
Nitheesh NH
Below, we illustrate the seven major components of the retail supply chain, and some of the technologies that can support processes at various stages – from product design to end consumer.
[caption id="attachment_94337" align="aligncenter" width="700"]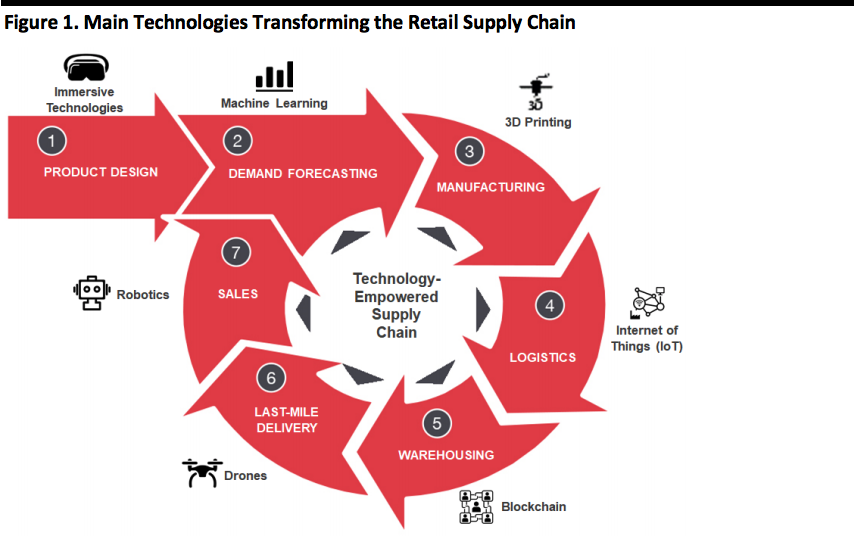 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
What is Robotic Process Automation?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) allows companies to deploy intelligent agents (virtual assistants) that can learn, through Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning, how specific tasks are performed, and then repeat those tasks, ultimately eliminating human error and reducing overhead costs. RPA virtual assistants can take various forms, from software to a wide array of technological steps that improves the input, flow, transformation and output of data.
Procter & Gamble (P&G) is implementing RPA through the use of virtual assistants to automate white-collar roles such as inventory management. Through RPA, P&G is hoping to achieve further savings in manufacturing, inventory costs and logistics, and to help business units innovate more rapidly, better respond to market trends and deliver better service.
The Business Case for RPA
Retailers, wholesalers and consumer product companies face an array of challenges, including rising production costs, new technology disruptions, labor uncertainty and rapidly changing customer expectations. RPA can transform work and boost productivity, enhance the customer experience and deliver more accurate and more reliable results.
The global market for RPA solutions is expected to grow 31% CAGR in the period 2018-2025, to be worth $3.97 billion by 2025, according to research firm Grand View Research. North America is expected to be the biggest market in nominal terms but Asia Pacific is anticipated to grow at the fastest rate.
How Supply Chain Operations Can Leverage RPA
RPA offers many benefits at various stages of the supply chain, including:
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
What is Robotic Process Automation?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) allows companies to deploy intelligent agents (virtual assistants) that can learn, through Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning, how specific tasks are performed, and then repeat those tasks, ultimately eliminating human error and reducing overhead costs. RPA virtual assistants can take various forms, from software to a wide array of technological steps that improves the input, flow, transformation and output of data.
Procter & Gamble (P&G) is implementing RPA through the use of virtual assistants to automate white-collar roles such as inventory management. Through RPA, P&G is hoping to achieve further savings in manufacturing, inventory costs and logistics, and to help business units innovate more rapidly, better respond to market trends and deliver better service.
The Business Case for RPA
Retailers, wholesalers and consumer product companies face an array of challenges, including rising production costs, new technology disruptions, labor uncertainty and rapidly changing customer expectations. RPA can transform work and boost productivity, enhance the customer experience and deliver more accurate and more reliable results.
The global market for RPA solutions is expected to grow 31% CAGR in the period 2018-2025, to be worth $3.97 billion by 2025, according to research firm Grand View Research. North America is expected to be the biggest market in nominal terms but Asia Pacific is anticipated to grow at the fastest rate.
How Supply Chain Operations Can Leverage RPA
RPA offers many benefits at various stages of the supply chain, including:
 Blue Prism
Blue Prism
Source: Blue Prism[/caption] Key Insights RPA offers numerous benefits to supply chain operations and the retail industry. Companies such as Walmart and Walgreens have adopted RPA. With RPA’s promise of greater efficiency, increased productivity and greater, we expect to see more retailers adopt this technology – as reflected by Grand View Research’s prediction that the global RPA market will grow at a 31% CAGR from 2018-2025, to be worth $3.97 billion.
 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
What is Robotic Process Automation?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) allows companies to deploy intelligent agents (virtual assistants) that can learn, through Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning, how specific tasks are performed, and then repeat those tasks, ultimately eliminating human error and reducing overhead costs. RPA virtual assistants can take various forms, from software to a wide array of technological steps that improves the input, flow, transformation and output of data.
Procter & Gamble (P&G) is implementing RPA through the use of virtual assistants to automate white-collar roles such as inventory management. Through RPA, P&G is hoping to achieve further savings in manufacturing, inventory costs and logistics, and to help business units innovate more rapidly, better respond to market trends and deliver better service.
The Business Case for RPA
Retailers, wholesalers and consumer product companies face an array of challenges, including rising production costs, new technology disruptions, labor uncertainty and rapidly changing customer expectations. RPA can transform work and boost productivity, enhance the customer experience and deliver more accurate and more reliable results.
The global market for RPA solutions is expected to grow 31% CAGR in the period 2018-2025, to be worth $3.97 billion by 2025, according to research firm Grand View Research. North America is expected to be the biggest market in nominal terms but Asia Pacific is anticipated to grow at the fastest rate.
How Supply Chain Operations Can Leverage RPA
RPA offers many benefits at various stages of the supply chain, including:
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
What is Robotic Process Automation?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) allows companies to deploy intelligent agents (virtual assistants) that can learn, through Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning, how specific tasks are performed, and then repeat those tasks, ultimately eliminating human error and reducing overhead costs. RPA virtual assistants can take various forms, from software to a wide array of technological steps that improves the input, flow, transformation and output of data.
Procter & Gamble (P&G) is implementing RPA through the use of virtual assistants to automate white-collar roles such as inventory management. Through RPA, P&G is hoping to achieve further savings in manufacturing, inventory costs and logistics, and to help business units innovate more rapidly, better respond to market trends and deliver better service.
The Business Case for RPA
Retailers, wholesalers and consumer product companies face an array of challenges, including rising production costs, new technology disruptions, labor uncertainty and rapidly changing customer expectations. RPA can transform work and boost productivity, enhance the customer experience and deliver more accurate and more reliable results.
The global market for RPA solutions is expected to grow 31% CAGR in the period 2018-2025, to be worth $3.97 billion by 2025, according to research firm Grand View Research. North America is expected to be the biggest market in nominal terms but Asia Pacific is anticipated to grow at the fastest rate.
How Supply Chain Operations Can Leverage RPA
RPA offers many benefits at various stages of the supply chain, including:
- Reducing human error: RPA can dramatically reduce the risk of human error, delivering greater precision in work.
- Lower cost: RPA can cut administrative overhead, lowering staffing costs.
- Greater productivity: With RPA doing the heavy lifting, output can be increased significantly. Workers can also be freed from manual tasks and apply their skills to more important projects.
- Supply chain efficiencies: RPA generates lots of data, which can be analyzed to identify how processes can be enhanced, continually improving efficiency and cutting waste.
- Returns management: RPA can manage returns, update the inventory database and the customer’s billing information.
- Customer support management: RPA can help retailers provide quicker, more convenient, 24x7 customer support and enable real-time updates on the status of the support.
- Supply chain management: RPA can help retailers maintain sufficient or determine optimal inventory levels by generating real-time notifications.
 Blue Prism
Blue PrismSource: Blue Prism[/caption] Key Insights RPA offers numerous benefits to supply chain operations and the retail industry. Companies such as Walmart and Walgreens have adopted RPA. With RPA’s promise of greater efficiency, increased productivity and greater, we expect to see more retailers adopt this technology – as reflected by Grand View Research’s prediction that the global RPA market will grow at a 31% CAGR from 2018-2025, to be worth $3.97 billion.