
albert Chan
Introduction
Relentless demands from global competition, steady share gains from savvy digital commerce companies and technological advances have prompted retailers to embrace software-based tools in their supply chains.
As competition has intensified and become global, supply chains have become global as well, dramatically increasing complexity and spreading across multiple countries, factories and currencies. Production problems such as inclement weather, factory fires or labor unrest can occur anywhere around the globe, and it is no longer acceptable for a supply manager to have to place phone calls to find out why a shipment did not arrive on time. Commerce moves so quickly that supply-chain managers need this information as it happens, to know in advance if deadlines will be missed and to shift production to another source if necessary.
This level of complexity can generate data that is beyond the human capacity to interpret, but software excels in classifying and interpreting data. The state of software has continually improved, and new tools such as machine learning can make future predictions and offer suggestions to remedy problems.
Broad technological advances such as the move to cloud-based services and software have also encouraged retailers to adopt these new solutions, as they free retailers from having to own, maintain and upgrade data centers: Much supply-chain software is in the cloud.
There are also new software technologies such as machine learning that enable retailers to glean insights and make predictions from the vast amounts of data they collect, in addition to supporting other hardware and software technologies such as 3D printing, IoT, robots and drones.
Supply-chain software can perform a wide variety of functions within an enterprise, generally focusing on getting goods from the warehouse to the customer. Other tasks include processing orders, handling distribution, warehouse management and replenishment. The software can also manage the sourcing side, collecting information and vetting and selecting suppliers as well as managing them. Once the goods go out the door, supply chain software can monitor their whereabouts as well as the vehicles that carry them. Supply-chain software can also include tools for analyzing and making predictions from data.
Although supply chain software seems unglamorous, this software represents the nervous system at the center of a retailer’s operations, coordinating business planning and the production and distribution of goods throughout the enterprise.
Supply Chain Software
Supply-chain management software provides a real-time platform that analyzes and manages the flow of product and information across the entire supply chain. The software manages production, inventory, sourcing, logistics as well as forecasts product demand. The software gives the entire organization visibility into these categories, and can issue alerts about problems, outages and shortages, while leading-edge software anticipates problems and suggests remedies before the problems occur.
Supply chain software typically performs the following functions:
- Order processing.
- Sales and distribution.
- Inventory management and optimization.
- Warehouse management/replenishment.
- Supplier management/sourcing.
- Planning and forecasting.
- Supply chain monitoring.
- Transportation and logistics.
The software can also work closely with e-commerce functions, such as communicating with point-of-sale hardware and using electronic data interchange protocols, which incorporate standards for sharing data electronically among businesses.
The figure below illustrates several functions in the commerce cycle and how emerging technologies are transforming them.
[caption id="attachment_92633" align="aligncenter" width="700"]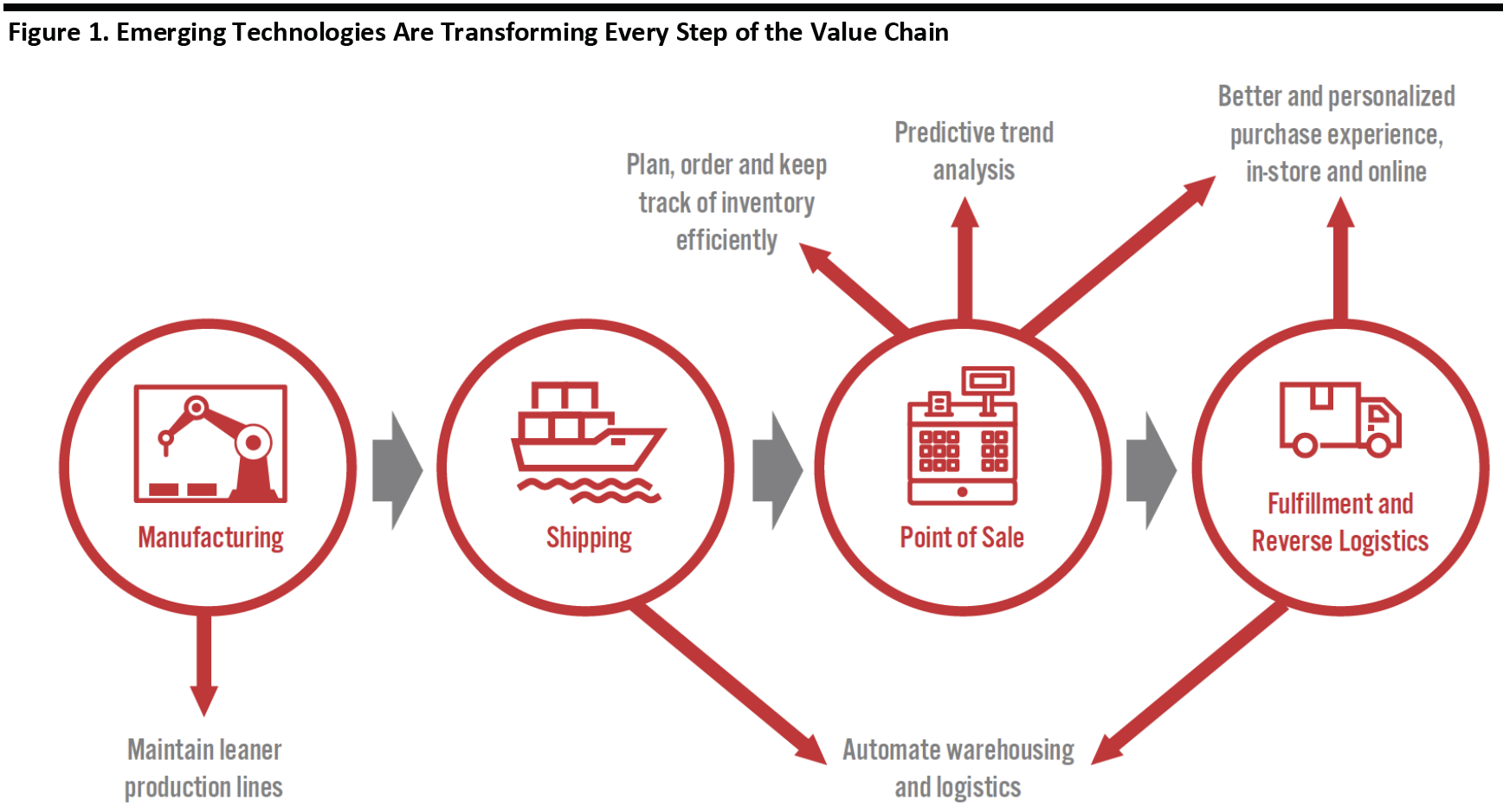 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Market Size and Growth
Supply-chain software is part of the global market for enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, which is expected to be worth an estimated $84.0 billion in 2019 and to grow at a 0.7% CAGR during 2015-2022, according to a forecast from Apps Run the World.
The global supply chain management software market is estimated to be worth more than $14 billion in 2019 and expected to grow at a 9.5% CAGR during 2016-2025E, based on a forecast from Allied Market Research.
The graph shows that manufacturing execution and transportation management are the highest growing market segments, followed by supply chain planning.
[caption id="attachment_92623" align="aligncenter" width="700"]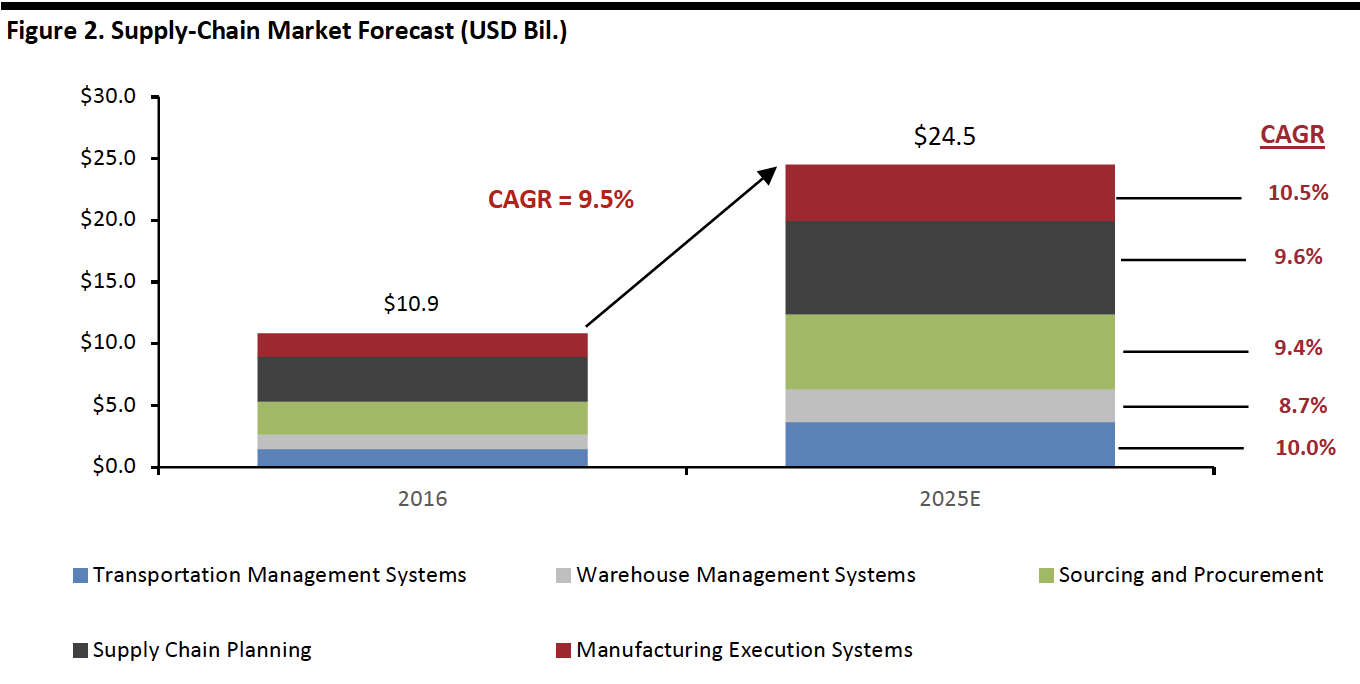 Source: Allied Market Research[/caption]
Source: Allied Market Research[/caption]
Supply Chain Application Market
The supply chain management application market was estimated to be worth $7.7 billion in 2017, and growing at a 2.2% CAGR through 2022, according to estimates from Apps Run the World. The breakdown of the 2017 market by share is shown below. The graph shows that the top five vendors account for roughly half the market, and the top 10 vendors account for nearly two thirds of the market.
[caption id="attachment_92624" align="aligncenter" width="700"]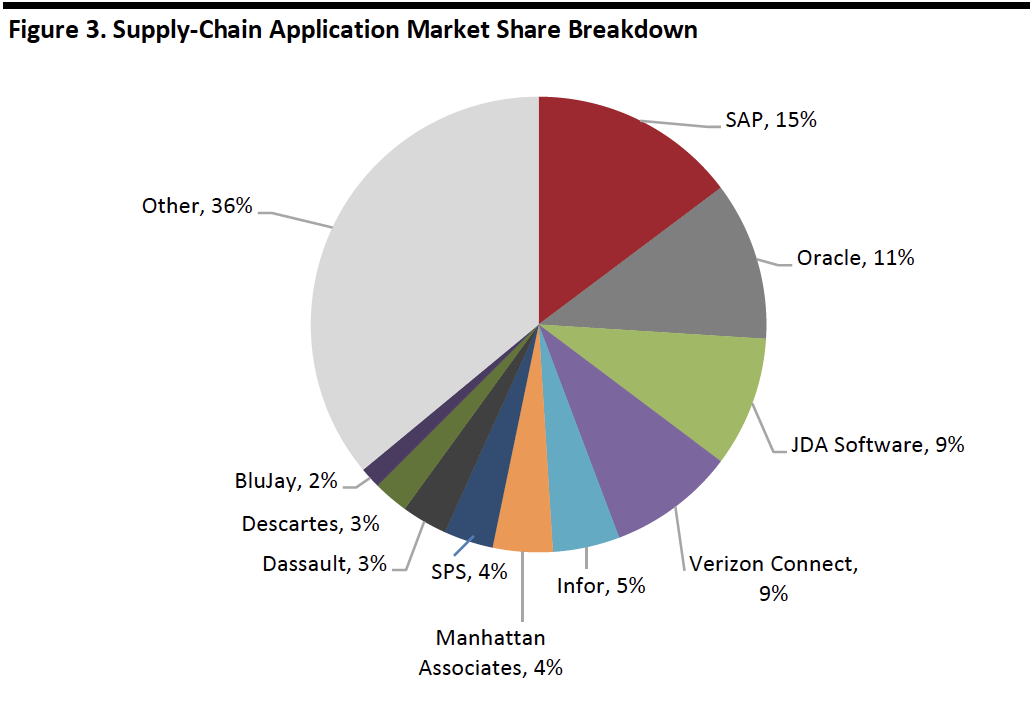 Source: Apps Run the World[/caption]
Source: Apps Run the World[/caption]
In 2016, most companies (73%) kept their SCM software on-premise, and this is expected to remain so through 2025. However, cloud-based SCM software is expected to grow at a higher rate during that period, according to Allied Market Research.
[caption id="attachment_92625" align="aligncenter" width="700"]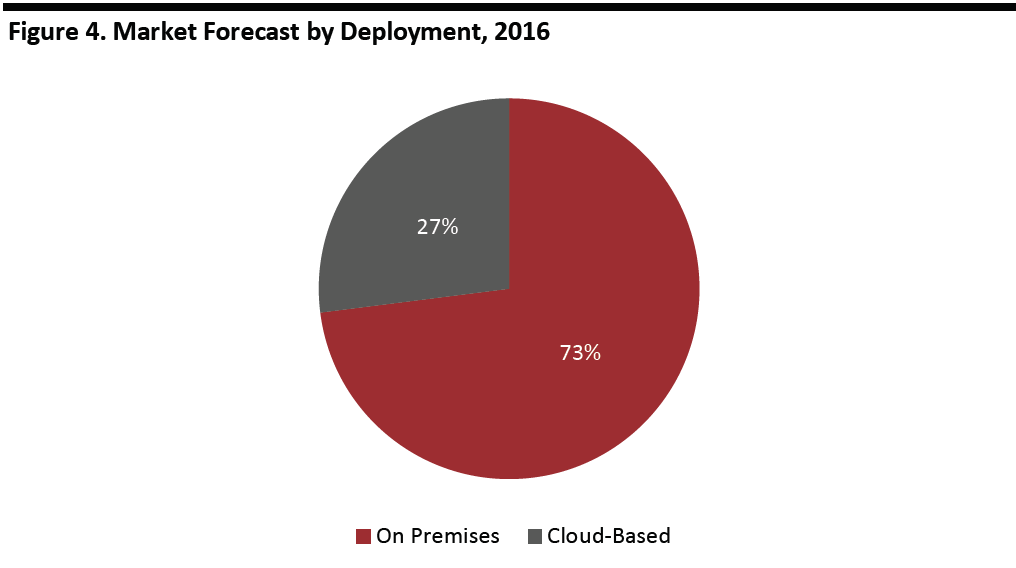 Source: Allied Market Research[/caption]
Source: Allied Market Research[/caption]
Supply Chain Analytics Market
Analytics are a key function of the supply chain, including determining optimal quantities and the locations of goods, which requires predictions of future demand. Supply-chain software increasingly relies on artificial-intelligence (AI) tools such as machine learning to forecast demand, identify outages or low-inventory situations before they occur and offer suggestions on remedies.
The supply chain analytics market is estimated to be worth $4.1 billion this year, growing at a 14.6% CAGR during 2016-2023E, according to a forecast from Markets and Markets, as shown below.
[caption id="attachment_92626" align="aligncenter" width="700"]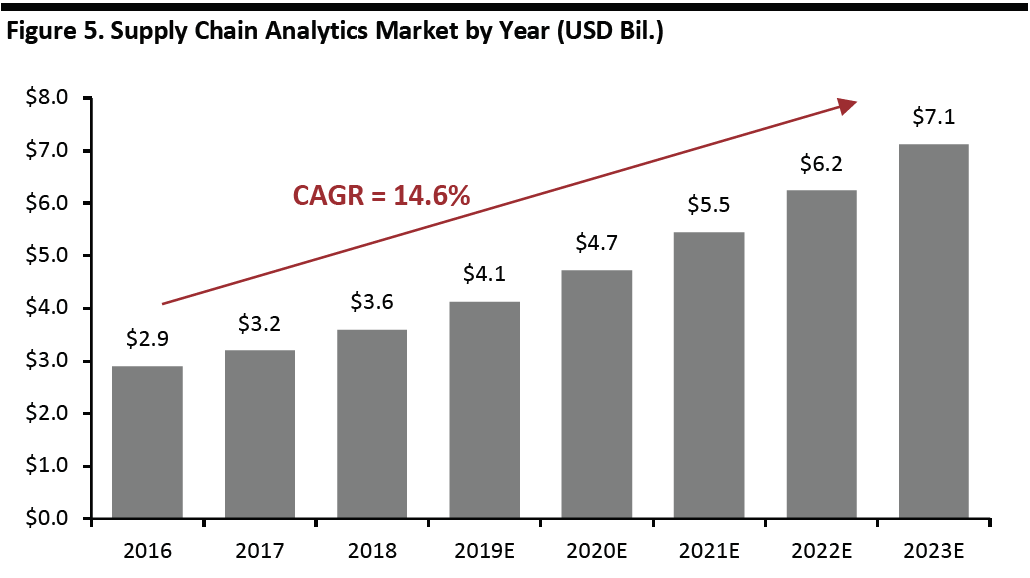 Source: Markets and Markets[/caption]
Source: Markets and Markets[/caption]
The supply chain analytics market breaks down geographically as depicted below. North America is the largest market, followed by Europe and Asia Pacific.
[caption id="attachment_92627" align="aligncenter" width="700"]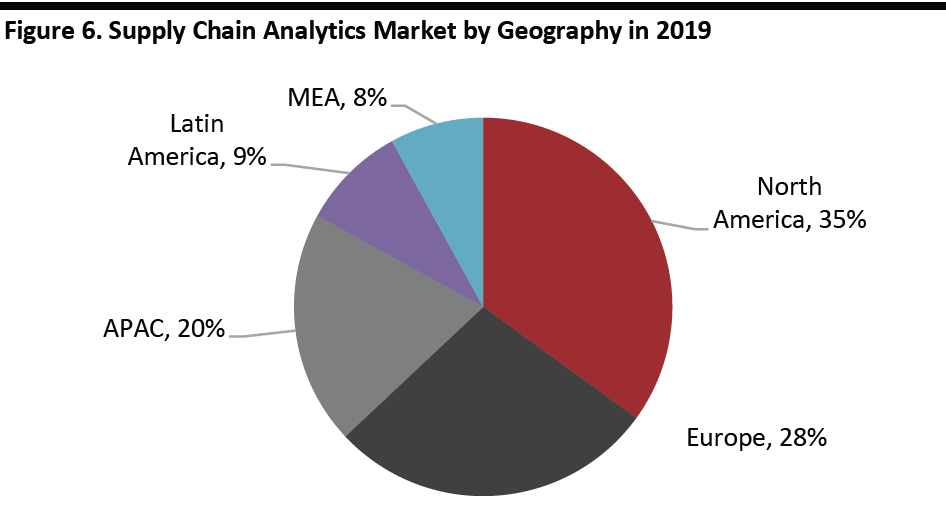 Source: Markets and Markets[/caption]
Source: Markets and Markets[/caption]
Growth Drivers
In addition to the relentless need to keep pace with the competition and minimize cost, factors driving retailers to embrace or upgrade supply chain software include the following:
- Global supply chains.
- The need for one comprehensive software platform to manage complex supply chains.
- Move to cloud-based enterprise resource planning software.
- Availability of new technologies.
- Demand for transportation-management systems.
- Opportunities from IoT.
The section below discusses the benefits of machine learning and IoT.
Machine Learning
The key strengths of machine learning’s algorithms and applications are finding anomalies, patterns and making predictions based on large amounts of data. Supply chain problems are optimizations under several constraints such as time, cost and resources, which make them ideal candidates for machine learning.
Other applications of machine learning in supply chains include:
- Coordination with IoT(see below).
- Reduction of human error.
- Reducing variance in quality from suppliers.
- Detecting fraud.
- Prediction of demand.
- Anticipation of potential supply shortages.
- Work with large data sets.
IoT
IoT enables a network of connected devices to collect and share data about their status with other objects connected to the network. This data can be analyzed to determine actions for the devices to execute or to make business decisions. Many devices on an IoT network can act autonomously.
The benefits of IoT include the ability to track materials and products more quickly and accurately, to monitor the quality of goods in real time and achieve higher efficiency through seamless communication.
IoT also offers the following benefits for retailers:
- Optimize quality and prevent waste.
- Maintain production and ensure preventative maintenance.
- Optimize logistics processes.
- Enable more accurate delivery.
- Enhance the shopping experience.
For more information on IoT in the supply chain, read the Coresight Research report Supply Chain Briefing: The Internet of Things Brings Efficiency and Accuracy to the Supply Chain as well as our upcoming report on IoT in retail, to be published in mid-July 2019.
Key Companies
The supply-chain software segment is very active, containing many large, established companies coexisting with a flourishing group of emerging innovators. The table below highlights key players in the supply-chain market, accompanied by a brief description of their activities, followed by introductions of selected emerging innovators in the space.
 [caption id="attachment_92629" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
[caption id="attachment_92629" align="aligncenter" width="700"] Source: Company reports[/caption]
Source: Company reports[/caption]
There are also several emerging companies engaged in inventory management, including the following:
- Clearmetal offers software for transport lead-time planning, predictive transport visibility and logistics ecosystem collaboration that improves operational efficiency and reduces air freight and expenses.
- Darkstore transforms free space in store and mall storage facilities into fulfillment centers, which enables brands and companies to fulfill product deliveries faster.
- Elementum offers a supply chain automation platform as a software-as-a-service. Its platform provides insights on the flow of goods across destinations, and facilitates extensive availability of information, this means products are timely delivered at the optimum price.
- Lanetix utilizes collaboration, CRM and workflow software to help logistics service providers streamline bid desks, increase margins, improve sales productivity and reduce risk in solution design and delivery.
- Rootstock Software is built on the Salesforce platform and offers management of sales, order processing, engineering, supply chain, production, inventory, logistics and financials.
- Supply Vision provides cloud-based software that aggregates the components of managing shipments by air, sea, rail or ground into a unified solution that allows customers to streamline operations, which in turn increases overall efficiency, including a mobile feature that allows for data access on any device in real-time.
Key Insights
As competition has intensified and become global, supply chains have become global as well, dramatically increasing complexity and stretching across multiple countries, factories and currencies. This level of complexity can generate data that is beyond the human capacity to interpret, but software excels in classifying and interpreting data. The state of software has continually improved, and currently uses tools such as machine learning to make future predictions and offer suggestions to solve problems. There are also new software technologies such as machine learning that enable retailers to glean insights and make predictions from data, in addition to other hardware and software technologies. Supply chain software now represents the nervous system that sits at the center of retailer operations, coordinating business planning, production and distribution of goods throughout the enterprise.