
DIpil Das
Below, we illustrate the seven major components of a retail supply chain, and some of the technologies that can support processes at various stages – from product design to end consumer.
[caption id="attachment_91374" align="aligncenter" width="700"]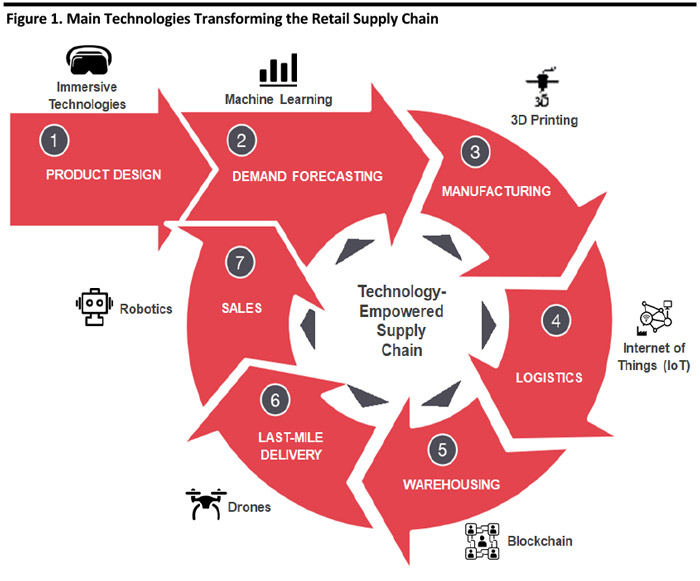 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Robotics is a branch of engineering that involves the conception, design, manufacture, and operation of robots, which overlaps with electronics, computer science and artificial intelligence. Global spending on robotics and drones will grow from $115.7 billion in 2019 to $210.3 billion by 2022, according to market intelligence company International Data Corporation.
Robotics can bring greater speed and efficiency to various stages of the retail supply chain, as we note below.
[caption id="attachment_91375" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Robotics is a branch of engineering that involves the conception, design, manufacture, and operation of robots, which overlaps with electronics, computer science and artificial intelligence. Global spending on robotics and drones will grow from $115.7 billion in 2019 to $210.3 billion by 2022, according to market intelligence company International Data Corporation.
Robotics can bring greater speed and efficiency to various stages of the retail supply chain, as we note below.
[caption id="attachment_91375" align="aligncenter" width="700"]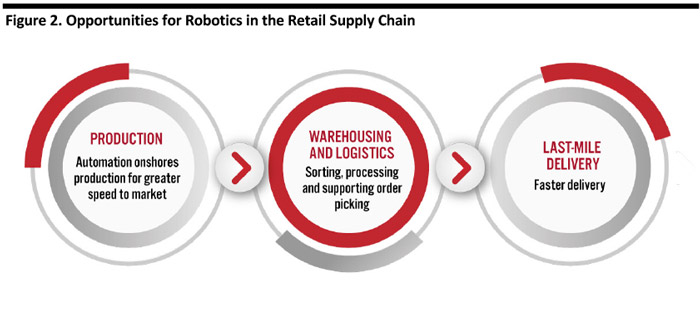 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Below, we outline applications of robotics and the benefits the technology offers.
Production: Robotics Enhances Speed to Market
Adidas has been piloting robotics in its product sourcing cycle with SpeedFactory since 2016, a completely automated production facility that makes tailored, limited edition, high-end sneakers. With facilities in Germany and the US, Adidas’ SpeedFactory produces robot-built AM4 series shoes designed for London and New York respectively. SpeedFactory facilities are likely to complement traditional offshore production facilities, to give the company more flexible and faster production and supply cycles for custom items or swift replenishment of fast-selling items.
[caption id="attachment_91376" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Below, we outline applications of robotics and the benefits the technology offers.
Production: Robotics Enhances Speed to Market
Adidas has been piloting robotics in its product sourcing cycle with SpeedFactory since 2016, a completely automated production facility that makes tailored, limited edition, high-end sneakers. With facilities in Germany and the US, Adidas’ SpeedFactory produces robot-built AM4 series shoes designed for London and New York respectively. SpeedFactory facilities are likely to complement traditional offshore production facilities, to give the company more flexible and faster production and supply cycles for custom items or swift replenishment of fast-selling items.
[caption id="attachment_91376" align="aligncenter" width="700"]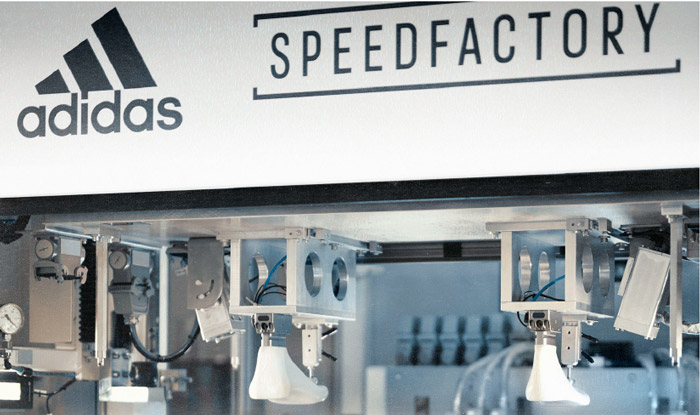 Adidas SpeedFactory
Adidas SpeedFactory
Source: SpeedFactory [/caption] Warehousing and Logistics: Robotics Improves Logistics Processes During the Machine Learning, Automation, Robotics and Space (MARS) conference in Las Vegas in June 2019, Amazon unveiled Pegasus, a new sorting system. Pegasus was developed in collaboration with autonomous warehouse robotics startup Canvas. Amazon will install the new robotics system at hundreds of Amazon’s sorting and distribution facilities to improve the speed and reliability of package sorting. Amazon claims Pegasus can cut misplaced goods by 50% and minimize workplace injuries. Amazon had previously used robots from Kiva to support picking and packing. [caption id="attachment_91377" align="aligncenter" width="700"] Amazon’s Pegasus robot Source: Amazon [/caption]
Cainiao, a logistics firm majority-owned by China-based Alibaba, opened a warehouse with over 700 robots in October 2018 to get ready for Singles Day the following month. The robots automatically picked up parcels and delivered them to another part of the warehouse, to be collected by the last-mile delivery firm. Cainiao said the robotic warehouse brought significant time savings, but did not quantify those savings.
[caption id="attachment_91378" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
Amazon’s Pegasus robot Source: Amazon [/caption]
Cainiao, a logistics firm majority-owned by China-based Alibaba, opened a warehouse with over 700 robots in October 2018 to get ready for Singles Day the following month. The robots automatically picked up parcels and delivered them to another part of the warehouse, to be collected by the last-mile delivery firm. Cainiao said the robotic warehouse brought significant time savings, but did not quantify those savings.
[caption id="attachment_91378" align="aligncenter" width="700"] Cainiao’s robotic warehouse
Cainiao’s robotic warehouse
Source: Alizila [/caption] Last-Mile Delivery: Robotics Innovates Delivery with Speed Retailers are looking for greater efficiency in last-mile delivery as consumer expectations of speed and convenience increase. Robotics could be one solution, and a number of companies have trialed robotic deliveries. UK retail giant Tesco has been testing robotics for last mile delivery. Since January 2019, customers at the Tesco Extra store in Milton Keynes, UK can have groceries delivered by robots manufactured by Starship Technologies. Tesco customers can use Starship’s smartphone app to order groceries. The order is picked up in-store by a Starship employee who puts the items into the robot. The robot then navigates using cameras, GPS, radar and ultrasound sensors. The robots can deliver as quickly as in 15 minutes within a two-mile radius of the store. Using the app, customers can track the robot as it makes its way to the home. [caption id="attachment_91379" align="aligncenter" width="700"] Starship delivery robots (left) and Starship delivery app (right)
Starship delivery robots (left) and Starship delivery app (right)
Source: Starship Technologies [/caption] Similarly, UK food delivery company Just Eat delivered over 1,000 meals to the London boroughs of Greenwich and Southwark in August 2017, also using robots from Starship Technologies. Retailer Kroger partnered with robotics company Nuro in May 2019 to use robots to deliver grocery orders to customers in Houston. [caption id="attachment_91380" align="aligncenter" width="700"] Kroger and Nuro test driverless groceries
Kroger and Nuro test driverless groceries
Source: Kroger [/caption] Key Insights and Implications for Retailers Heavy industry has used robotics for decades – but now the technology is gaining traction in apparel and retail. Robots offer improvement in supply chain by enhancing speed to market, better logistics, better warehousing and speedier last-mile delivery. With further advancements and lower cost, we expect to see wider adoption in the coming years.
 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Robotics is a branch of engineering that involves the conception, design, manufacture, and operation of robots, which overlaps with electronics, computer science and artificial intelligence. Global spending on robotics and drones will grow from $115.7 billion in 2019 to $210.3 billion by 2022, according to market intelligence company International Data Corporation.
Robotics can bring greater speed and efficiency to various stages of the retail supply chain, as we note below.
[caption id="attachment_91375" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Robotics is a branch of engineering that involves the conception, design, manufacture, and operation of robots, which overlaps with electronics, computer science and artificial intelligence. Global spending on robotics and drones will grow from $115.7 billion in 2019 to $210.3 billion by 2022, according to market intelligence company International Data Corporation.
Robotics can bring greater speed and efficiency to various stages of the retail supply chain, as we note below.
[caption id="attachment_91375" align="aligncenter" width="700"] Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Below, we outline applications of robotics and the benefits the technology offers.
Production: Robotics Enhances Speed to Market
Adidas has been piloting robotics in its product sourcing cycle with SpeedFactory since 2016, a completely automated production facility that makes tailored, limited edition, high-end sneakers. With facilities in Germany and the US, Adidas’ SpeedFactory produces robot-built AM4 series shoes designed for London and New York respectively. SpeedFactory facilities are likely to complement traditional offshore production facilities, to give the company more flexible and faster production and supply cycles for custom items or swift replenishment of fast-selling items.
[caption id="attachment_91376" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Below, we outline applications of robotics and the benefits the technology offers.
Production: Robotics Enhances Speed to Market
Adidas has been piloting robotics in its product sourcing cycle with SpeedFactory since 2016, a completely automated production facility that makes tailored, limited edition, high-end sneakers. With facilities in Germany and the US, Adidas’ SpeedFactory produces robot-built AM4 series shoes designed for London and New York respectively. SpeedFactory facilities are likely to complement traditional offshore production facilities, to give the company more flexible and faster production and supply cycles for custom items or swift replenishment of fast-selling items.
[caption id="attachment_91376" align="aligncenter" width="700"] Adidas SpeedFactory
Adidas SpeedFactory Source: SpeedFactory [/caption] Warehousing and Logistics: Robotics Improves Logistics Processes During the Machine Learning, Automation, Robotics and Space (MARS) conference in Las Vegas in June 2019, Amazon unveiled Pegasus, a new sorting system. Pegasus was developed in collaboration with autonomous warehouse robotics startup Canvas. Amazon will install the new robotics system at hundreds of Amazon’s sorting and distribution facilities to improve the speed and reliability of package sorting. Amazon claims Pegasus can cut misplaced goods by 50% and minimize workplace injuries. Amazon had previously used robots from Kiva to support picking and packing. [caption id="attachment_91377" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
 Amazon’s Pegasus robot Source: Amazon [/caption]
Cainiao, a logistics firm majority-owned by China-based Alibaba, opened a warehouse with over 700 robots in October 2018 to get ready for Singles Day the following month. The robots automatically picked up parcels and delivered them to another part of the warehouse, to be collected by the last-mile delivery firm. Cainiao said the robotic warehouse brought significant time savings, but did not quantify those savings.
[caption id="attachment_91378" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
Amazon’s Pegasus robot Source: Amazon [/caption]
Cainiao, a logistics firm majority-owned by China-based Alibaba, opened a warehouse with over 700 robots in October 2018 to get ready for Singles Day the following month. The robots automatically picked up parcels and delivered them to another part of the warehouse, to be collected by the last-mile delivery firm. Cainiao said the robotic warehouse brought significant time savings, but did not quantify those savings.
[caption id="attachment_91378" align="aligncenter" width="700"] Cainiao’s robotic warehouse
Cainiao’s robotic warehouse Source: Alizila [/caption] Last-Mile Delivery: Robotics Innovates Delivery with Speed Retailers are looking for greater efficiency in last-mile delivery as consumer expectations of speed and convenience increase. Robotics could be one solution, and a number of companies have trialed robotic deliveries. UK retail giant Tesco has been testing robotics for last mile delivery. Since January 2019, customers at the Tesco Extra store in Milton Keynes, UK can have groceries delivered by robots manufactured by Starship Technologies. Tesco customers can use Starship’s smartphone app to order groceries. The order is picked up in-store by a Starship employee who puts the items into the robot. The robot then navigates using cameras, GPS, radar and ultrasound sensors. The robots can deliver as quickly as in 15 minutes within a two-mile radius of the store. Using the app, customers can track the robot as it makes its way to the home. [caption id="attachment_91379" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
 Starship delivery robots (left) and Starship delivery app (right)
Starship delivery robots (left) and Starship delivery app (right) Source: Starship Technologies [/caption] Similarly, UK food delivery company Just Eat delivered over 1,000 meals to the London boroughs of Greenwich and Southwark in August 2017, also using robots from Starship Technologies. Retailer Kroger partnered with robotics company Nuro in May 2019 to use robots to deliver grocery orders to customers in Houston. [caption id="attachment_91380" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
 Kroger and Nuro test driverless groceries
Kroger and Nuro test driverless groceries Source: Kroger [/caption] Key Insights and Implications for Retailers Heavy industry has used robotics for decades – but now the technology is gaining traction in apparel and retail. Robots offer improvement in supply chain by enhancing speed to market, better logistics, better warehousing and speedier last-mile delivery. With further advancements and lower cost, we expect to see wider adoption in the coming years.