
DIpil Das
Introduction
Social media has transformed from a platform that connects people to a marketplace where consumers can share their experiences and make purchases. We expect the coronavirus crisis to amplify social media’s role as a shopping platform: Faced with store closures and depressed consumer demand, US retailers must turn to channels such as social media to engage shoppers, communicate empathy, provide customer service and drive sales. This is the final report in a four-part series in which we explore the results of a Coresight Research survey of US consumers on their use of social media for shopping. This series will include three thematic reports and an overall summary of our findings. We surveyed 1,509 US Internet users aged 18 and above in November 2019. We asked respondents about a number of topics relating to their use of social media for shopping, including the following:- How often they research and discover products through social media, and specifically Instagram
- What products they have recently bought on social media, and specifically Instagram
- How often influencers and celebrities on social media and Instagram affect their shopping
- Where they shop both online and offline
- How much they spend on discretionary items and select categories
- How often they share information about their purchases on social media
Insights from Our Survey
Social media platforms most popular for shopping: Facebook and Instagram Facebook is the most widely used social media platform for shopping among US social media users, but Instagram is the most popular among respondents aged 18–24. Instagram’s image-focused nature makes it a natural starting point for consumers who want to discover products—and our survey suggests that the platform goes beyond that starting point to drive conversion to making purchases, many of which we suspect to be impulse buys. Categories most shopped on social media: Apparel and beauty Apparel and beauty are the top categories for researching and discovering or purchasing on social media—reflecting these categories’ image-driven nature. Our data suggests that these categories also see the highest rate of conversion from browsing to buying, suggesting that social media is successful in prompting impulse-driven purchases in frequently bought discretionary categories where aesthetics are key. Analysis of discretionary spending by US social media shoppers US consumers who use social media as part of the shopping process are likely to spend more on discretionary goods than those who do not. Some 11.9% of those who use social media as part of the shopping process spend over $300 a month on discretionary shopping, compared to 6.7% of consumers who do not use social media for shopping that spend the same amount. Social media influencers have an impact on shopping behavior Influencers on social media have a real impact on shopping, especially those on Instagram: 26.5% of Instagram shoppers aged 18–34 stated that their shopping is “often/always” affected by Instagram influencers and celebrities, versus the 19.7% average across all social media platforms. More males use influencers when shopping than females—to a significant degree on both social media generally and Instagram specifically. As retailers and brands rethink their media marketing mix, we advise using influencers with a niche following, whose influence may carry more weight and drive conversion better than widely followed influencers who could be perceived as opportunistic and lacking authenticity. Shoppers abandon purchases due to lack of built-in functionality Among respondents who use social media to discover products or research purchases as part of the shopping process, 17.5% will “often/always” give up the purchase due to a platform’s lack of built-in functionality. Less than one-quarter of those shoppers will continue to purchase through other channels. Post-purchase activities Our survey results suggest that respondents of all ages post information about their shopping journey, such as photos and videos of their purchases. Overall, 12.9% of respondents who use social media as part of the shopping process “often/always” post about their experiences, and the proportion peaked among shoppers aged 25–34. Implications for brands For brands and retailers, it is crucial to provide a one-step discover-to-purchase solution that will remove friction in the consumer journey and drive improved conversion rates. If the platform lacks built-in purchase functionality after consumers discover or research products, less than one-quarter of them will continue to purchase through other channels. We found that consumers with an annual income between $75,000 and $100,000 are most likely to use social media as part of shopping process, and social media shoppers tend to spend more on discretionary goods in the apparel and beauty categories. This underlines thatdeveloping a social media/commerce strategy is imperative for companies hoping to capture the custom of big spenders, especially fashion and beauty brands and retailers. Now, more than ever, retailers must embrace social channels to recover sales lost through store closures and economic disruption due to the coronavirus pandemic.Social Commerce Is Here: Top-Line Findings
Fully 92.3% of respondents said they use social media platforms. Of these social media users, 61.3% said they use social media as part of their shopping process, which includes discovering products, researching purchases or buying products—that is equivalent to 57% of all respondents. [caption id="attachment_107160" align="aligncenter" width="700"]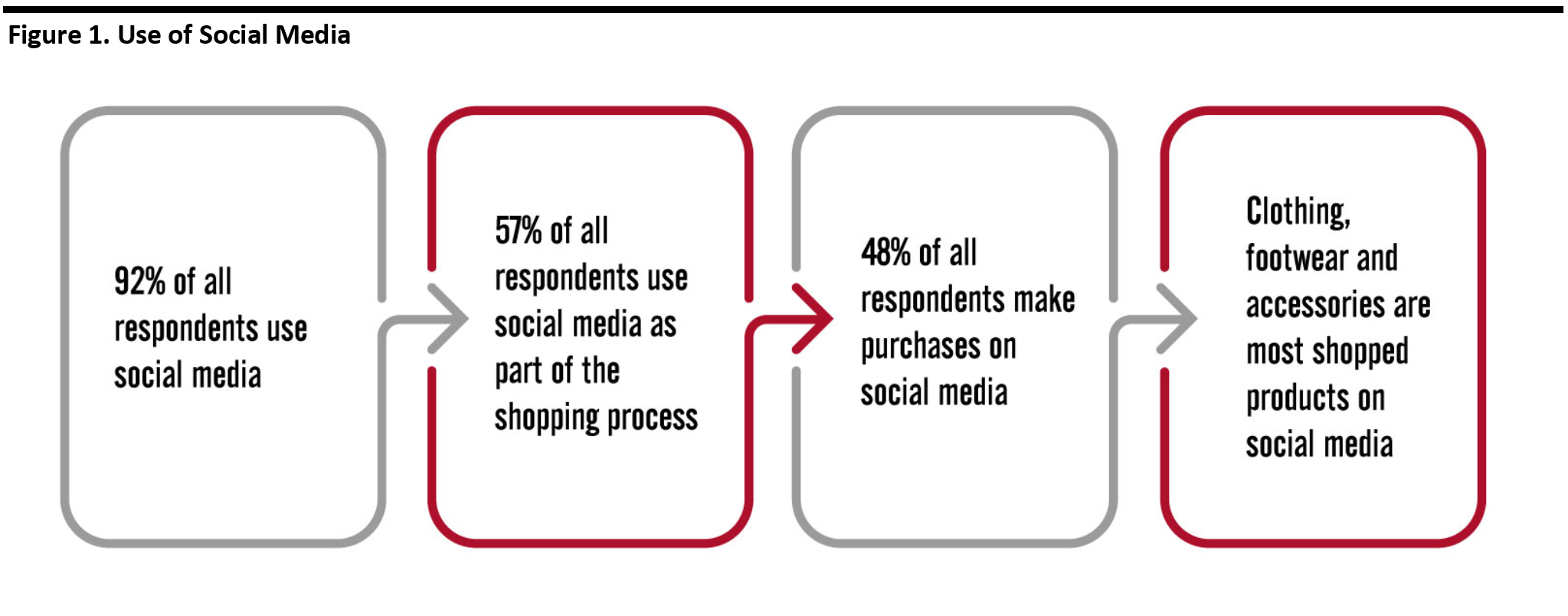 All data in this chart are shown as percentage of all respondents; later charts show percentages of subsets of respondents
All data in this chart are shown as percentage of all respondents; later charts show percentages of subsets of respondents Base; 1,509 US Internet users aged 18+, surveyed in November 2019
Source: Coresight Research [/caption] Consumers of all ages use social media as part of the shopping process, but this online channel is especially popular among 18—34 year olds (as shown in Figure 2). To effectively leverage the social media opportunity, brands and retailers should produce and share content on relevant platforms that resonates with consumers in the various age groups. [caption id="attachment_107161" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
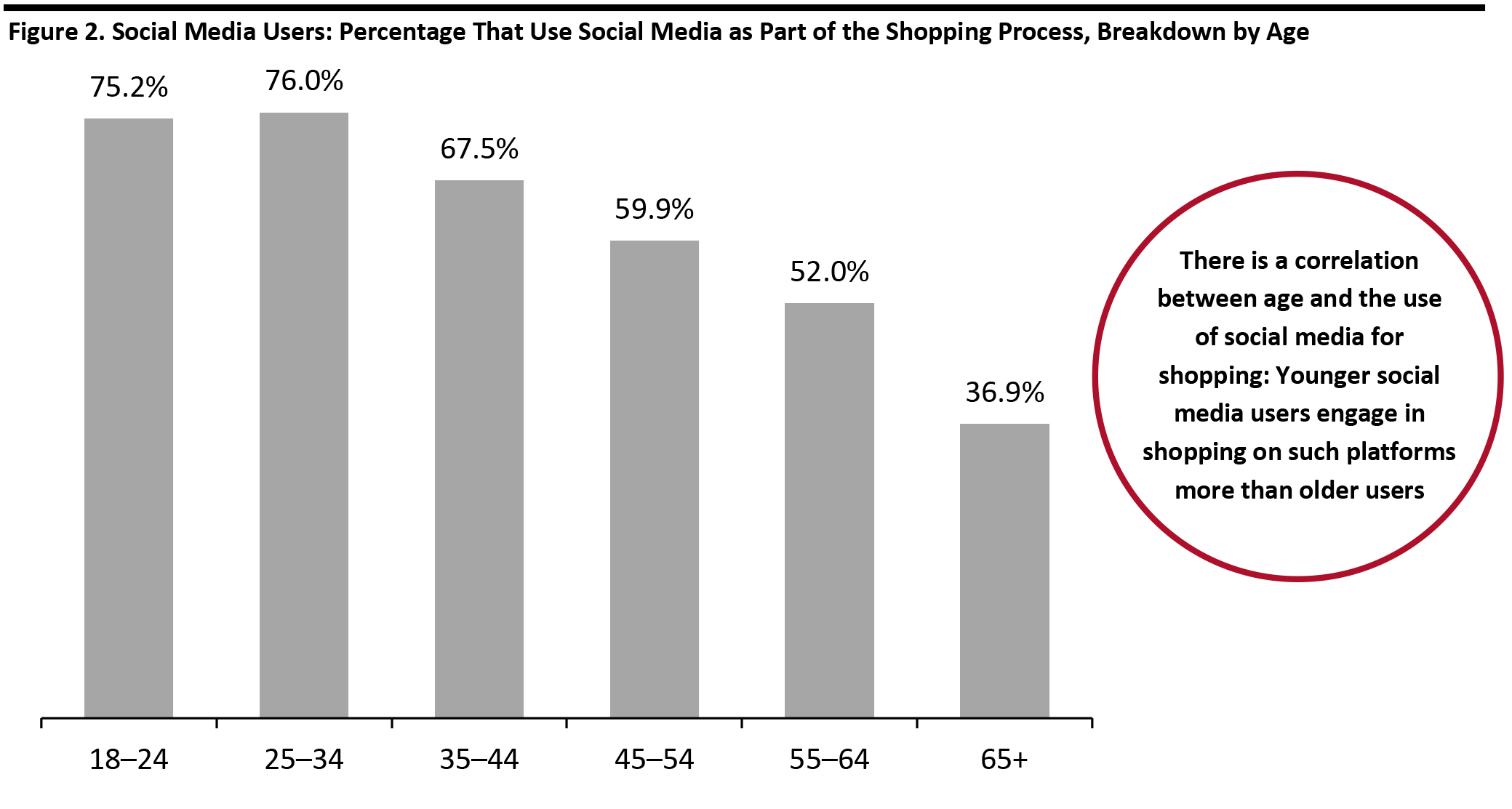 Using social media for shopping is defined as “discovering products, researching purchases or buying products on social media”
Using social media for shopping is defined as “discovering products, researching purchases or buying products on social media” Base: 1,393 US Internet respondents aged 18+ who use social media
Source: Coresight Research [/caption] Among the respondents using social media as part of the shopping process, Facebook is used by 72% for shopping, making it the most popular platform—and representing a significant lead over Instagram’s 33.0%. [caption id="attachment_107162" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
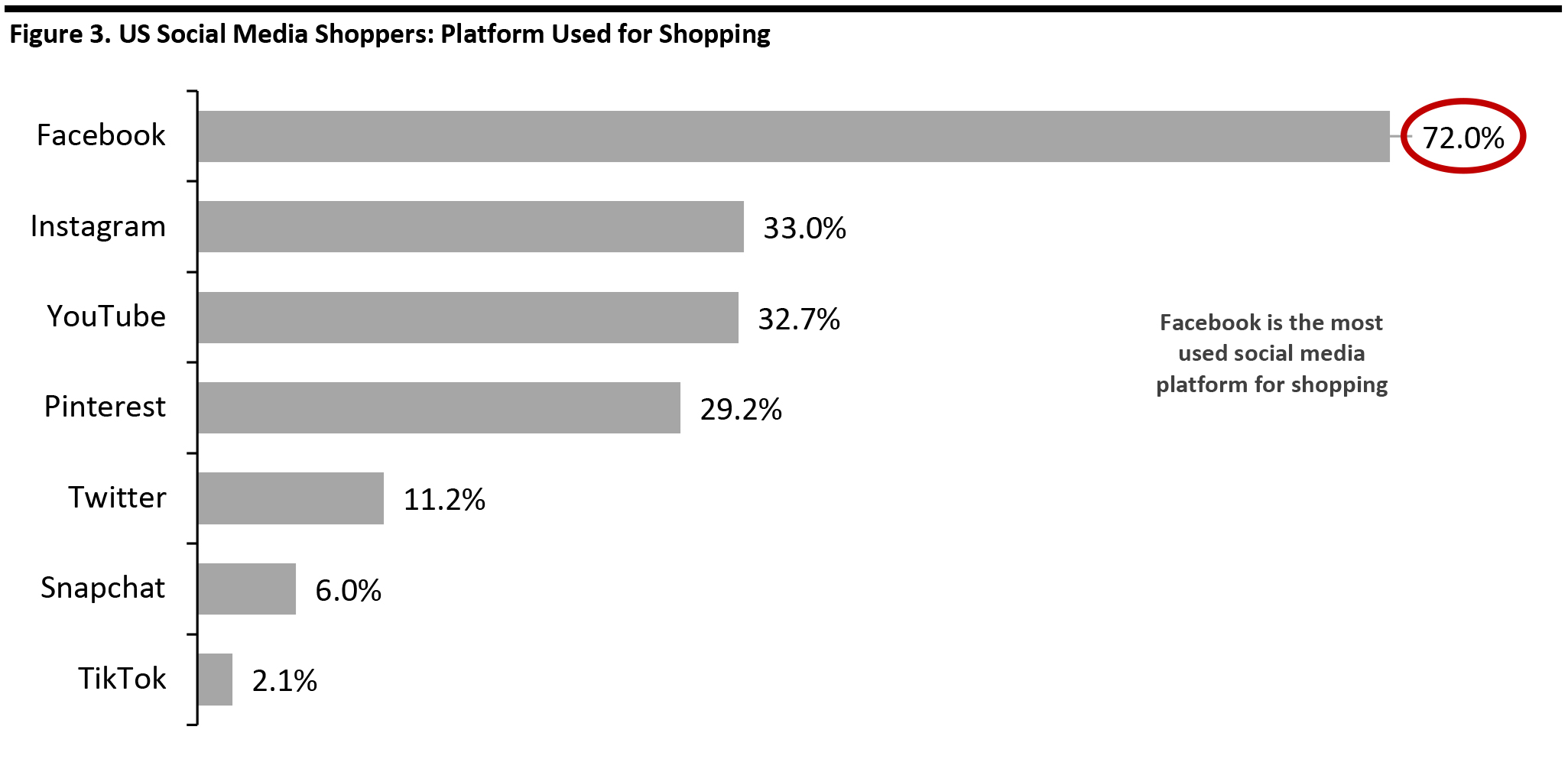 Using social media for shopping is defined as “discovering products, researching purchases or buying products on social media”
Using social media for shopping is defined as “discovering products, researching purchases or buying products on social media” Base: 854 US Internet respondents aged 18+ who use social media as part of the shopping process
Source: Coresight Research [/caption] However, Instagram proved to be the most popular platform for social media users aged 18–24: Just over two-thirds of the youngest adult age group use Instagram for shopping, with Facebook placing second (45.1%). [caption id="attachment_107163" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
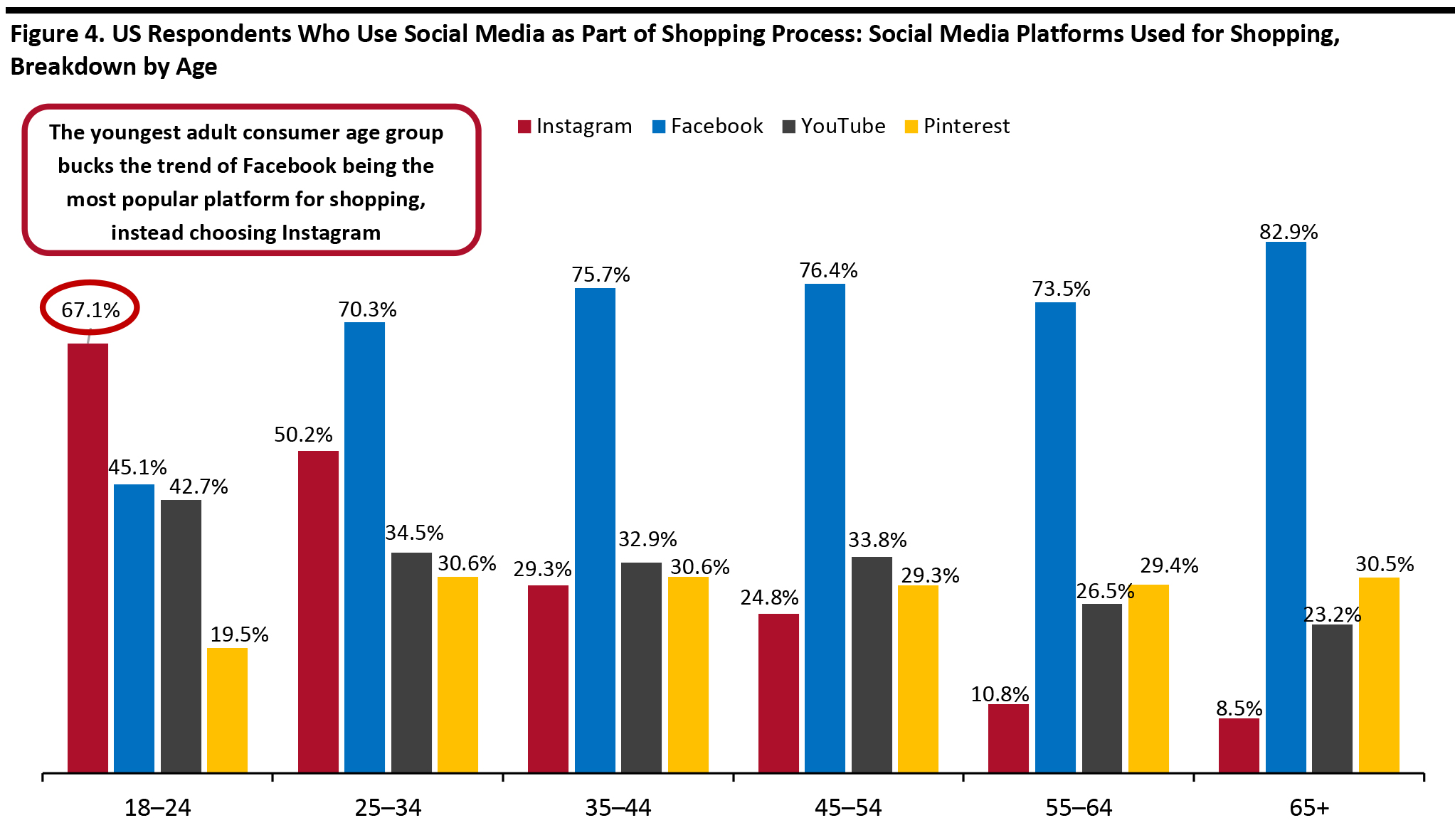 Base: 854 US Internet respondents aged 18+ who use social media as part of the shopping process
Base: 854 US Internet respondents aged 18+ who use social media as part of the shopping process Source: Coresight Research [/caption]
Categories Most Shopped on Social Media: Apparel and Beauty
For our survey, we identified shopping on social media as two discrete stages:- Discovering products or researching purchases on social media
- Purchasing via the platform
- Note that the respondent base for the two sets of bars in the chart below are different: the proportions are the percentage of respondents who discover/research and purchase, respectively.
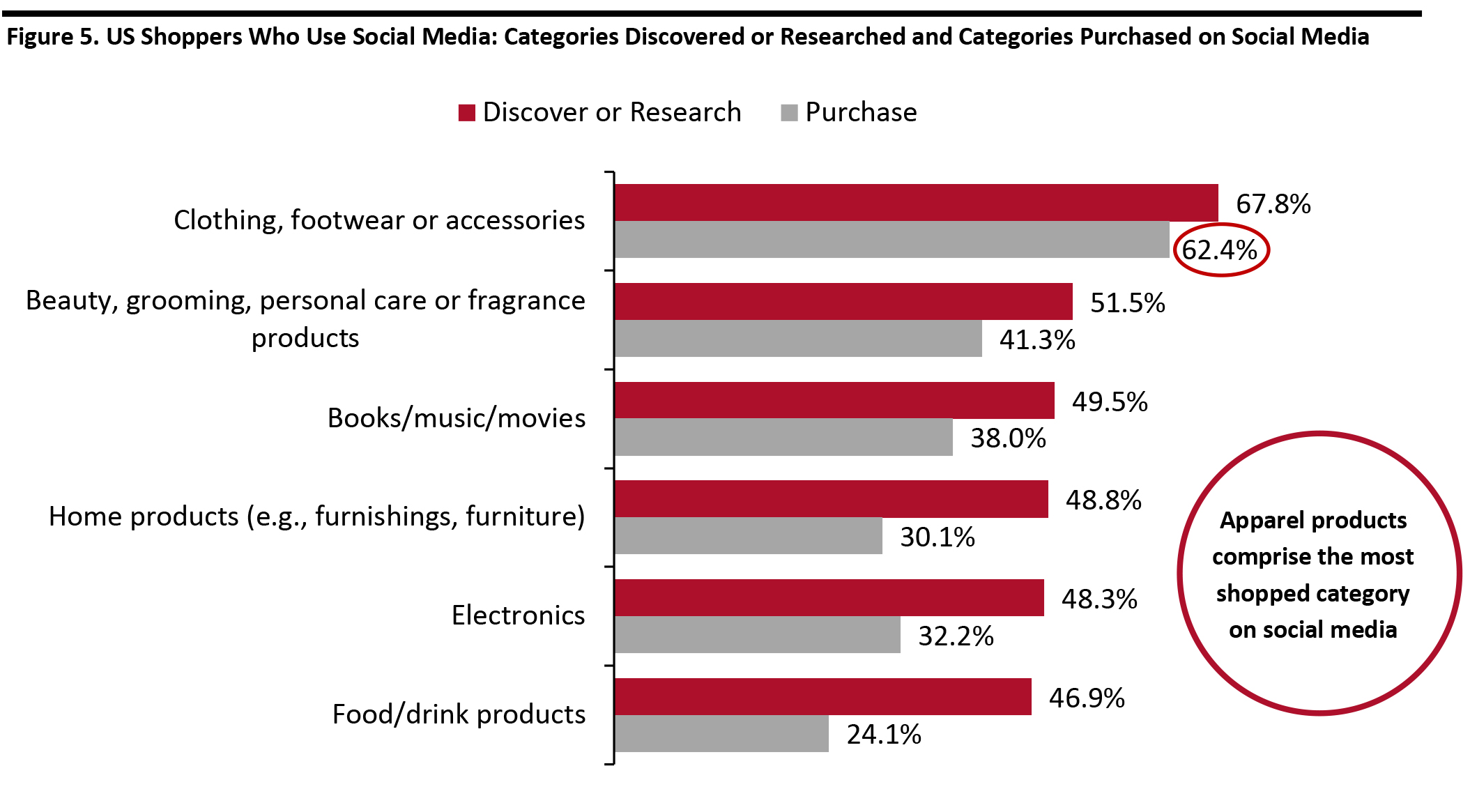 Base: 851 US Internet respondents aged 18+ who use social media to discover products or research purchases, and 731 US Internet users aged 18+ who use social media to purchase products
Base: 851 US Internet respondents aged 18+ who use social media to discover products or research purchases, and 731 US Internet users aged 18+ who use social media to purchase products Source: Coresight Research [/caption] From our data on discovery versus purchase, we can analyze the “buying-to-discovery” ratio by category—the proportion of those who make purchases on social media represented as a percentage of respondents who say they use social media to discover or research products. The apparel and beauty segments led in terms of discovery translating to purchasing on social media. This perhaps suggests that there is a bias of content towards these categories on social media platforms and/or that influencers are driving sales of these products. The high numbers could also be a product of the highly image-driven nature of apparel and beauty purchases, with inspirational visuals likely to prompt purchasing more than in other categories. The survey data suggests that social media is successful in prompting impulse-driven purchases in those frequently purchased, discretionary categories where aesthetics are key. For categories such as electronics or food, where other factors such as product specifications or ingredients, respectively, come into play, we see much lower buying-to-discovery ratios. [caption id="attachment_107165" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
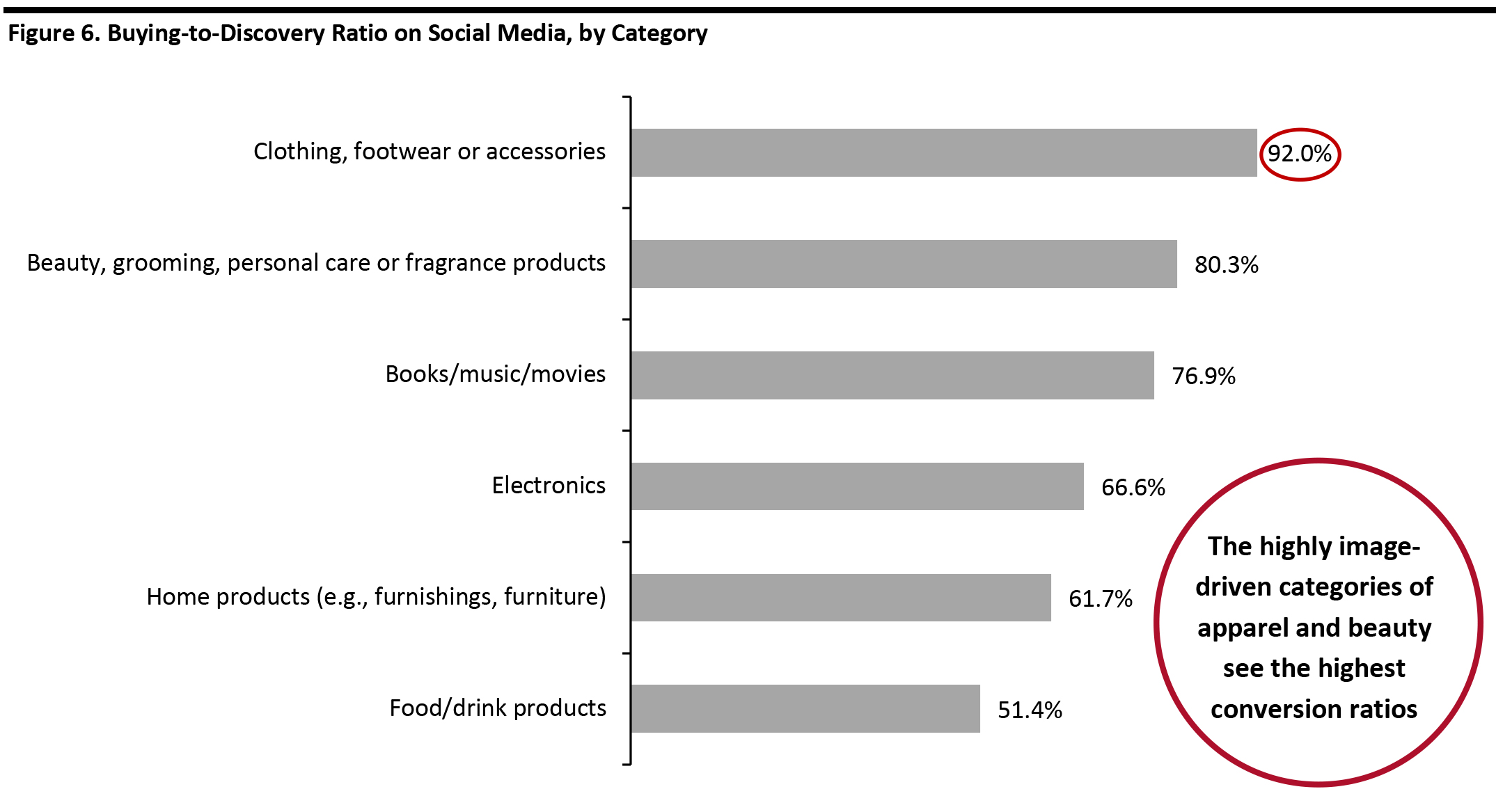 The ratio shows the proportion of those who use social media to make purchases as a percentage of those who use social media for product discovery or research
The ratio shows the proportion of those who use social media to make purchases as a percentage of those who use social media for product discovery or research Base: 854 US Internet respondents aged 18+ who use social media as part of the shopping process
Source: Coresight Research [/caption]
Analysis of Discretionary Spending by US Social Media Shoppers
People with higher incomes are more likely than other shoppers to use social media as part of shopping process. On average, 61.3% of social media users use such platforms as part of shopping process, but those with an annual income of between $75,000 and $99,999 had a significantly higher penetration rate, followed by those who make between $100,000 and $150,000 annually (shown in Figure 7). To optimize their social media strategy for maximum return (marketing ROI), brands and retailers should pay close attention to consumers who make more than $75,000 annually. [caption id="attachment_107168" align="aligncenter" width="700"]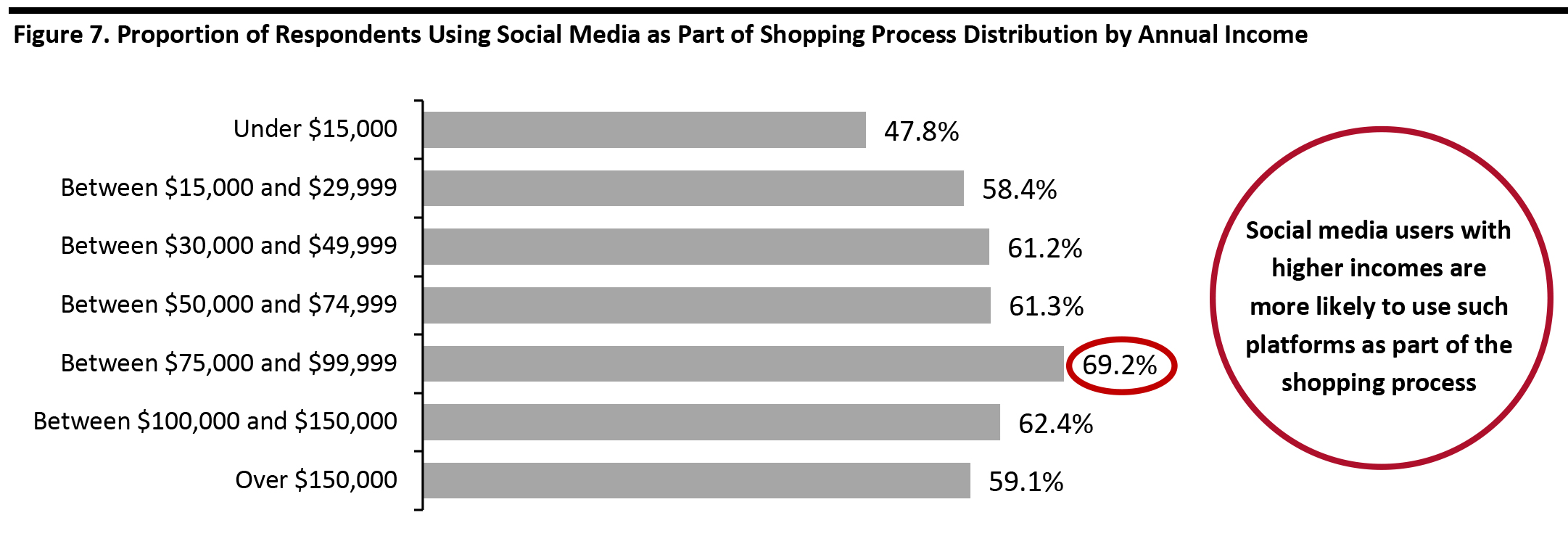 Base: 1,393 US Internet respondents aged 18+ who use social media
Base: 1,393 US Internet respondents aged 18+ who use social media Source: Coresight Research [/caption] We asked our survey respondents how much they spend on discretionary purchases, and the results showed that those using social media as part of the shopping process tend to spend more on non-essential purchases. For non-essential retail spending, US consumers who use social media as part of the shopping process are more likely to spend more than those who do not. Of respondents who do not use social media as part of the shopping process, 56.8% spend less than $50 on non-essential retail purchases per month, and only 6.7% spend more than $300 on the same category monthly. [caption id="attachment_107169" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
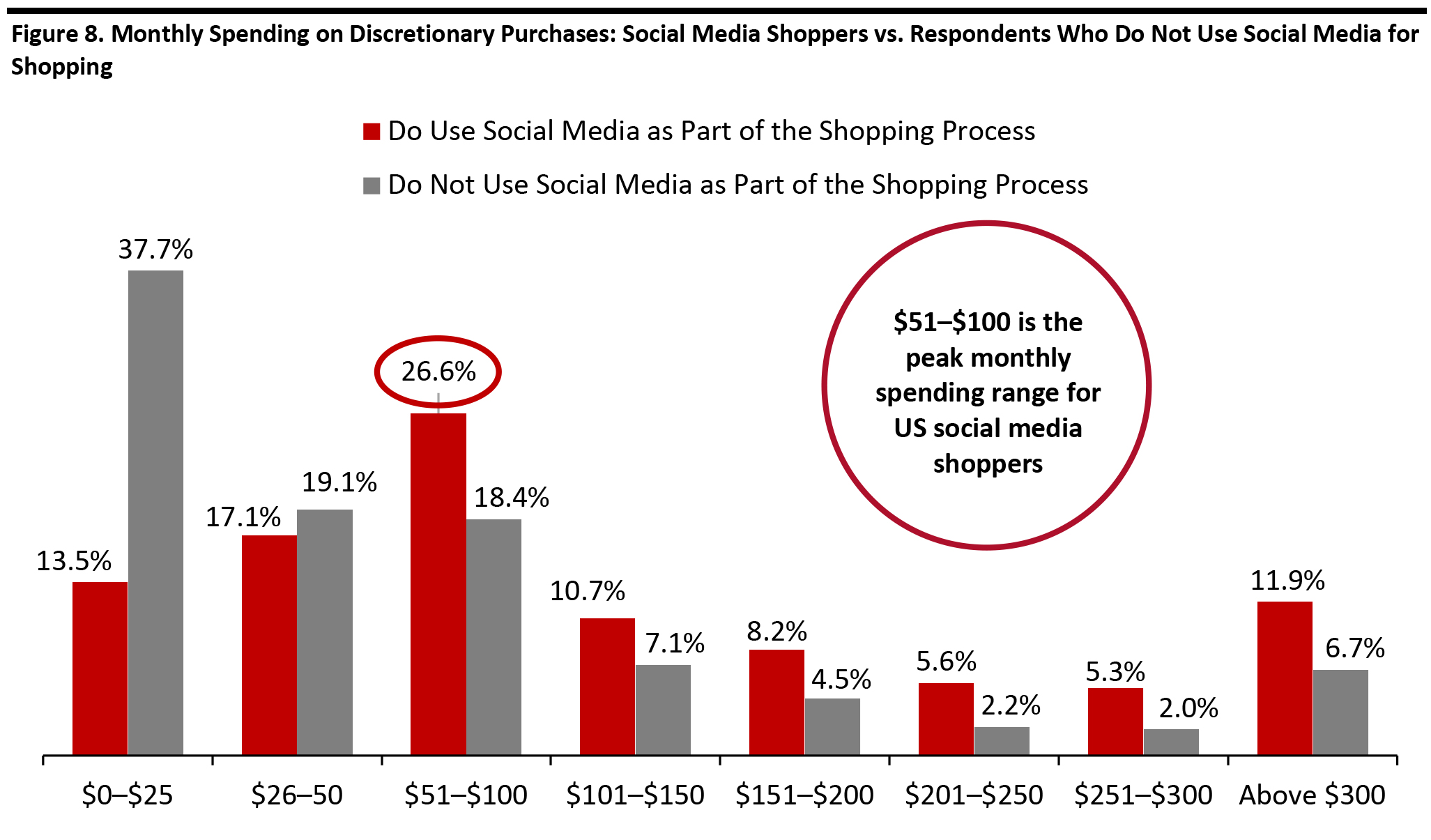 Base: 1,509 US Internet respondents aged 18+. Of those, 854 use social media as part of shopping process
Base: 1,509 US Internet respondents aged 18+. Of those, 854 use social media as part of shopping process Source: Coresight Research [/caption]
Social Media Influencers Have an Impact on Shopping Behavior
Our survey revealed that 51.6% of respondents who use social media as part of the shopping process follow influencers or celebrities on social media. The proportion decreases as age increases: Respondents aged 18–24 have the highest rate across all age groups, with 85% stating that they follow influencers or celebrities on social media. The proportion of Instagram shoppers following influencers or celebrities is 82.6%, which is much higher than overall social media shoppers. As could be expected due to the trend mentioned above, the highest proportion of respondents that follow Instagram influencers are aged 25–34, followed by the 18–24 age group. However, it is interesting to note that the percentages only slightly drop off for the more mature age groups, compared to the low proportions of older respondents that follow influencers on social media in general (shown in Figure 9). A potential reason for Instagram achieving higher proportions of influencer followers than general social media could be that the platform is based around visual content—images and videos—which users may find more engaging and personable than the text-based nature of other social media. [caption id="attachment_107166" align="aligncenter" width="700"]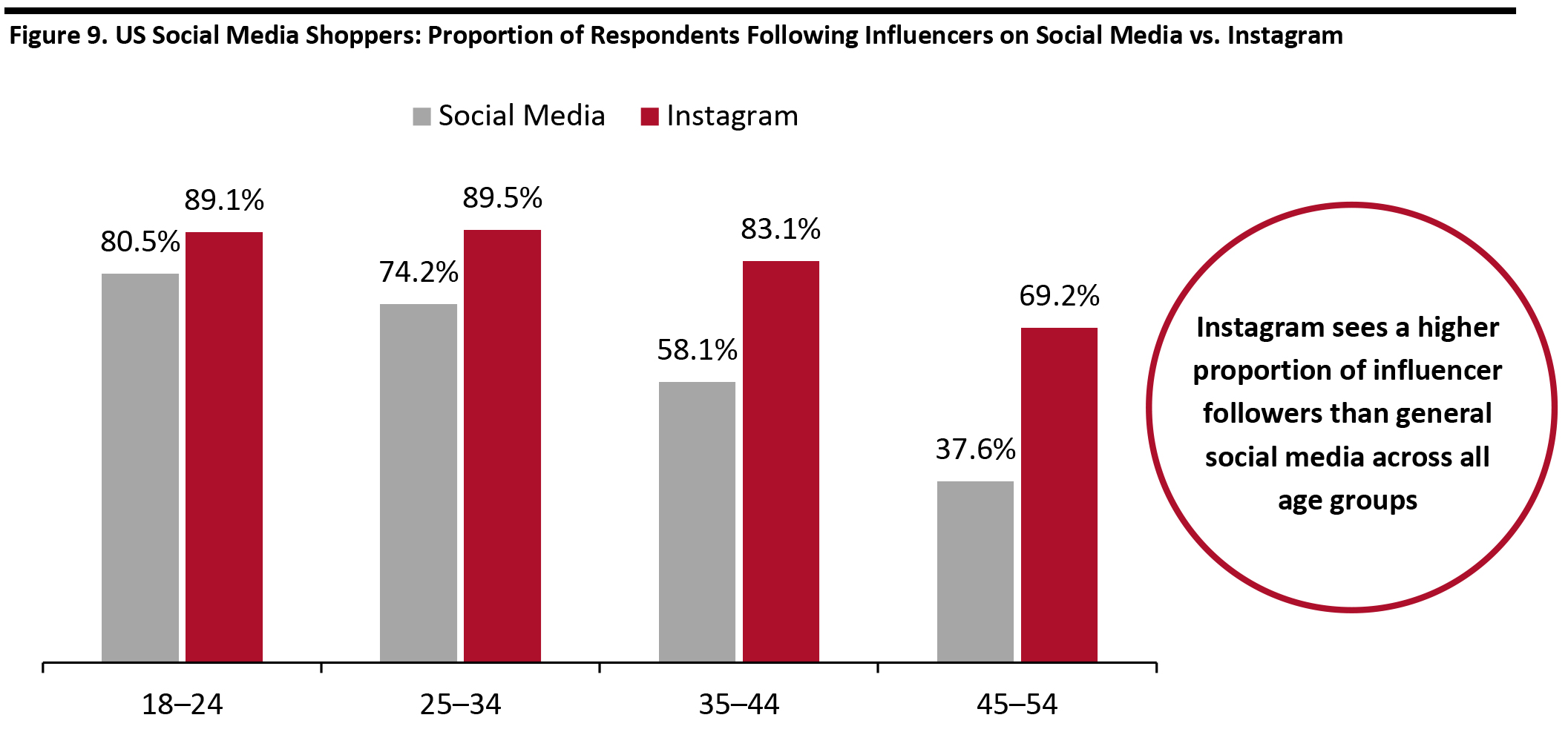 Not all age groups shown due to small sub-samples for some age groups
Not all age groups shown due to small sub-samples for some age groups Base: 854 US Internet respondents aged 18+ who use social media as part of the shopping process. Of those, 282 use Instagram as part of the shopping process.
Source: Coresight Research [/caption] Social media influencers are shown to have an impact on consumer purchasing decisions. In addition to harnessing a higher proportion of followers than general social media, Instagram is outperforming other platforms in terms of its influencers driving consumer shopping behaviors: 23.6% of Instagram shoppers who follow influencers on the platform stated their shopping is “often/always” affected by influencers or celebrities on Instagram, which is more than the 19.7% of general social media shoppers who follow influencers. [caption id="attachment_107170" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
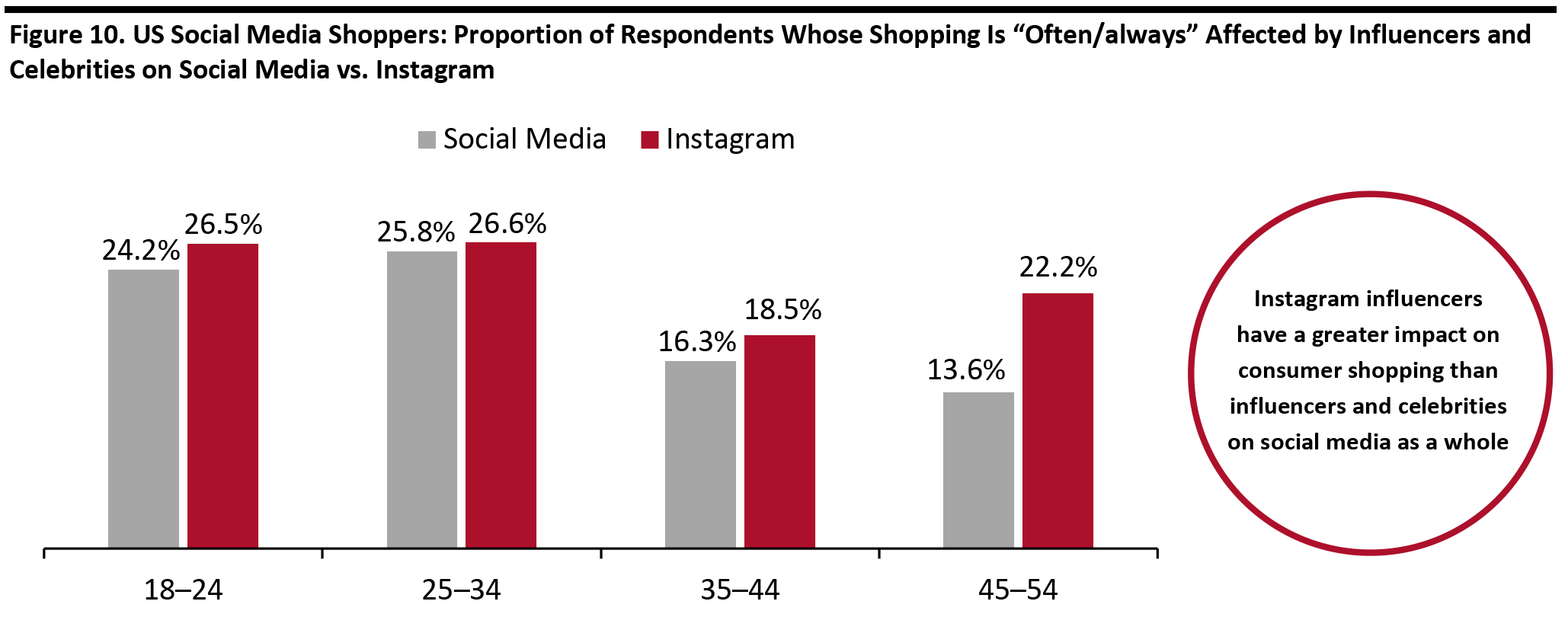 Not all age groups shown due to small sub-samples for some age groups
Not all age groups shown due to small sub-samples for some age groups Base: 854 US Internet respondents aged 18+ who use social media as part of the shopping process. Of those, 282 use Instagram as part of the shopping process and follow Instagram influencers.
Source: Coresight Research [/caption] The rising casualization trend in workplace attire is resulting in new apparel categories, often called “workleisure” or “performance professional.” Driven by this trend, men are venturing beyond suits. Naturally, social media influencers have become a source of fashion advice. Men are also more likely to engage with their peers on social media and Instagram for gaming and fitness advice. It is therefore not unexpected that Instagram influencers were shown in the survey results to have a higher impact on male respondents than female respondents. In addition, 33.0% of male Instagram shoppers stated that their shopping is “often/always” affected by Instagram influencers or celebrities, which is higher than the 28.6% of male social media shoppers who follow influencers. The same trend was observed in female respondents. [caption id="attachment_107171" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
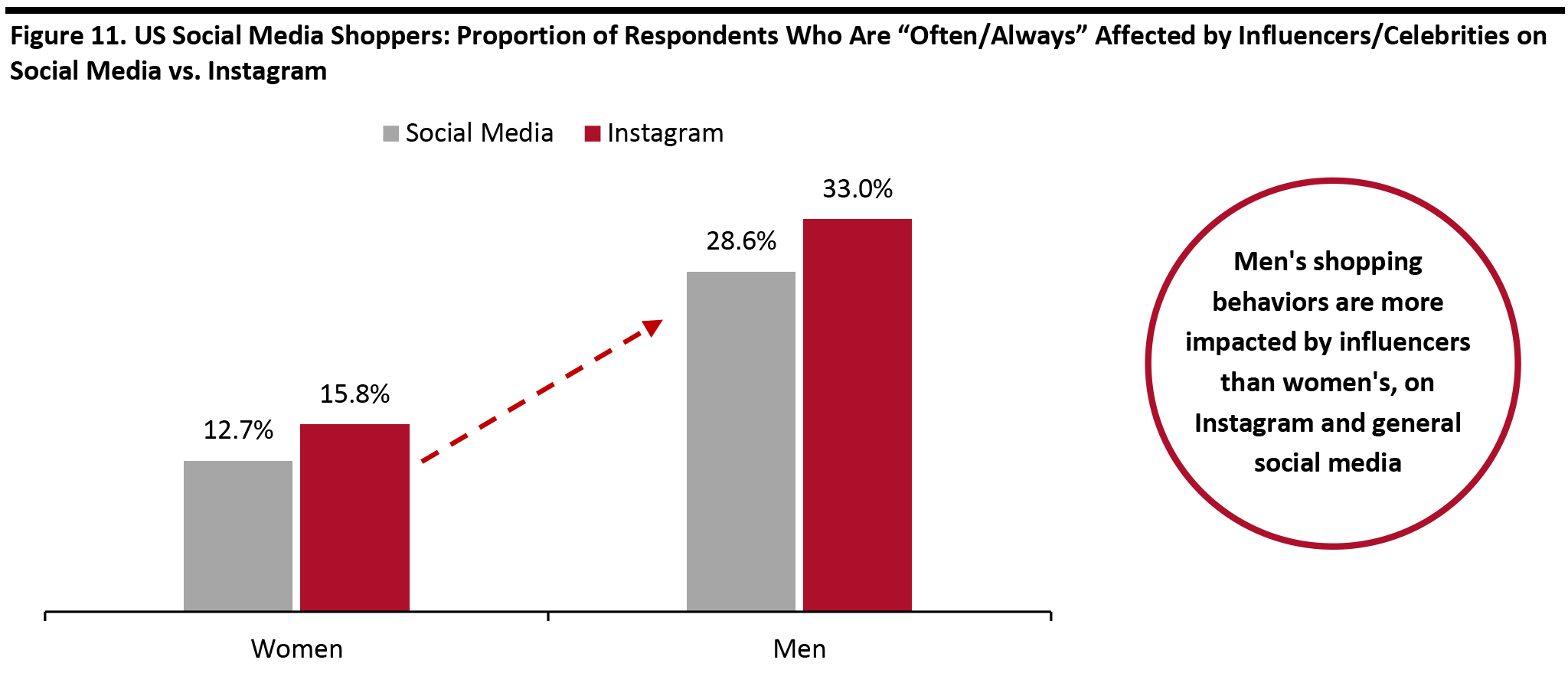 Base: 441 US Internet respondents aged 18+ who use social media as part of the shopping process and follow influencers/celebrities. Of those, 233 are Instagram shoppers who follow Instagram influencers.
Base: 441 US Internet respondents aged 18+ who use social media as part of the shopping process and follow influencers/celebrities. Of those, 233 are Instagram shoppers who follow Instagram influencers. Source: Coresight Research [/caption]
Abandoning Purchases
Among respondents who use social media to discover products or research purchases as part of the shopping process, 17.5% will “often/always” give up the purchase due to a platform’s lack of built-in functionality. Less than one-quarter of those shoppers will continue to purchase through other channels. For brands and retailers, it is crucial to provide a one-step discover-to-purchase solution that will remove friction in the consumer journey and drive improved conversion rates. [caption id="attachment_107172" align="aligncenter" width="700"]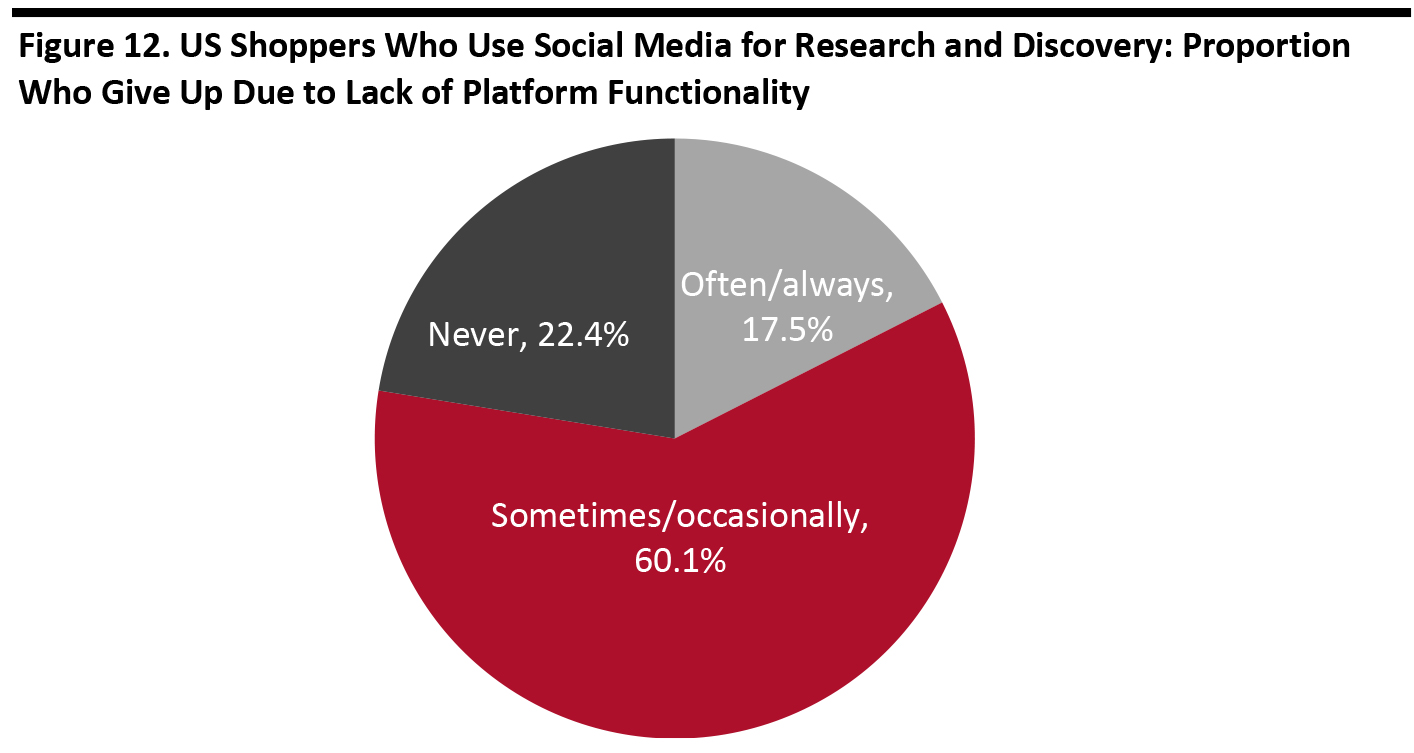 Base: 851 US Internet respondents age 18+ who use social media to discover products or research purchases as part of the shopping process
Base: 851 US Internet respondents age 18+ who use social media to discover products or research purchases as part of the shopping process Source: Coresight Research [/caption]
Post-Purchase Activities
Sharing content is an important feature of social commerce. Overall, 12.9% of respondents who use social media as part of the shopping process “often/always” post about their experiences. Survey results suggest that respondents of all ages post information about their shopping journey, such as photos and videos of their purchases. We see a sharp tail-off in the number of consumers sharing content about their purchases over the 45–54 age group. [caption id="attachment_107173" align="aligncenter" width="700"]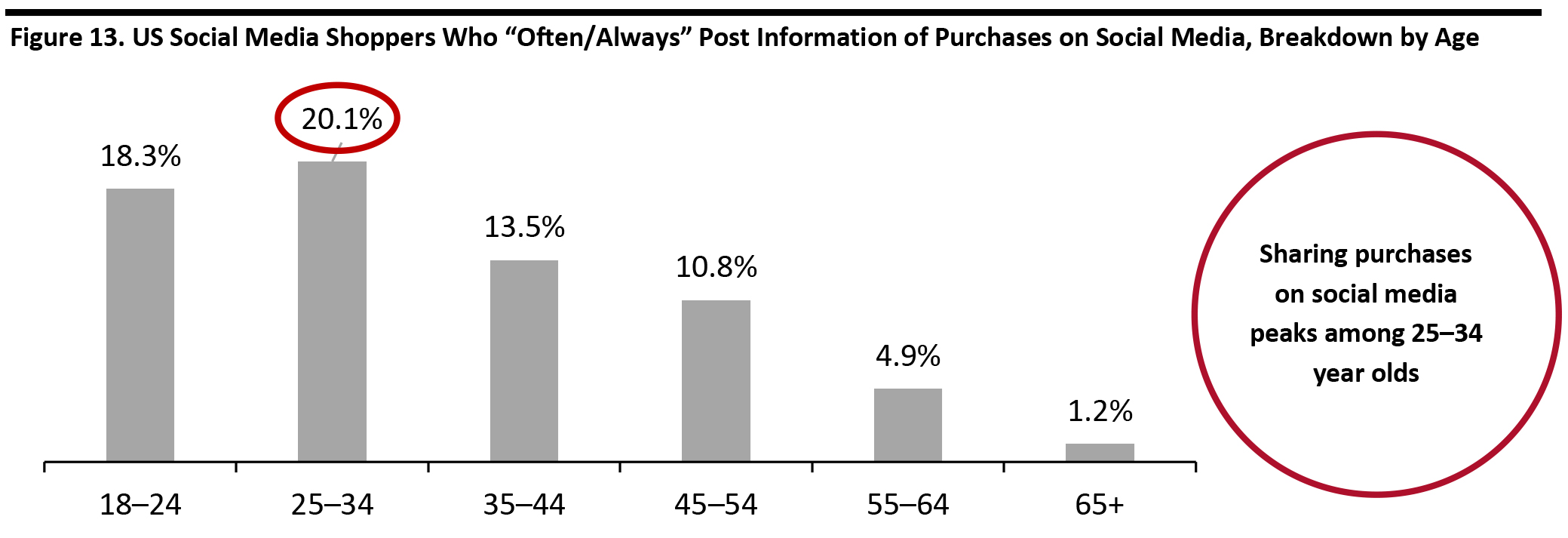 Base: 854 US Internet respondents aged 18+ who use social media as part of the shopping process, surveyed in November 2019
Base: 854 US Internet respondents aged 18+ who use social media as part of the shopping process, surveyed in November 2019 Source: Coresight Research [/caption]