
albert Chan
Introduction
SAP, a pioneer and powerhouse in the enterprise resource planning software industry, is leveraging its strong foundation to expand into adjacent areas such as CRM software and redirecting its focus to the customer experience.
SAP started out life in Germany in the 1970s and initially developed financial software for enterprises. It later expanded it into a platform to manage virtually every element of an industrial business, such as purchasing, manufacturing, inventory management, financial reporting and analysis.
The company has moved into new major categories over the decades through strategic acquisitions, such as adding business intelligence capabilities via its 2007 acquisition of Business Objects; adding human capital management through its acquisition of SuccessFactors; adding sales tools via CallidusCloud; and, perhaps its most important acquisition, Qualtrics, which provides a suite of product, brand, employee and customer-experience capabilities.
SAP’s current strategy has evolved dramatically from the company’s initial focus on finance and operations. Today, the company uses advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning to offer retailers capabilities that help them enhance the experience for customers and employees.
Coresight Research’s Take
SAP is moving quickly to embrace customer experience, after nearly 50 years developing business software that makes enterprises run efficiently. The company has built upon its core strength in operations and finance through several key acquisitions that make it relevant and competitive in today’s key areas of business intelligence, e-commerce, cloud software and customer experience, and SAP is currently refashioning its product portfolio around customer experience. While the company spent much of its early history developing the unfashionable infrastructure that makes enterprises run, SAP is now directing its portfolio at the retail and fashion verticals, having added several well-known names in fashion to its customer list.
Key Recent Developments in Retail
SAP’s retail and fashion verticals have announced several key initiatives:
- The company announced an agreement with global IT firm Wipro in March 2020 to codevelop new solutions for the retail and fashion companies to help them manage business processes and the customer experience. The platform aims to offer a retail management solution, offer advanced fashion manufacturing functionality and provide a cloud-based intelligent store solution.
- Areas of focus at the NRF 2020 show in January included intelligent enterprise and customer experience.
o In intelligent enterprise, the company highlighted the benefits of combining its SuccessFactors HCM software with its Qualtrics customer experience platform to leverage operational data to capture employee insight on engagement, major work events, as well as culture and benefits.
o In customer experience, the company demonstrated its Runway by SAP software, which enables consumers to interact with runway shows, recognizing items which consumers can consumers can like, add to a wish list or preorder in real time.
o In its fashion showcase, provided an analysis of an imagined brand in terms of the circular economy and sustainability. The demo leveraged consumer data collecting their interest and purchasing intent related to sustainability.
- SAP has employed its SAP Commerce Cloud platform to help Hong Kong retailers such as Asia Miles, HKTVmall and Foodwise expand their e-commerce capabilities during the coronavirus outbreak.
Company Overview
SAP SE, headquartered in Walldorf, Germany, is a pioneer in ERP software.
The company was founded by a five former IBM engineers in 1972, its name a fusion of “system analysis and program development.” In July 2014, the company became a Societas Europaea, i.e., a public company registered in the European Union.
Major SAP milestones include:
- 1975: Applications for financial accounting, invoice verification, and inventory management
- 1979: Release two (R/2) of the platform
- 1988: IPO in Germany
- 1992: International expansion and launch of version R/3 of the software
- 1998: IPO on the New York Stock Exchange
- 1999: Update of the software to address the Internet
- 2015: SAP S/4HANA launch
- 2019: Qualtrics acquisition
The left-hand side of the figure below breaks down SAP’s 2019 revenues by segment, showing that the cloud segment made up a quarter of sales. The right-hand side shows that EMEA and the Americas represent SAP’s largest markets.
[caption id="attachment_107774" align="aligncenter" width="700"]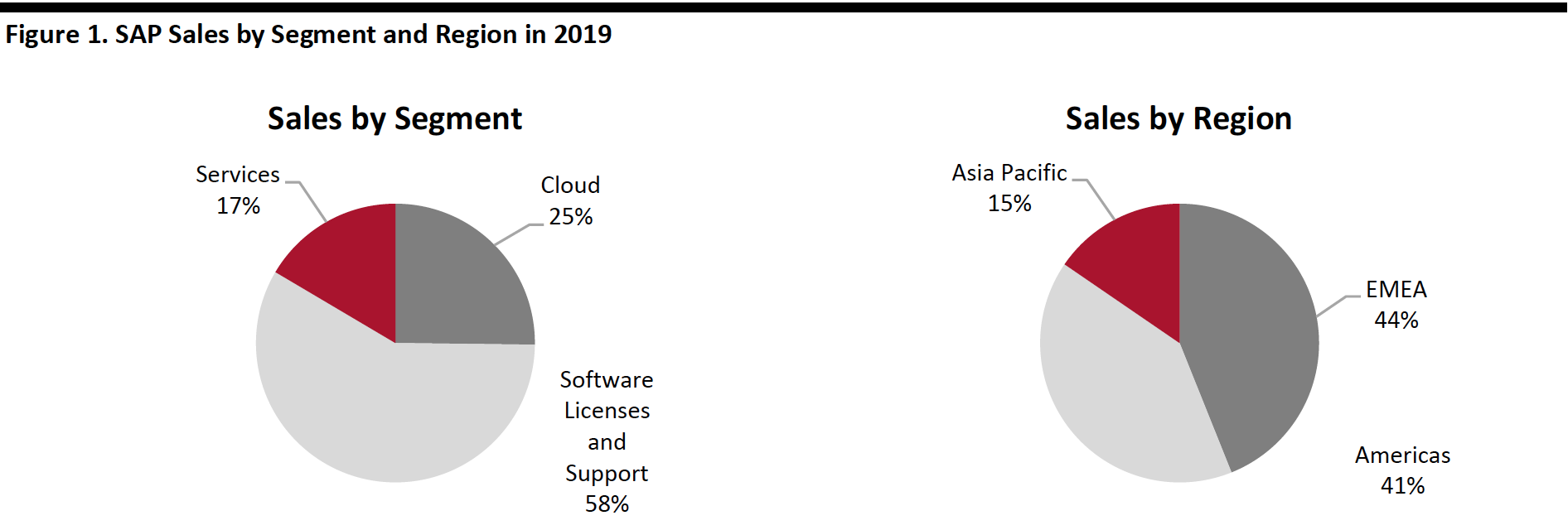 Total sales=€29.5 billion ($31.9 billion)
Total sales=€29.5 billion ($31.9 billion)Source: Company reports[/caption]
Key Acquisitions
The table below lists select key SAP acquisitions, nine of which exceeded $1 billion (of 11 deals). We see that most major acquisitions (excluding Concur) expand the company into new sectors, including customer experience, e-commerce, HR management and business intelligence, transforming SAP from its manufacturing roots and positioning it as a broad, cloud-based ERP software company.
[caption id="attachment_107775" align="aligncenter" width="700"]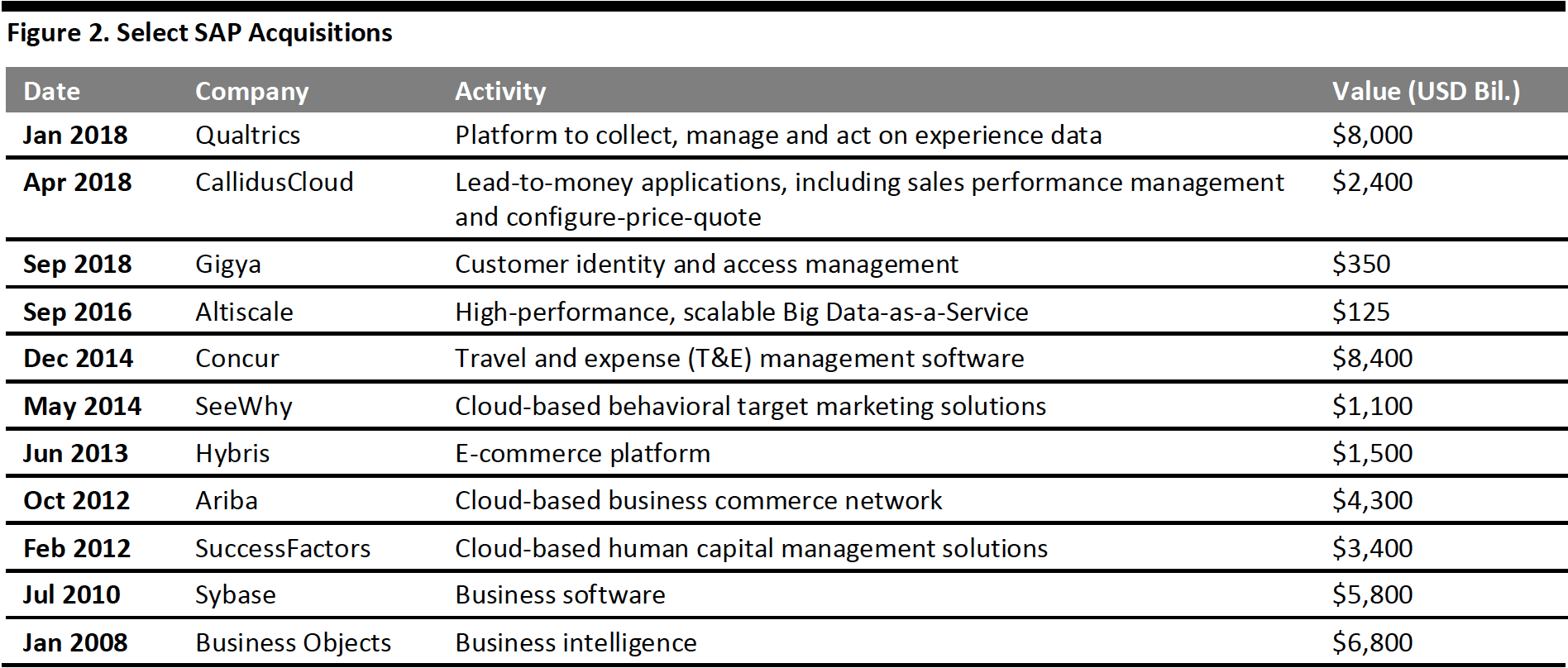 Source: Company reports[/caption]
Source: Company reports[/caption]
Strategy
Corporate Strategy
SAP’s general public strategy is as follows:
- Create a new end-to-end customer experience through an experience-management platform for businesses to collect and act on data on employees, products and brands in real time.
- Leverage artificial intelligence/machine learning to bring productivity to the next level by enhancing every part of business processes.
- Help companies reach total workforce engagement, including full- and part-time workers.
At the company’s Capital Markets Day in November 2019, its recently named co-CEOs pledged to focus on the following areas to improve and grow:
- Start and end with the customer.
- Define one set of priorities for the company.
- Ensure a focus based on clear priorities.
- Review the business through three realities (market, product and financial).
- Drive accountability through focus.
Retail Strategy
SAP aims to offer an integrated suite of applications, intelligent technologies and a digital platform for retailers to pursue innovative business models and deliver relevant personalized customer experiences. The company has identified five strategic priorities to help retailers to transform their business:
- Be customer-centric across the value chain: The company wants to offer retailers deep data and predictive insights from data generated at every customer touch point: physical, digital and social.
- Serve the segment of one: The next generation of personalization will serve the segment of one.
- Implement digital supply chains: SAP says it can help improve effectiveness using a connected, end-to-end supply chain by providing real-time consumer insights to internal and external fulfillment teams, distribution centers, manufacturers and suppliers.
- Run smart stores: The company plans to provide a smart-store platform in the cloud, in addition to the existing comprehensive inventory-management solution for in-store merchandise.
- Sell outcomes beyond products: SAP expects most retail revenue will come from services developed from insights harvested from consumer insights and experience data in 2025 and that new business models will include subscription, pay-per-use and outcome-based models.
SAP targets specific industry verticals. In consumer, the company focuses on agribusiness, consumer products, fashion, life sciences, retail and wholesale distribution.
Products
SAP groups its products into six major categories, as depicted below. While listed separately to emphasize their functionality, Marketing Cloud, Sales Cloud and Commerce Cloud are parts of C/4HANA, now called SAP Customer Experience (rather than CRM).
[caption id="attachment_107776" align="aligncenter" width="700"]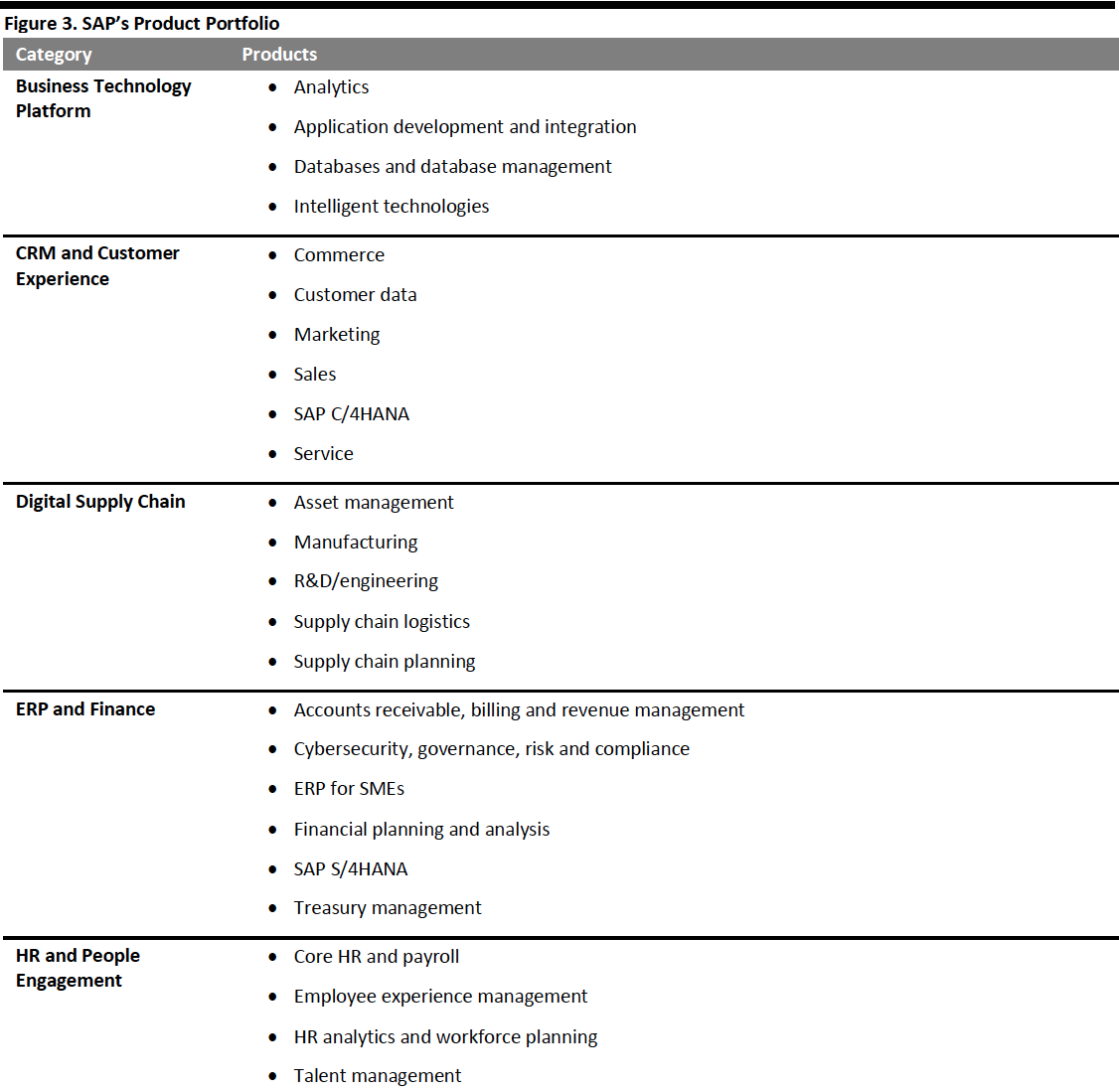 Source: Company reports[/caption]
Source: Company reports[/caption]
SAP S/4HANA is the latest generation of the platform, optimized for large enterprises. (HANA stands for “High performance ANalytic Appliance.”) SAP C/4HANA is the company’s CRM and customer experience platform, combining products from the CoreSystems, Gigya and Hybris solutions. SAP claims it has more than 12,000 licensed customers of S/4HANA, including the Hershey Company and smart speaker manufacturer SONOS:
The figure below illustrates how SAP envisions its cloud-based product portfolio, with experience management at the center comprising the customer and human experience branches, based on the intelligent spend framework. Qualtrics connects the customer to the human experience platforms.
[caption id="attachment_107777" align="aligncenter" width="700"]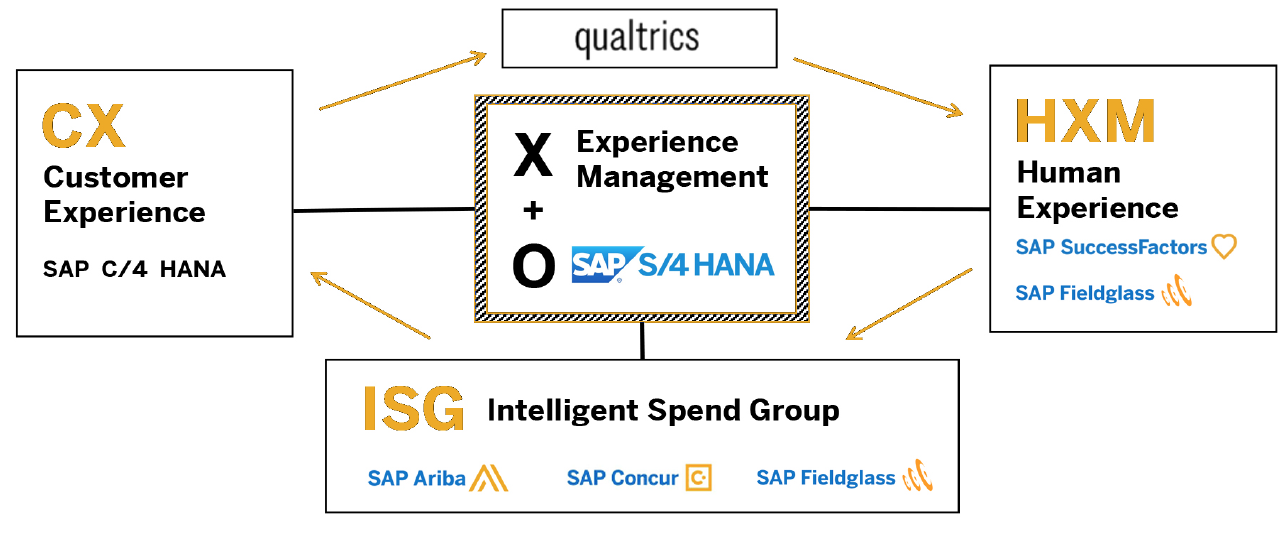 Source: Company reports[/caption]
Source: Company reports[/caption]
Products for Retail
SAP says it helps clients in retail reach more customers and deliver individualized experiences by becoming an intelligent enterprise. Its main platforms are S/4HANA Cloud and Customer Activity repository, which serve the following broad categories and functions:
- Omnichannel marketing: single-customer view, consent-based marketing and marketing execution.
- Customer-centric merchandising: merchandising intelligence, product design and development, master data management, merchandise and assortment planning and pricing and promotions.
- Procurement: sourcing and contracting, supplier and risk management, merchandise buying, indirect buying, invoicing and payments.
- Digital supply chain: forecasting, allocation and replenishment; omnichannel inventory and order response; warehouse management; yard logistics; transportation management; and, track-and-trace and logistics networks.
- Omnichannel customer experience: commerce management and personalization; retail store management; omnichannel sales order management; customer service; and, customer experience management.
Financial Overview
During 2016–2020E, SAP’s revenues are expected to grow at a 7.5% CAGR, greatly outpacing its end markets. Most of this growth can be attributed to its cloud business, which is driven by businesses digitalizing and moving to the cloud. Excluding its cloud segment, SAP revenues are expected to grow 2.2%, more in line with its end markets.
[caption id="attachment_107778" align="aligncenter" width="550"]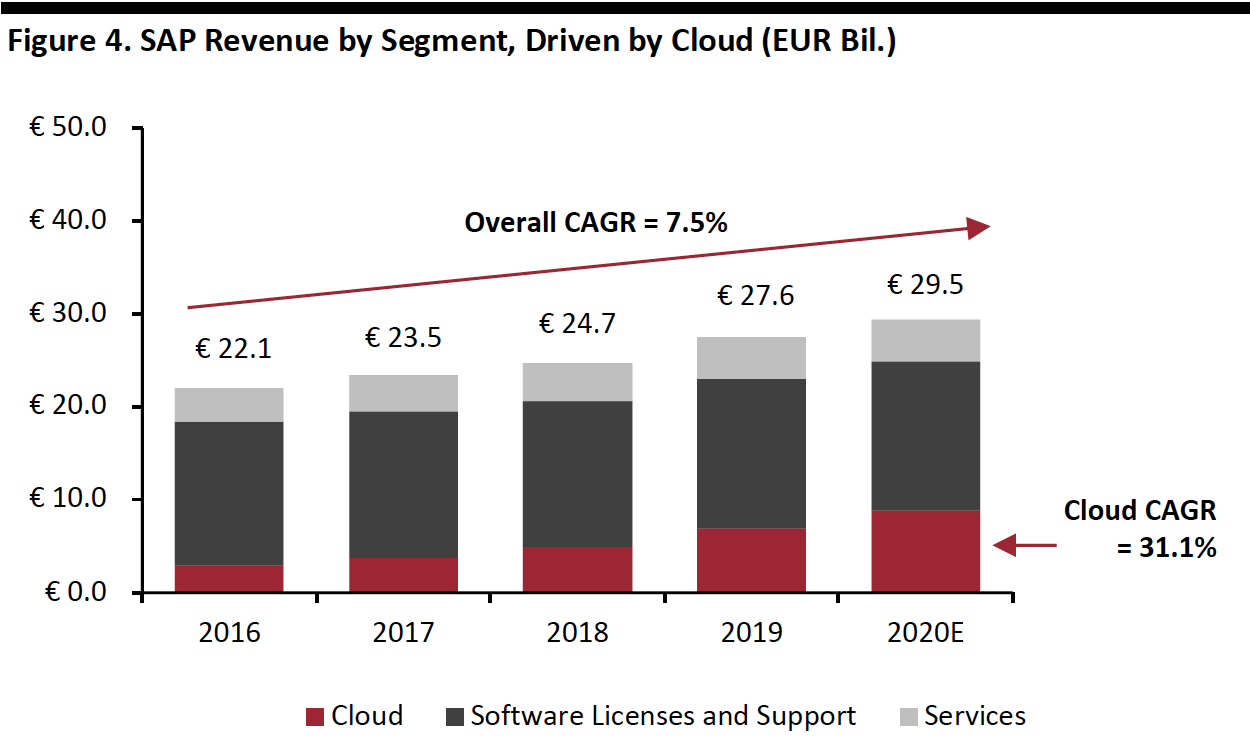 Source: Company reports/Coresight Research[/caption]
Source: Company reports/Coresight Research[/caption]
SAP calls its longer-term growth plan “ambition,” and the company is targeting €35 billion in revenues in 2023, which would represent a 7.2% CAGR from 2018. The company is also targeting an 11% CAGR in operating-income growth and raising margins to 34% from 29% during the 2018-2023.
Recent Results
In 4Q20, the company reported IFRS revenues of €27.6 billion, up 12% year over year, driven by a 39% increase in cloud revenue. EPS declined 18% to €2.80 due to higher acquisition-related charges from the Qualtrics acquisition, charges from a global restructuring and higher share-based compensation.
Markets
The global ERP market is large and mature, worth $93.3 billion in 2020 and estimated to grow at a modest 1.2% CAGR during 2018-2023E.
[caption id="attachment_107779" align="aligncenter" width="700"]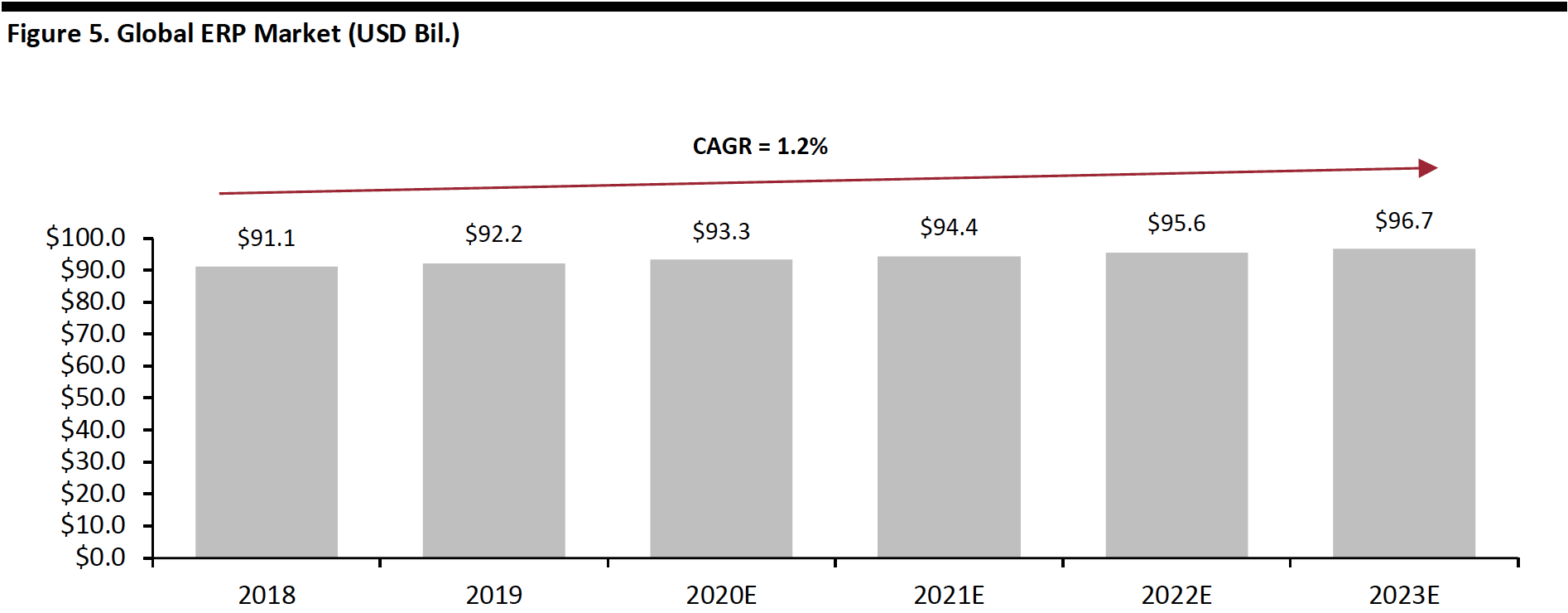 Source: Apps Run the World[/caption]
Source: Apps Run the World[/caption]
The US ERP market is estimated to be worth $16.4 billion in 2019, projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.2% during 2016-2021, according to Statista.
SAP is the ERP global market leader, with 8% of the market in 2017, as shown below.
[caption id="attachment_107780" align="aligncenter" width="700"]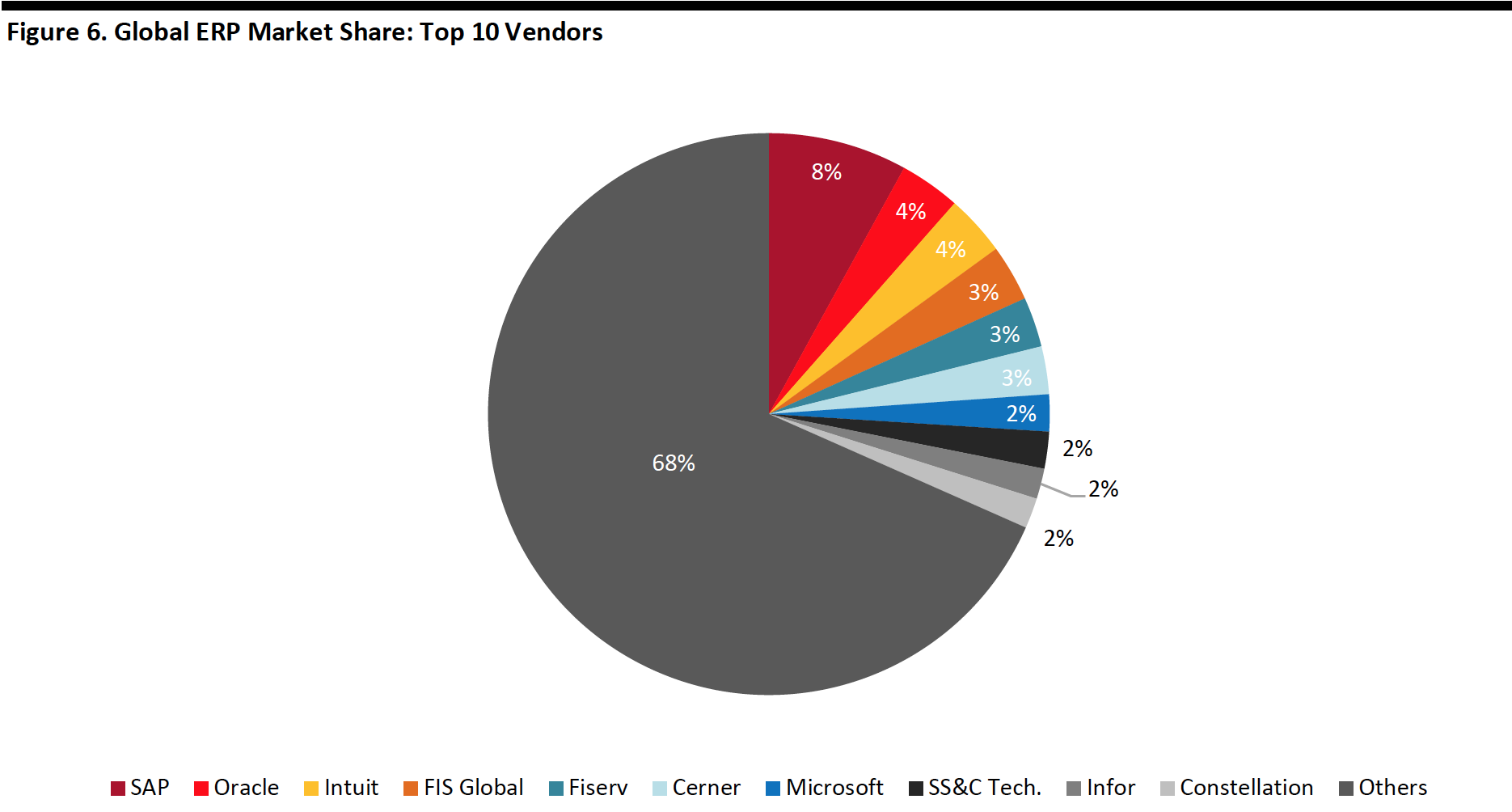 Source: Apps Run the World[/caption]
Source: Apps Run the World[/caption]
SAP also claims the following positions within the following markets:
[caption id="attachment_107781" align="aligncenter" width="550"]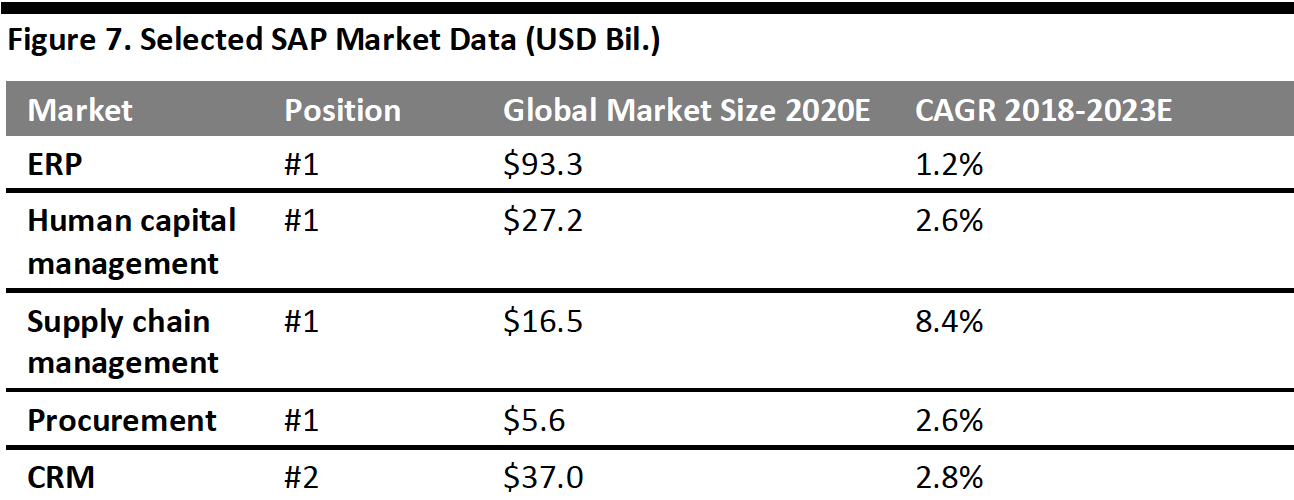 Source: Company reports/Apps Run the World/Statista/Coresight Research[/caption]
Source: Company reports/Apps Run the World/Statista/Coresight Research[/caption]
Customers
SAP serves a diverse group of global customers in diverse industries. Select customers include:

Competitive Landscape
As depicted above, the global ERP market (and submarkets) are fragmented, comprising global technology leaders and smaller, focused companies.
The figure below shows annual revenues for the three major ERP companies. Although Salesforce has lower revenues, it dominates the CRM segment (which both Oracle and SAP have entered) and is steadily adding new verticals and capabilities to its platform. SAP’s strategy focuses on the customer experience, which has been Salesforce’s longstanding focus.
[caption id="attachment_107783" align="aligncenter" width="550"]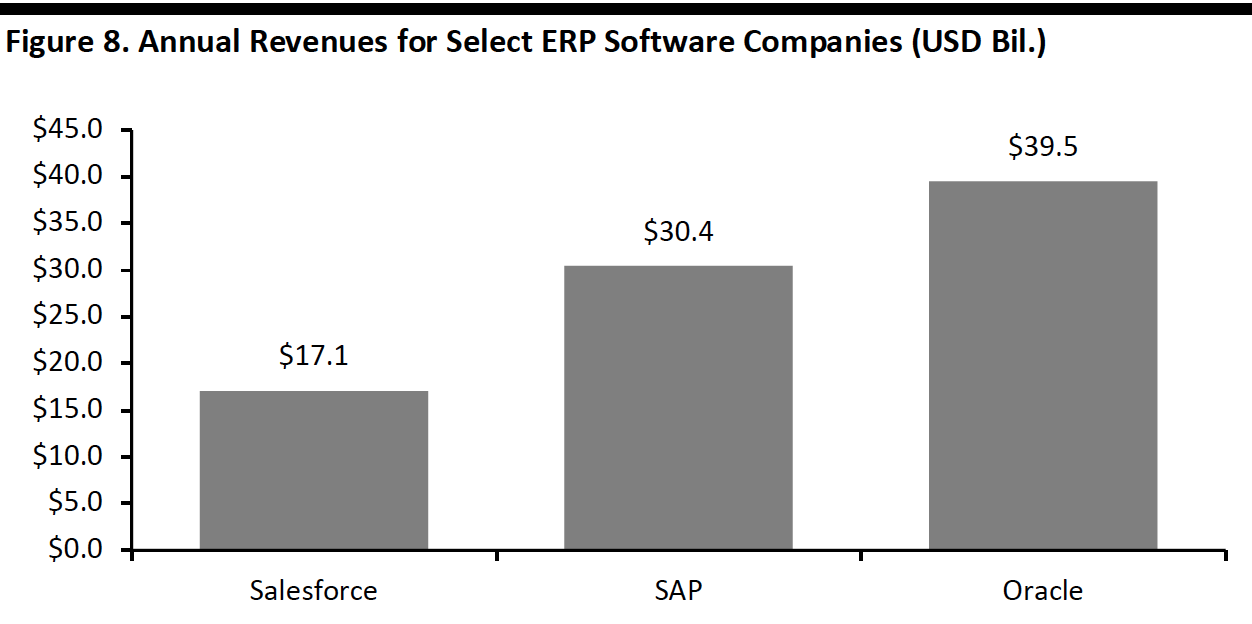 Source: Company reports/Xe.com/Coresight Research[/caption]
Source: Company reports/Xe.com/Coresight Research[/caption]
SAP’s major competitors in major categories include the following companies.
[caption id="attachment_107784" align="aligncenter" width="550"]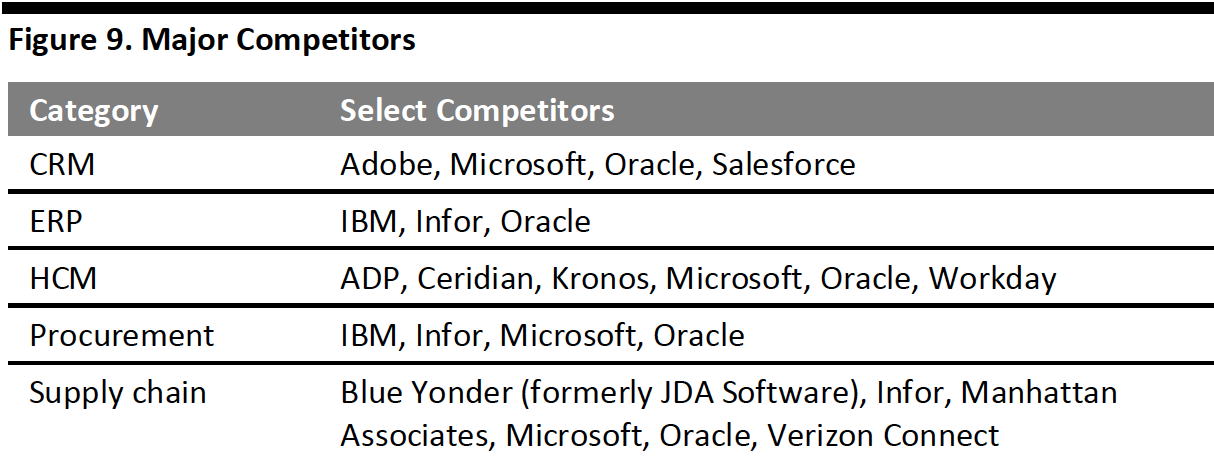 Source: Company reports/Apps Run the World[/caption]
Source: Company reports/Apps Run the World[/caption]
Other vendors of ERP and other business software include Epicor, Jesta I.S. and MI9 Retail.
Competitive Advantages
SAP has enormous reach and scale. The company is global, with more than $30 billion in revenues and more than 100,000 employees, and is active in more than 180 countries.
SAP is expanding from its early market leadership in ERP software, initially for manufacturing, branching out into other product categories such as CRM, HCM and customer experience.
The company’s $135+ market capitalization also enables it to make transformative acquisitions of emerging leaders. For example, SAP’s $8 billion acquisition of Qualtrics (just one day before its scheduled IPO) added the customer-experience platform that sets the tone for the company’s current strategy.
Challenges/Risks
SAP’s key challenges center on those of managing any large global company in the software industry, in which companies are constantly nervous about a disruptor launched in a founder’s garage. Despite its strengths in finance and manufacturing, sectors such as CRM and customer experience have entrenched incumbents, and SAP also competes against global tech powerhouses such as IBM and Oracle. The company’s renewed focus on execution and profitability suggests that it had taken its eye off its core business, but the new co-CEOs seem to have a clear execution plan.
Other Coresight Research
ERP Software—the Nervous System of Modern Enterprises