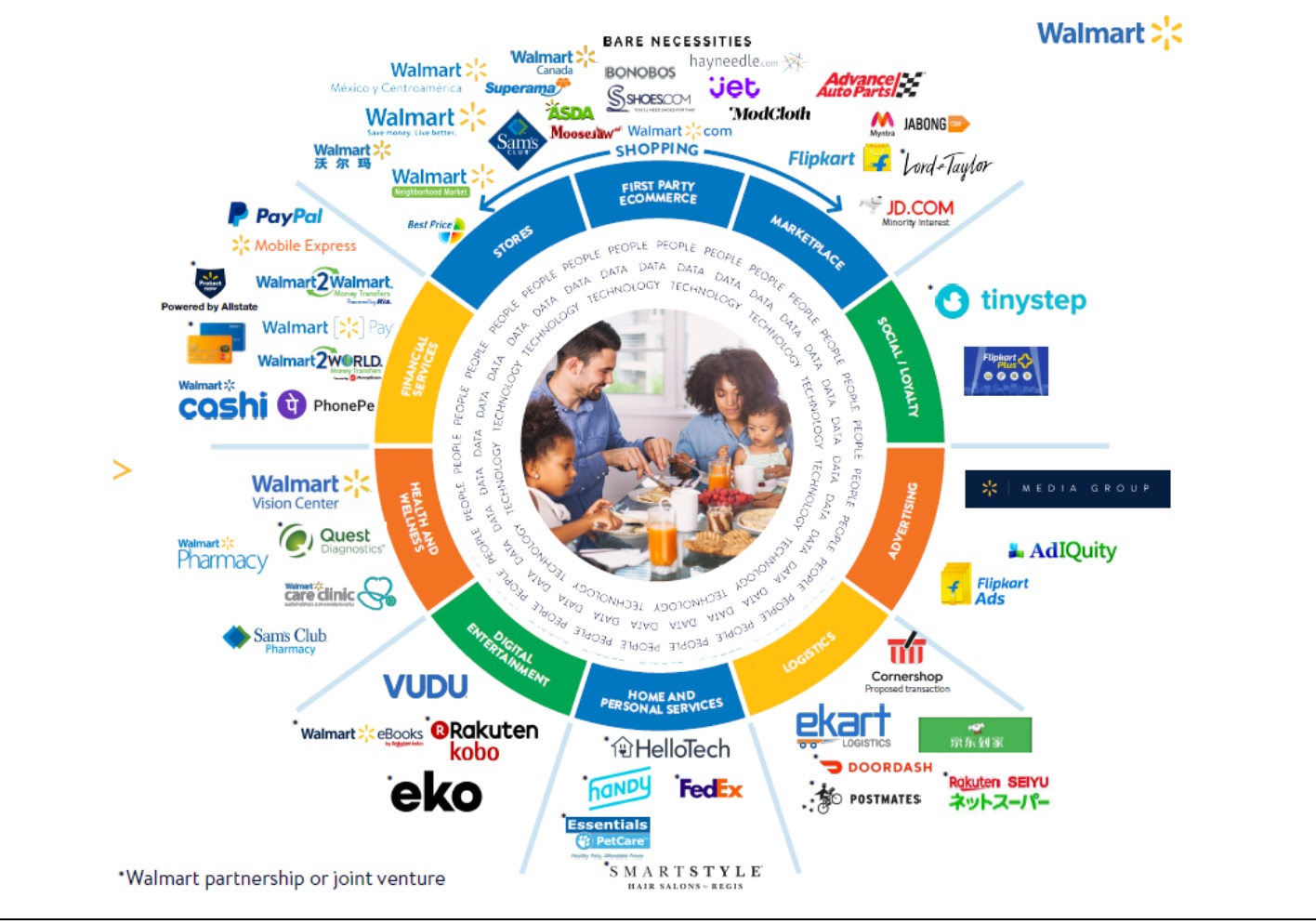 Walmart’s ecosystem
Source: Company presentation
Walmart’s ecosystem
Source: Company presentation
Finally, McMillon offered a preview of the CFO’s remarks in his pledge to operate with discipline and invest thoughtfully while striking a balance between the company’s short- long-term objectives.
McKenna’s Thoughts at the Investment Community Meeting
McKenna said that Walmart had registered $118 billion in international sales, which made it the largest retailer outside the US. In a dynamic world with changing consumer expectations, an evolving competitive landscape and growing macro complexity, Walmart’s proactive actions, such as acquisitions and divestitures, have: positioned it for success with strong local businesses; improved its omnichannel capabilities; and helped it prioritize resources and gain access to growth.
Examples of strong local businesses, which McKenna referenced, include:
- Canada, where Walmart is partnering with Penguin Pick-Up in Toronto for grocery and general merchandise and with Food-X, a company that specializes in last mile delivery of local non-organic groceries in Vancouver.
- Mexico, where Walmex is a local leader, with $30 billion in sales last year and 7.5% comparable sales so far this year. The company has recently launched Cashi, a digital payment app that serves the Mexican market, which has many unbanked consumers.
- China, where Walmart is rebalancing its business, differentiating its omnichannel value proposition and partnering for success in omnichannel, particularly with 2,500-square-foot urban fulfillment centers that offer 2,000 items, which can be picked within five minutes by associates.
- India, where Walmart has been operating for 10 years and aims to benefit from the young median age of 28, a growing middle class and good GDP growth, as well as a base of 300 million smartphone users. Flipkart’s universe is illustrated in the figure below.
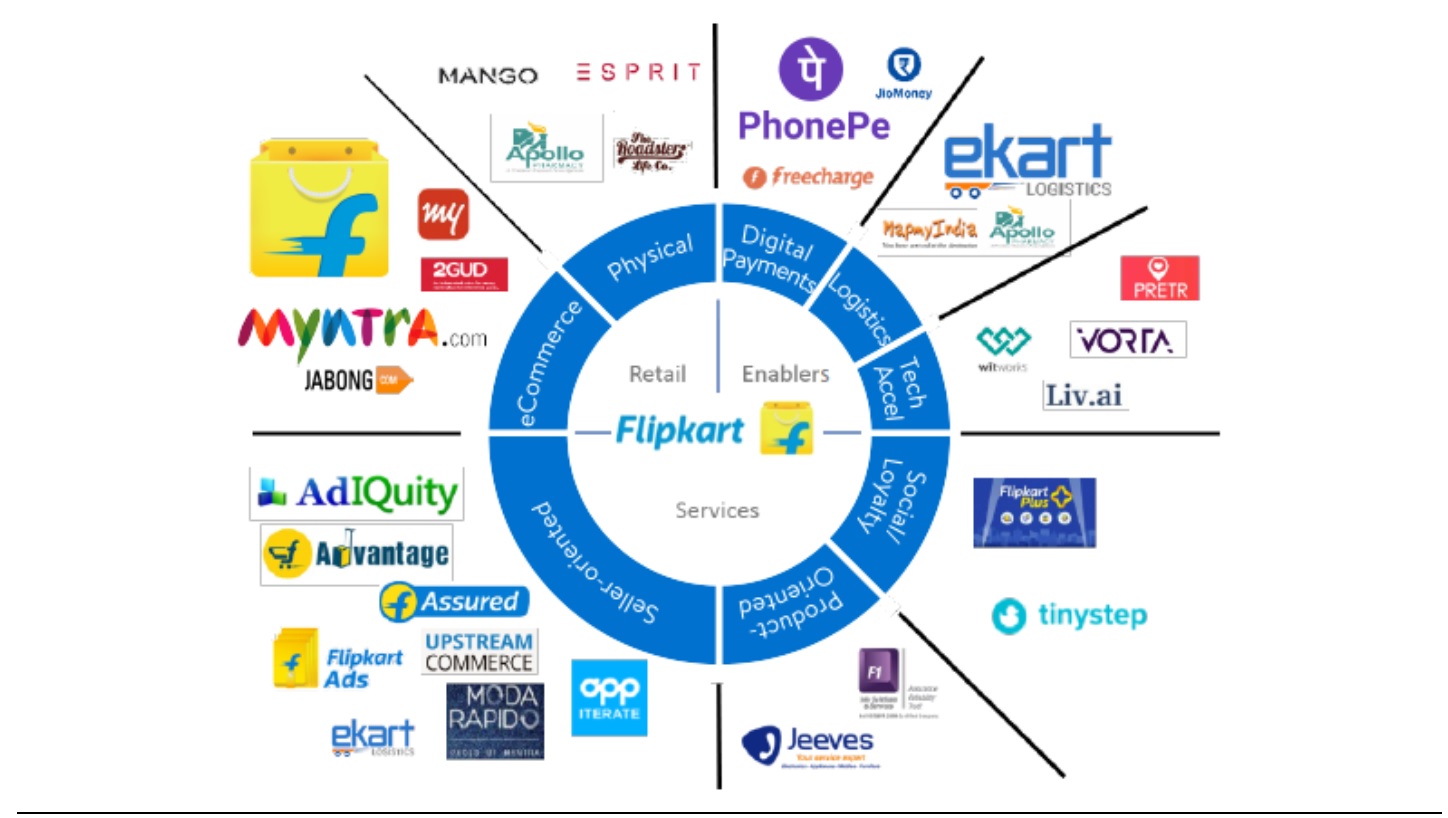 Flipkart’s ecosystem
Source: Company presentation
Flipkart’s ecosystem
Source: Company presentation
Whiteside’s Thoughts at the Investment Community Meeting
Whiteside, who joined Walmart just 11 weeks before the conference, presented the results of analyzing an enormous amount of proprietary and external data, which show that 90% of the US population shops at Walmart at least one a year and that these customers are primarily concerned with value, i.e., price.
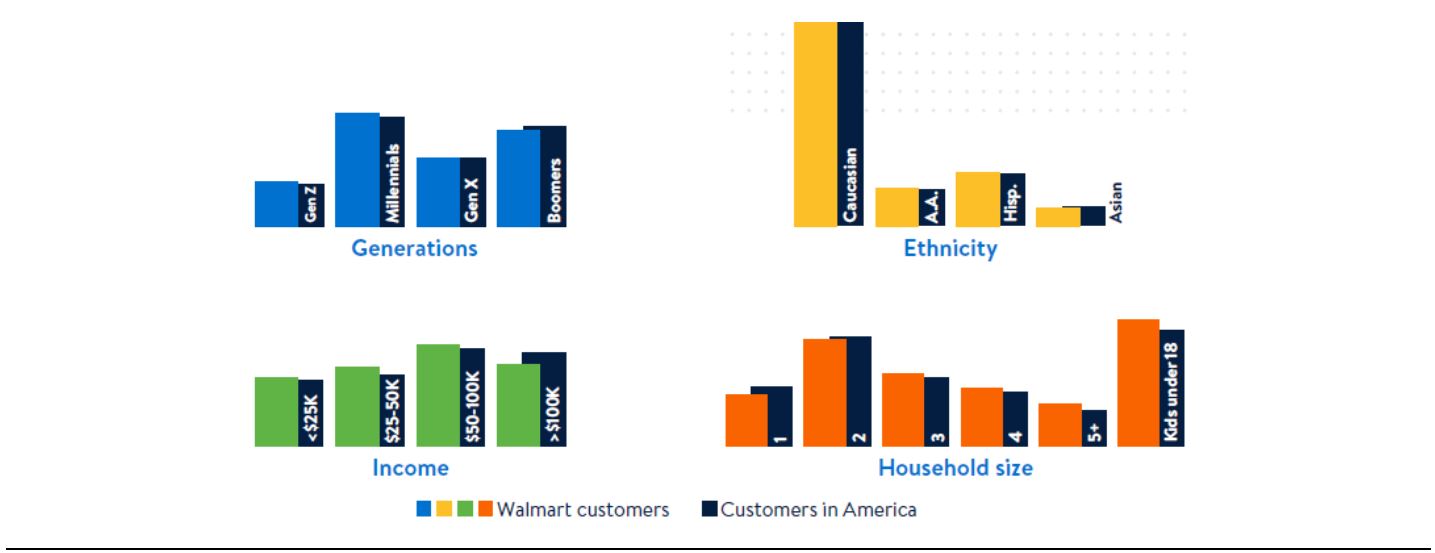 Walmart customer demographics reflect the demographics of US consumers
Source: Company presentation
Walmart customer demographics reflect the demographics of US consumers
Source: Company presentation
Lore’s Thoughts at the Investment Community Meeting
Lore presented his views in three main categories: getting traction on the fundamentals; playing offense, especially with same-day delivery; and building companies to shape future of retail.
He said that Walmart continues to expect an acceleration in e-commerce sales growth, which is expected to hit about 40% in FY19 and 35% in FY20. This growth depends on the following three pillars:
- Nail the fundamentals: Lore said he is focused on driving the customer value index (CVI) and net promoter score higher, through “have it, find it, display it, price it and deliver it.” “Have it” means offering a broader product line through partnerships with retailers and the acquisition of specialty retailers (as depicted in the figure below). “Deliver it” means accelerating delivery speed. In addition, Walmart has revamped its e-commerce webpages.
 Walmart’s new partnerships and acquisitions of specialty retailers
Source: Company presentation
Walmart’s new partnerships and acquisitions of specialty retailers
Source: Company presentation
- Leverage unique assets to play offense: Walmart can play offense: through its more than 4,700 stores which are within 10 miles of 90% of the US population; by offering same-day delivery to 40% of US households in FY19 and targeting 60% in FY20; and, offering digitally native veridical brands.
- Innovate for the future: Walmart’s innovation includes its Store No. 8 technology lab, the new Jetblack brand and three other items that will come next year.
Foran’s Thoughts at the Investment Community Meeting
Foran discussed the shift in Walmart’s focus from fixing to leading to deliver on its core strategy of running great stores, delivering value, being great merchants and providing convenience through:
- Retail fundamentals, which include delivering value, offering a great fresh food business and winning on assortment;
- Tech-empowered stores, which enhance the customer experience and support associate productivity; and
- Omnichannel capabilities, which offer anytime access and the stores become fulfillment centers.
The virtuous circle showing the benefits from transitioning from fixing to leading is illustrated below.
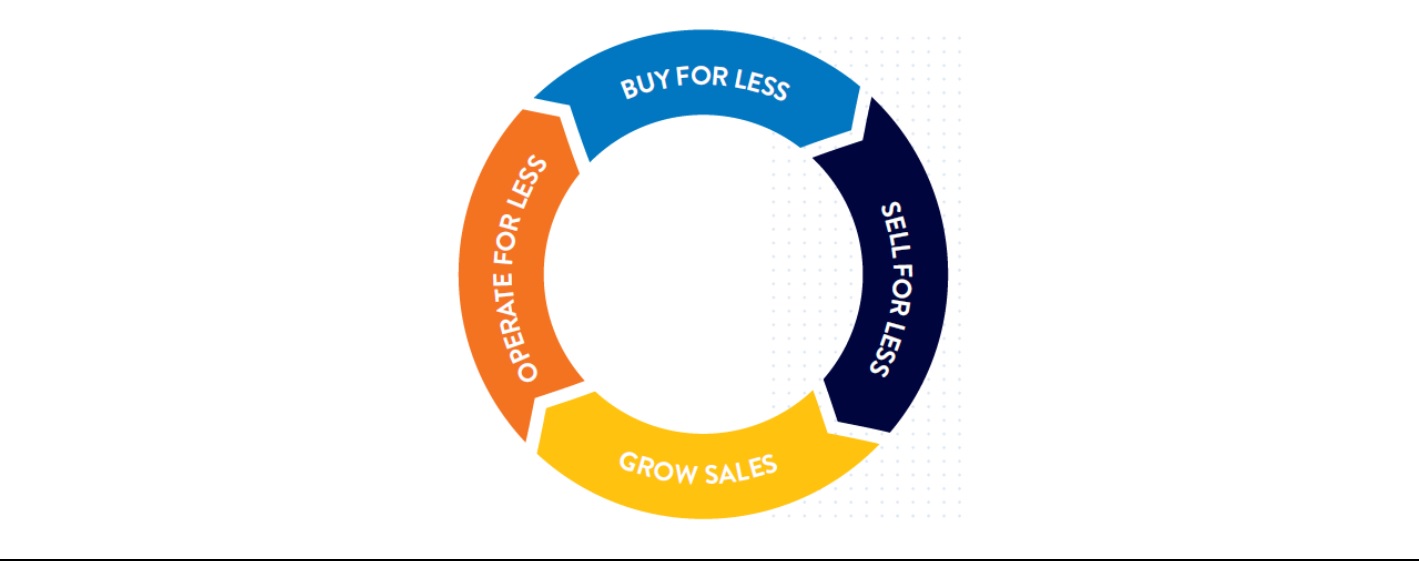 Benefits of moving from fixing to leading
Source: Company presentation
Benefits of moving from fixing to leading
Source: Company presentation
Bratspies’s Thoughts at the Investment Community Meeting
Bratspies commented that despite strong momentum in the business, there is more to do and that includes:
- Offering price leadership;
- Building a great assortment, which includes simplicity, quality and innovation;
- Creating a great customer experience, which includes the store space and customer apps; and
- Leveraging assets to drive efficiency.
Methods of increasing efficiency, suggested by Bratspies, are illustrated in the figure below.
 Methods of driving efficiency
Source: Company presentation
Methods of driving efficiency
Source: Company presentation
Ibbotson’s Thoughts at the Investment Community Meeting
Ibbotson began his remarks by discussing how tech-empowered stores support associate productivity, through training, managing inventory and growing sales.
In addition, he said, Walmart is innovating with technology and automation, as shown in the figure below.
 Walmart’s use of technology and automation
Source: Company presentation
Walmart’s use of technology and automation
Source: Company presentation
Finally, Walmart is testing future innovations for pickup and delivery, such as:
- Robot pick;
- Auto-dispense; and
- Electronic shelf-edge labels.
Furner’s Thoughts at the Investment Community Meeting
Furner discussed Sam’s Club’s focus on:
- Targeting members, from households with annual incomes of $75,000–$125,000;
- People, who are merchants, associates and technologists;
- Products, which are fresh items and private-label brands; and
- Going digital, by offering e-commerce, scan-&-go, mobile tools and at the workplace.
These factors have led to: growth in the number of members of Sam’s Club; growth in renewal rates; increased penetration; growth in the number of members per club; and the number of signups.
Biggs’s Thoughts at the Investment Community Meeting
Biggs’s presentation focused on six major points:
- Transforming to win: Biggs highlighted Walmart’s acquisitions (including Jet, Flipkart and ModCloth), partnerships (such as the one with JD.com), divestitures (such as Walmart Brasil) and tests (such as home delivery), in addition to the company’s scale and unique assets, as depicted in the figure below.
 Areas of Walmart’s transformation
Source: Company presentation
Areas of Walmart’s transformation
Source: Company presentation
- Recent investments are paying off: Recent benefits from investments in US stores, omnichannel sales, Walmart.com, and technology and process include improved customer experience scores, the opening of around 2,000 pickup locations, and 40% growth in Walmart U.S.’s e-commerce sales in the first half. Financial benefits include efficient store operations, operating expense leverage and a reduction in working capital.
- Financial priorities remain consistent: Walmart remains focused on generating strong and efficient growth, exercising efficient operating discipline and performing strategic capital allocation.
- Delivering against guidance: Biggs reiterated Walmart’s FY19 guidance, excluding the adjustment for the dilution form the Flipkart acquisition.
- Making progress on costs: Walmart is seeking to achieve the sustainable lowest cost to serve, with consistent working capital management, while focusing on technology and process, which should realize about 20 basis points (bps) of annual expense leverage.
- Good momentum: Walmart posted solid results in the first half, in terms of comparable sales, and in-store and e-commerce sales growth.

 Walmart’s strong execution (Note: Results are for the first half of 2018.)
Source: Company presentation
Walmart’s strong execution (Note: Results are for the first half of 2018.)
Source: Company presentation Walmart’s ecosystem
Source: Company presentation
Walmart’s ecosystem
Source: Company presentation Flipkart’s ecosystem
Source: Company presentation
Flipkart’s ecosystem
Source: Company presentation Walmart customer demographics reflect the demographics of US consumers
Source: Company presentation
Walmart customer demographics reflect the demographics of US consumers
Source: Company presentation Walmart’s new partnerships and acquisitions of specialty retailers
Source: Company presentation
Walmart’s new partnerships and acquisitions of specialty retailers
Source: Company presentation Benefits of moving from fixing to leading
Source: Company presentation
Benefits of moving from fixing to leading
Source: Company presentation Methods of driving efficiency
Source: Company presentation
Methods of driving efficiency
Source: Company presentation Walmart’s use of technology and automation
Source: Company presentation
Walmart’s use of technology and automation
Source: Company presentation Areas of Walmart’s transformation
Source: Company presentation
Areas of Walmart’s transformation
Source: Company presentation