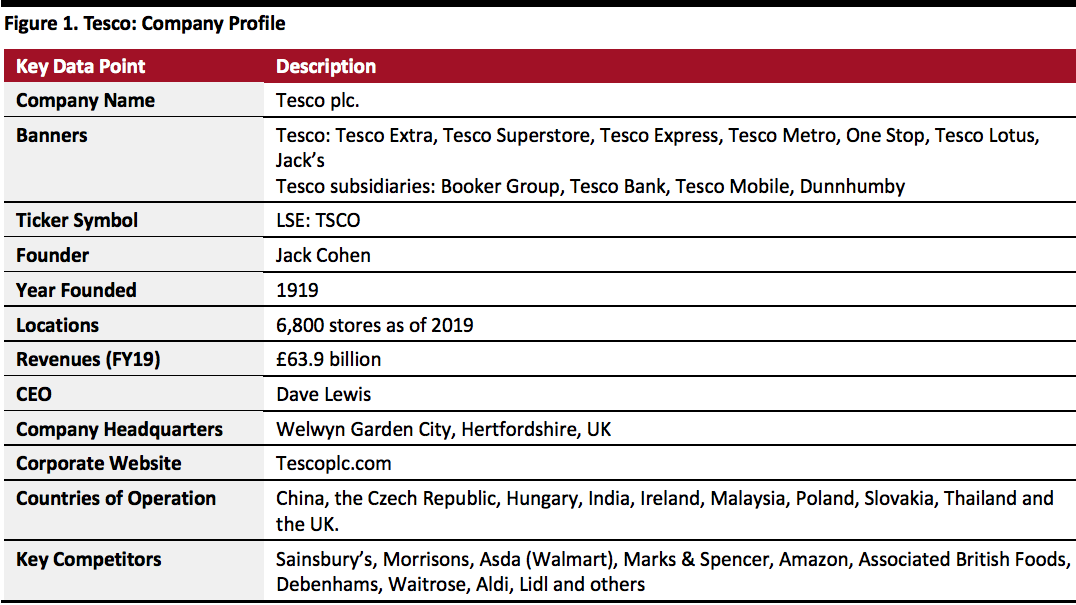
Tesco: Company Description
Tesco is a UK-based grocery and general-merchandise retailer. It runs multiformat stores, including convenience stores and hypermarkets, discount stores, petrol stations and in-store pharmacies. The company also engages in wholesaling and online retailing. Additionally, it offers retail banking solutions and insurance services. Tesco serves its customers through 6,800 stores located in 10 countries.
[caption id="attachment_97046" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
 Source: Company reports
Source: Company reports[/caption]
Key Events Overview
2017-2019: Under the helm of CEO Dave Lewis, Tesco has been divesting non-core assets and pulling out of loss-making ventures in a bid to revive its domestic business and reduce debt. Through a series of divestments and store closures, the company managed to slash its debt from £21.7 billion in 2015 to £12 billion in 2019.
In 2014, Tesco was involved in accounting fraud for overstating company profits by £263 million in first half of 2014. In 2017, the UK’s Serious Fraud Office fined Tesco £129 million to settle the probe over accounting fraud. In addition, the Financial Conduct Authority ordered Tesco to pay £85 million as compensation to its investors.
As part of its cost reduction program, Tesco Bank confirmed the sale of its residential mortgage portfolio to Lloyds Banking Group, operating under the Halifax brand, for £3.8 billion in September 2019. The company expects the sale will reduce the bank’s operating and funding costs as it trims down the number of products and services available for customers. Tesco plans to use the sales proceeds to reinvest in its existing businesses.
Tesco launched
Project Reset in 2015, under which it planned to cut up to 30% of its product ranges which it classed as no longer attractive to customers. In line with this effort, the company removed a number of household brands from its shelves in fiscal year 2019, as well as reducing its supplier base and relaunching 10,000 private-label products in the UK. This move will enable Tesco to improve efficiency and keep pace with its low-cost rivals Aldi and Lidl.
Although Tesco pulled out of its underperforming businesses in Japan in 2011 and South Korea in 2015, it remains committed to continuing investment in other Asian countries, including India, Malaysia and Thailand. For example, the company plans to open 750 new Tesco Lotus convenience stores in Thailand during 2019-21 and will expand its online business in the country to cover more urban areas in addition to Bangkok, Chiang Mai and Phuket. Trent Hypermarket, a 50:50 joint venture between Tesco and Tata Group, plans to open 50 retail stores and a distribution center in India during the period 2018-2021.
In keeping with the drive to enhance its omnichannel capabilities, Tesco launched a same-day grocery click-and-collect service in 2016. This service allows customers to order groceries online and pick them up in store within three hours. In January 2019, the company slashed its minimum basket spend from £40 to £25 for all click-and-collect grocery orders.
As part of its digital transformation plans, Tesco partnered with US-based autonomous robotic delivery vehicle manufacturer Starship Technologies in 2017. The two companies have developed a grocery delivery service using six-wheeled robots, an app for was launched by Tesco this year for customers in Milton Keynes, UK. The robots, which are equipped with GPS technology, are able to carry items up to two-mile from stores or delivery hubs in as little as 15 minutes.
In 2018, in line with its sustainability program, Tesco released a preferred packaging material list for its UK suppliers, which categorizes materials into green, amber and red according to their recyclability. In collaboration with its suppliers, the company plans to remove the hard-to-recycle red materials from the packaging of its own-brand products by the end of 2019.
Tesco: Events Timeline, 2008–2019
[wpdatatable id=23]
Source: Company reports/S&P Capital IQ/Coresight Research

 Source: Company reports[/caption]
Source: Company reports[/caption]