
DIpil Das
Introduction
Oracle is a leading Silicon Valley technology company that was founded 1977 by current chairman and CTO Larry Ellison and two other partners to create a business from a new computer database technology at the time, called relational databases. These databases store data in several linked files, rather than in one large file, which offers certain performance benefits. Relational databases are commonplace today. Building on its strength in databases, which are the foundation for nearly all enterprise and business applications, Oracle has branched out into other software categories, becoming a leader in areas such as ERP software, finance, CRM and supply chain management. As businesses have digitalized and moved their businesses to the cloud, Oracle has evolved its offerings to include cloud-based applications and services, as well as moving its own line of platforms and products to the cloud. Today, the company has a broad product portfolio that spans databases, applications, analytics, services and even hardware, including high-performance appliances optimized for database performance. In retail, Oracle’s applications and services cover omnichannel, analytics, merchandising, planning and supply chain.Coresight Research’s Take
Oracle is helping retailers digitalize and move to the cloud—focusing on its Gen-2 cloud, which offers two key foundations needed by retailers: resilience (through autonomy) and security. The uncertainty and shifts in the retail market caused by the current coronavirus crisis underscores the need for retailers to have IT systems that are flexible, scalable and resilient. On its Gen-2 foundation, Oracle offers a broad line of intelligent platforms that help retailers to engage their customers, keep pace with the rapidly changing industry and run their businesses efficiently—including analytics, data management, integration and security. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are leveraged through many of the platforms and applications. Oracle is a large company within a mature segment. Retail is one of 15 verticals that Oracle targets so it is competing for corporate resources against the other 14.Key Recent Developments in Retail
At Oracle’s annual Analytics Summit in May 2020, the company announced the release of its new analytical cloud service, Analytics for Fusion HCM, which employs key performance indicators to generate actionable insights. It is the most recent addition to Oracle’s next-generation technologies and services for its Fusion-branded applications and middleware. Also at the event in May, the company announced the release of Analytics for Cloud HCM. At NRF 2020 Vision: Retail's Big Show in January 2020, Oracle announced the release of Retail Consumer Insights, which helps retailers to understand the characteristics of their best customers and find similar traits among the massive amount of customer data stored in the Oracle Data Cloud. The platform applies predictive and prescriptive analytics to profile-linked transaction-level sales data, for example, in addition to other demographic, geographic and interest attributes.Competitive Landscape
The global ERP market (and submarkets) are fragmented, comprising global technology leaders and smaller, focused companies. Figure 1 shows the annual revenues of three major ERP companies for fiscal year 2019: Oracle is the largest major enterprise-software company by revenue, followed by SAP and Salesforce (a leader in the CRM space). [caption id="attachment_110781" align="aligncenter" width="700"]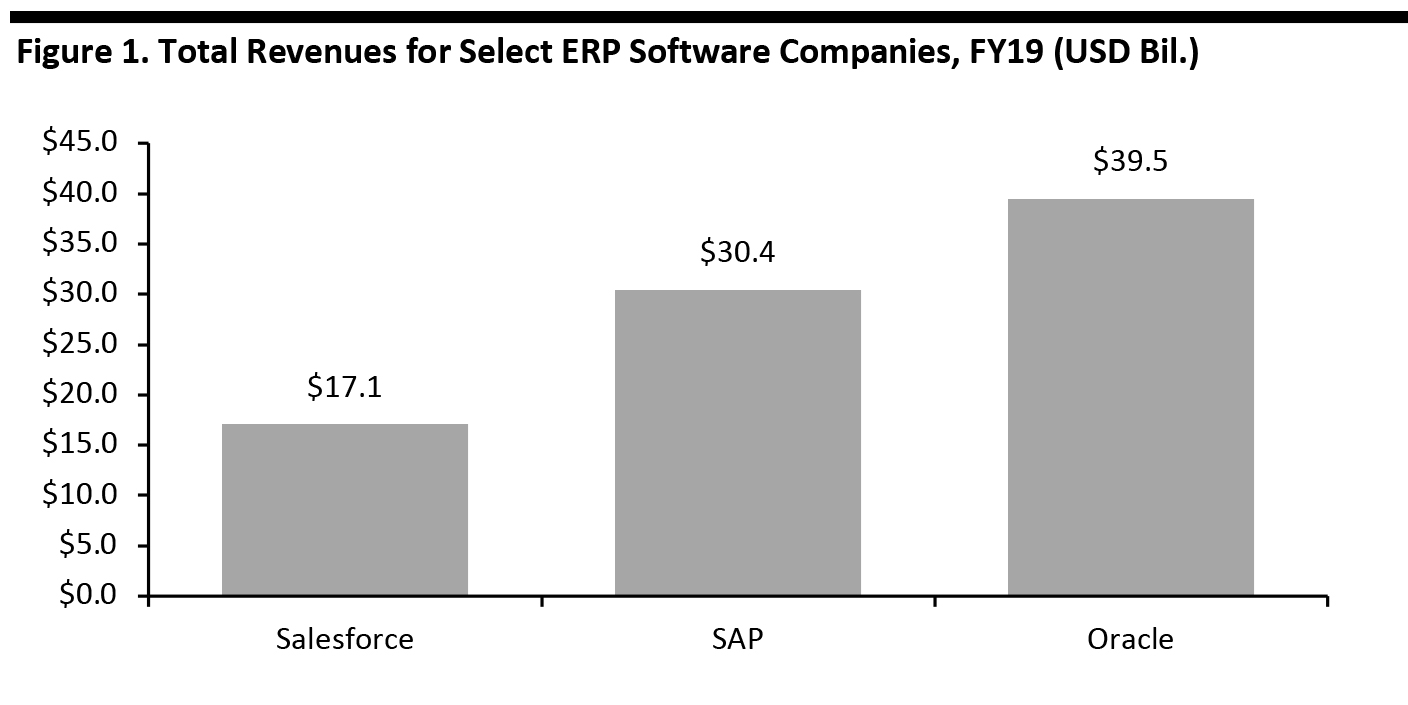 Source: Company reports/Xe.com/Coresight Research[/caption]
We identify Oracle’s major competitors across select categories in Figure 2. Other vendors of ERP and other business software include Epicor, Jesta I.S. and MI9 Retail.
Figure 2. Major Competitors, by Category
[wpdatatable id=214]
Source: Company reports/Apps Run the World
Source: Company reports/Xe.com/Coresight Research[/caption]
We identify Oracle’s major competitors across select categories in Figure 2. Other vendors of ERP and other business software include Epicor, Jesta I.S. and MI9 Retail.
Figure 2. Major Competitors, by Category
[wpdatatable id=214]
Source: Company reports/Apps Run the World
Competitive Advantages
Oracle has substantial reach and scale, driven by its near $40 billion in annual revenues—and the company invested $6 billion in R&D in fiscal year 2019. Oracle has an enormous technology base, built on its early leadership in database technology, which forms the foundation for modern enterprises. This is supplemented by the company’s key acquisitions in ERP, financial and cloud applications and software. Oracle has a $167 billion market capitalization and is a healthy acquirer of companies.Challenges/Risks
Oracle’s corporate revenues are growing modestly in the low, single digits, albeit faster than the industry, despite the rapid growth of cloud-based applications. This modest revenue growth mitigates the company’s ability to generate net income and making stock a less valuable acquisition currency. The company has become such as software giant that its size challenges the law of large numbers—i.e., Oracle participates in many segments, in both hardware and software, across multiple industry verticals; this can dilute the company’s focus on any one area and makes it a challenge to have a significant impact on the whole company.Framework Analysis
In our technology framework analysis, we analyze Oracle’s capabilities according to several criteria. The company is a leader in selected markets and in technology depth, operating within a mature category and focusing on retail alongside many other verticals. Figure 3. Technology Framework Analysis: Oracle [wpdatatable id=215] Source: Company reports/Burleson Consulting/Coresight ResearchRetail Strategy and Products
Retail Strategy Oracle believes that in the highly competitive retail market, retailers need transparency and flexibility to move rapidly to facilitate customer interactions, which are happening online, in store or in between, such as with BOPIS (buy online, pick up in store) services. The company’s retail strategy centers around bringing retailers to its Gen-2 cloud and autonomous database, combined with other tools such as analytics, data management, integration and security, as well as using technologies such as AI and blockchain. In addition, Oracle highlights the resiliency of its fault-tolerant applications as an advantage for retailers, as they contain redundancy and are able to withstand network, power and hardware outages to offer continuous service. Products for Retail Oracle offers commerce, operational and analytical tools to support the management of modern retail operations. Omnichannel- Commerce Cloud: Turns data into insights, drives personalization, supports brand and business-model expansion and leverages mobile and smart devices
- Customer Engagement Cloud: Provides customer management and segmentation, loyalty and awards management, campaign and deal management and gift-card management
- X-Store Point of Service: Provides a framework to give store associates visibility over inventory, increase workflow efficiency and offer actionable insights for managers
- Analytics Service: Offers customer insights and merchandising insights, powered by AI and ML
- Science Service: Offers clustering, customer segmentation, affinity analysis, attribute extraction, decision trees, an innovation workbench and profile science
- Allocation: Determines the need at the SKU level, offers role-based dashboards, employs multiple allocation methods and creates purchasing orders automatically
- Merchandising Insights Service: Offers descriptive, predictive and prescriptive insights for merchandising, financial planning, invoice matching, price management and category management
- Sales Audit: Validates sales information from all channels while managing discrepancies by exception
- Category Management Planning and Optimization: Category planning combines data points from multiple sources and recommends formal category roles, strategy and tactics. Assortment planning and optimization provides multiple approaches for creating optimized and customer-centric assortments.
- Offer Optimization Service: Creates optimal recommendations for promotions, markdowns and targeted offers to maximize profits and sell-through
- Merchandise Financial Planning: Improves plan accuracy, eliminates plan discrepancies, supports proactive retail management and enables receipt flow planning down to a weekly level
- Advanced Inventory Planning: Applies forecasted demand across all channels to enhance inventory ordering, allocation, replenishment and delivery plans
- Brand Compliance Management: Includes modules to enable brand owners to collaborate with their supply chains on the sourcing, development, labelling and quality of their products
- Demand Forecasting: Anticipates customer demand by applying ML, AI and decision science to data, simplifying forecast management while inspiring new customer engagement
Company Overview
Oracle was founded by Larry Ellison, Bob Miner and Ed Oates as Software Development Laboratories in 1977. The company originally pioneered relational databases, which use cross-referenced smaller tables linked by key fields—compared to traditional flat-file databases, which store all the data in one file. Oracle had approximately 136,000 full-time employees at the close of fiscal year 2019, ending May 31, 2019. We outline the company’s major milestones below.- 1982: Changes name to Relational Software Inc.
- 1986: Goes public on the NASDAQ under the ticker symbol ORCL
- 1987: Becomes the world’s largest database company, with $100 million in sales
- 1992: Releases Version 7 of its database software
- 2005: Acquires ERP software company PeopleSoft for $10.4 billion
- 2013: Updates Oracle Database for the cloud
- 2018: Launches first autonomous database
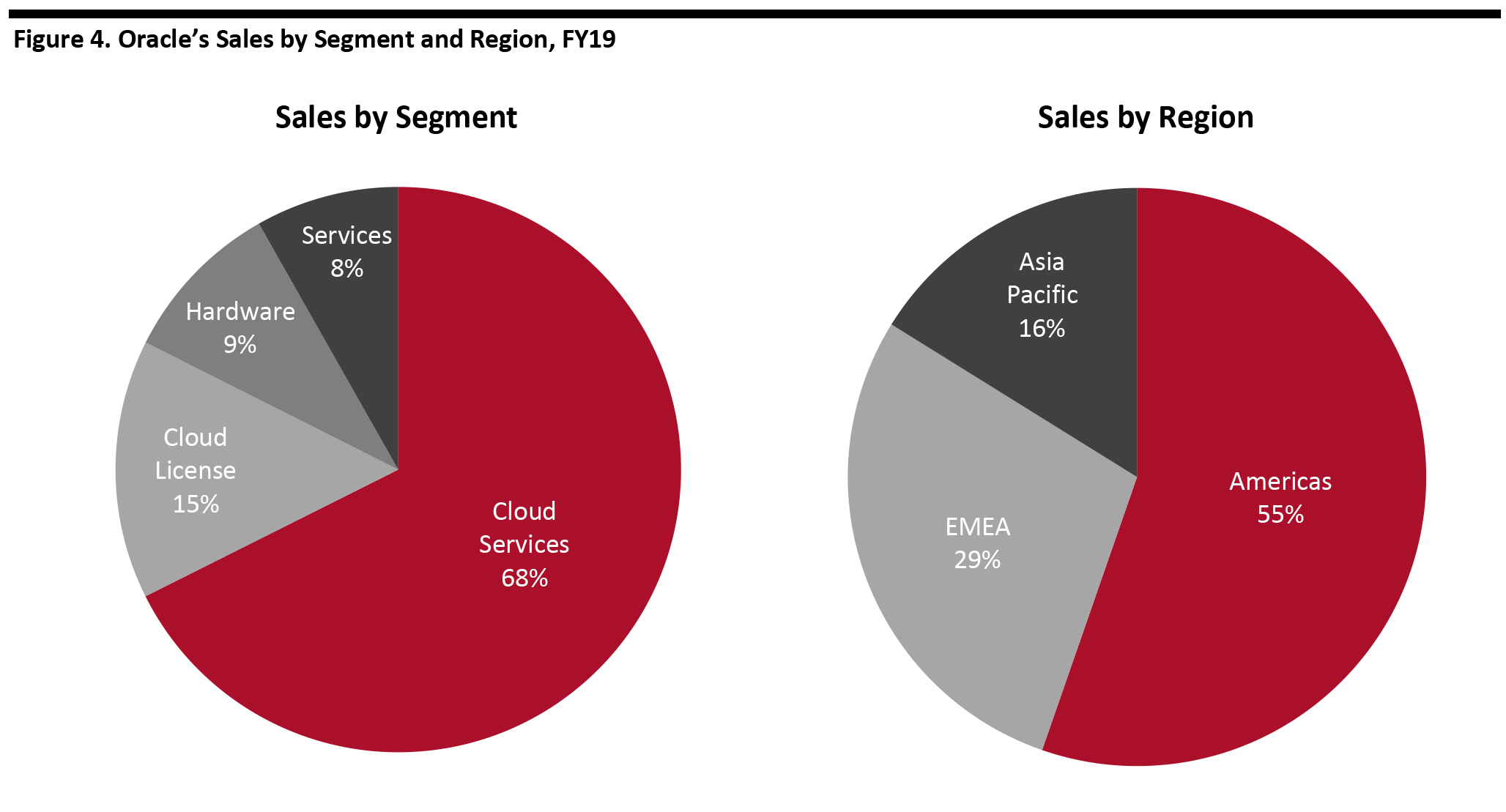 Total sales: $39.5 billion
Total sales: $39.5 billion Source: Company reports [/caption]
Key Acquisitions
Investor information discloses that Oracle has made 131 acquisitions in total, comprising 56 recent and 75 previous acquisitions, most of which were too small to report acquisition value. The recent acquisitions fall within four categories and show Oracle’s focus on the applications and industry verticals (see Figure 5). [caption id="attachment_110783" align="aligncenter" width="700"]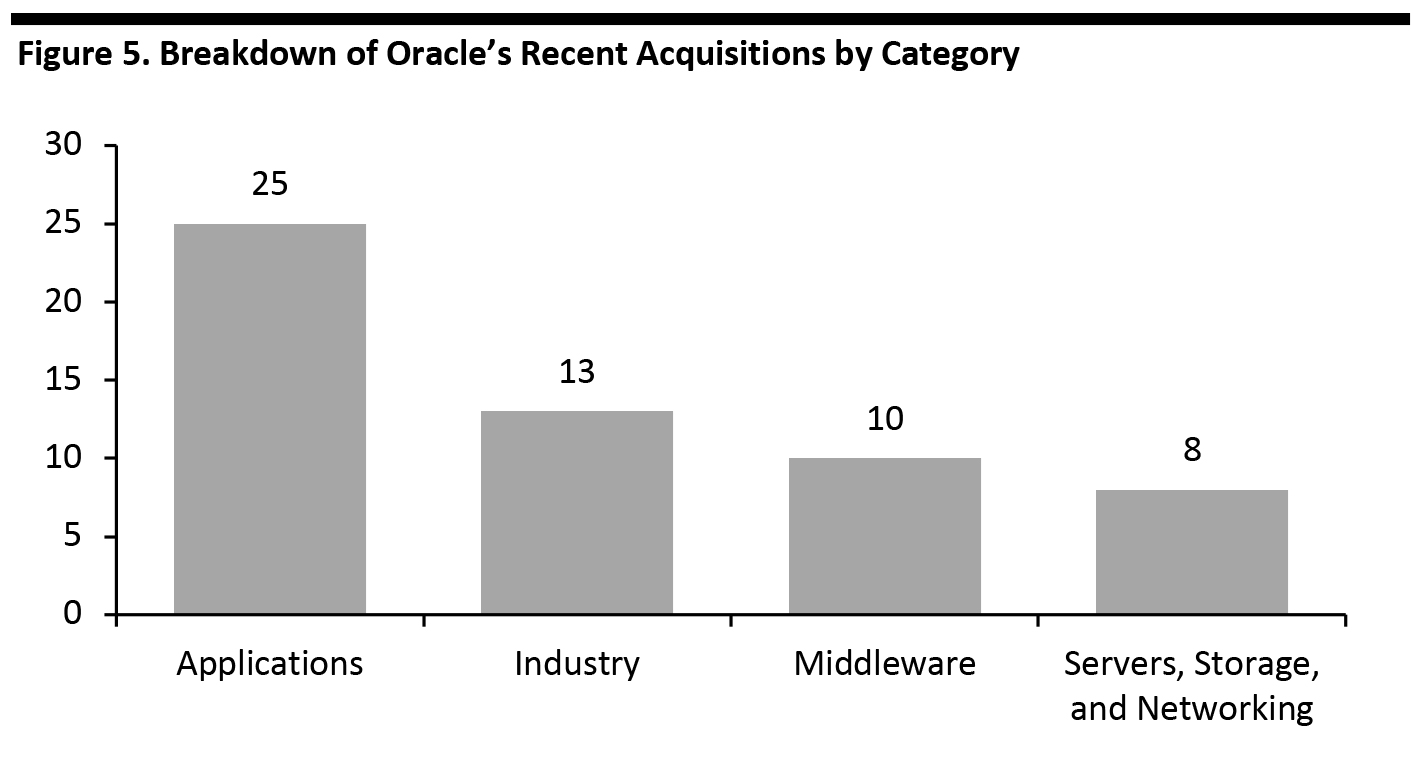 Source: Company reports/Coresight Research[/caption]
The table below lists Oracle’s largest acquisitions, which total $34.8 billion in value.
Figure 6. Select Oracle Acquisitions
[wpdatatable id=216]
Source: Company reports
Source: Company reports/Coresight Research[/caption]
The table below lists Oracle’s largest acquisitions, which total $34.8 billion in value.
Figure 6. Select Oracle Acquisitions
[wpdatatable id=216]
Source: Company reports
Strategy
Corporate Strategy Oracle’s strategy is as follows:- Pursue its cloud strategy, including offering SaaS (software as a service) and IaaS (infrastructure as a service)
- Offer customers broad, comprehensive, flexible and interoperable deployment models for Oracle applications and infrastructure technologies
- Invest in R&D of new products
- Make acquisitions to enhance product and service offerings
- Offer applications for customers in specific industries—including communications, construction and engineering, financial services, health sciences, hospitality, manufacturing, the public sector, retail and utilities
Products
Oracle offers products and services within the categories of Gen-2 cloud infrastructure, applications, on-premise infrastructure and industry solutions. Gen-2 Cloud Infrastructure Oracle’s Gen-2 cloud infrastructure is focused on autonomy and security—whereas the Gen-1 cloud is focused on being serverless and elastic. Gen-2 cloud products include the following:- Autonomous database—a family of self-operating, self-securing and self-repairing cloud services, which uses machine learning and automation to eliminate human labor, human error and manual tuning
- Data management—includes Oracle’s flagship Database 19c database cloud services and the autonomous database, autonomous transaction processing and data warehouse
- Analytics—includes Analytics Cloud, Analytics Server, Analytics for Fusion Applications and the Essbase data-visualization tool
- Compute—IaaS options including bare-metal servers, autonomous Linux, container engines and registry and graphics processing units and virtual machines
- Other services—The Gen 2 Exadata Cloud at Customer, application development, data center regions and a cloud application marketplace
- ERP: Functions include financials, project management, procurement, risk management, enterprise performance management, supply chain management, adaptive intelligent apps for ERP and analytics for cloud ERP.
- HCM: Functions include global human resources, talent management, workforce management and payroll.
- Supply chain management: Functions include supply chain planning, inventory management, manufacturing, maintenance, order management, logistics, product lifecycle management, procurement and support technologies such as Internet of Things and blockchain.
- Sales: Functions include salesforce automation, B2B (business-to-business) service centers, sales planning and performance management, partner relationship management, price quotes and B2B commerce.
- Service: Functions include B2B and B2C (business-to-consumer) service centers and field service.
- Marketing: Functions include Eloqua (marketing automation), Responsys (cross-channel orchestration), BlueKai (data-management platform), Maxymiser (testing and personalization) and Infintiy (digital analytics).
- Data Cloud: Functions include audiences, contextual intelligence, data management platform and Moat (to measure what matters and drive attention across campaigns).
- NetSuite Application Suite: The unified business management suite encompasses ERP, financials, CRM and e-commerce.
- Oracle Database: Oracle Database 19c runs on Linux, Windows, Solaris, HP/UX and AIX platforms and the Oracle Cloud. The company claims that the latest version of its database software offers performance, scalability, reliability and security.
- Java: The programming language runs on 3 billion devices worldwide, claims a base of 12 million developers and runs on more than 25 billion Java Cards (secure elements, SIMs and smartcards).
- Software: Includes analytics servers, Linux, the MySQL database, middleware and the GraalVM virtual machine that runs applications written in Java SE.
- Hardware: Includes engineered systems (which combine software, storage, compute and networking hardware), enterprise servers, infrastructure software and storage solutions. This category includes Oracle Exadata, a high-performance appliance optimized to run Oracle’s database software.
 Exadata database appliance
Exadata database appliance Source: Company reports [/caption] Industry Applications Oracle has developed industry-specific solutions for the following 15 verticals:
| • Automotive • Communications • Construction and engineering • Consumer goods • Education and research | • Financial services • Food and beverage • Healthcare • High technology • Hospitality | • Industrial manufacturing • Life sciences • Media and entertainment • Public sector • Retail Utilities |
Financial Overview
Oracle saw corporate revenues increase at a modest CAGR of 2.3% between fiscal years 2017 and 2019, comprising a 5.9% CAGR in Cloud Services that was partially offset by negative growth in the company’s other three segments. [caption id="attachment_110786" align="aligncenter" width="700"]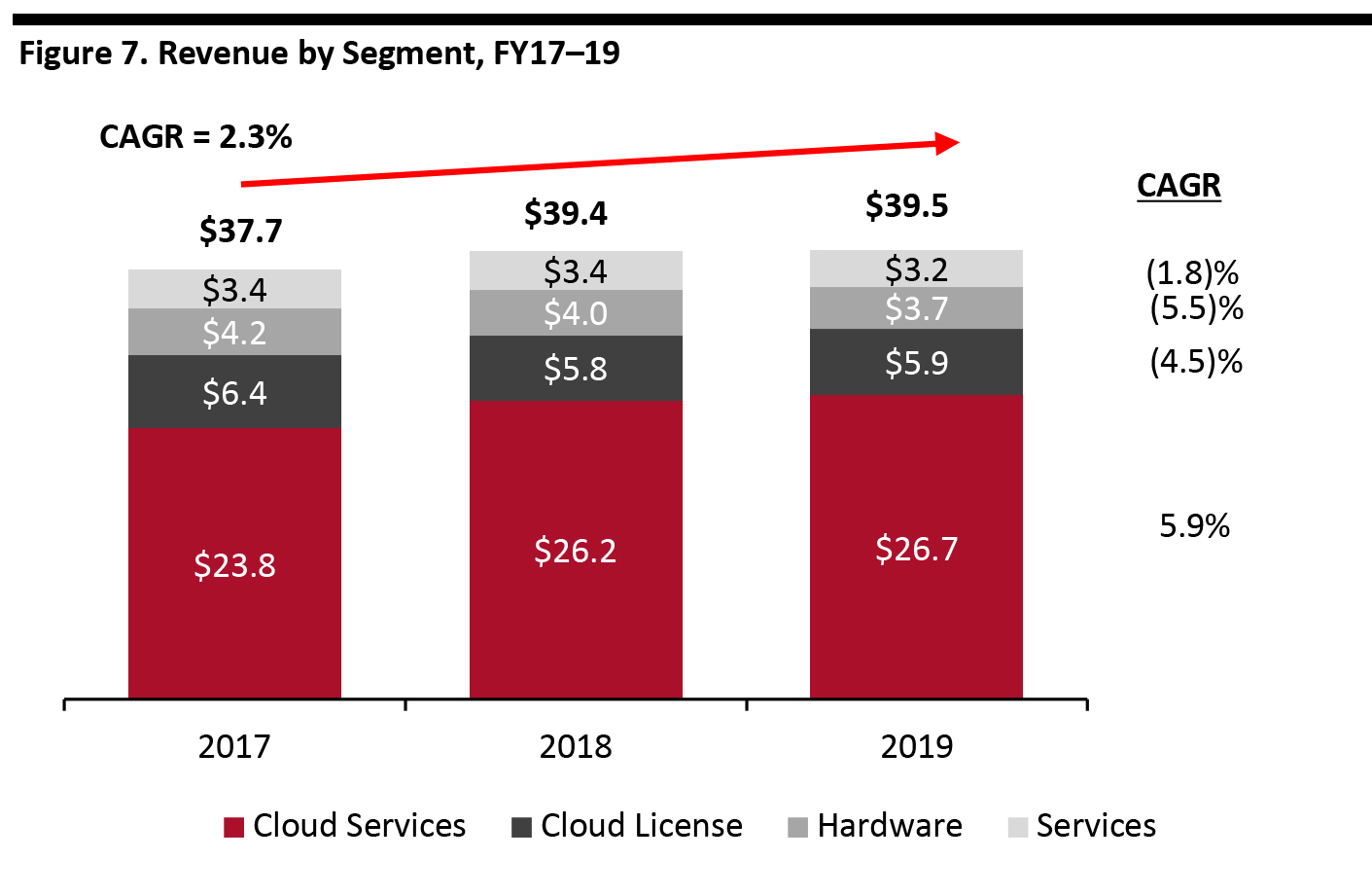 Source: Company reports/Coresight Research[/caption]
Oracle reported third-quarter revenues of $9.8 billion in fiscal year 2020, up 1.9% year over year, driven by 4.0% revenue growth in Cloud Services. The company reported that Fusion ERP Cloud revenues grew 37% year over year. Subscription revenues, which are recurring in nature, comprised 71% of total revenues and drove operating-margin expansion. Adjusted EPS was $0.97, up 1.5% year over year.
Source: Company reports/Coresight Research[/caption]
Oracle reported third-quarter revenues of $9.8 billion in fiscal year 2020, up 1.9% year over year, driven by 4.0% revenue growth in Cloud Services. The company reported that Fusion ERP Cloud revenues grew 37% year over year. Subscription revenues, which are recurring in nature, comprised 71% of total revenues and drove operating-margin expansion. Adjusted EPS was $0.97, up 1.5% year over year.
Markets
The global ERP market is large and mature, worth $93.3 billion in 2020 and estimated to grow at a modest 1.2% CAGR during 2018–2023E. [caption id="attachment_110787" align="aligncenter" width="700"]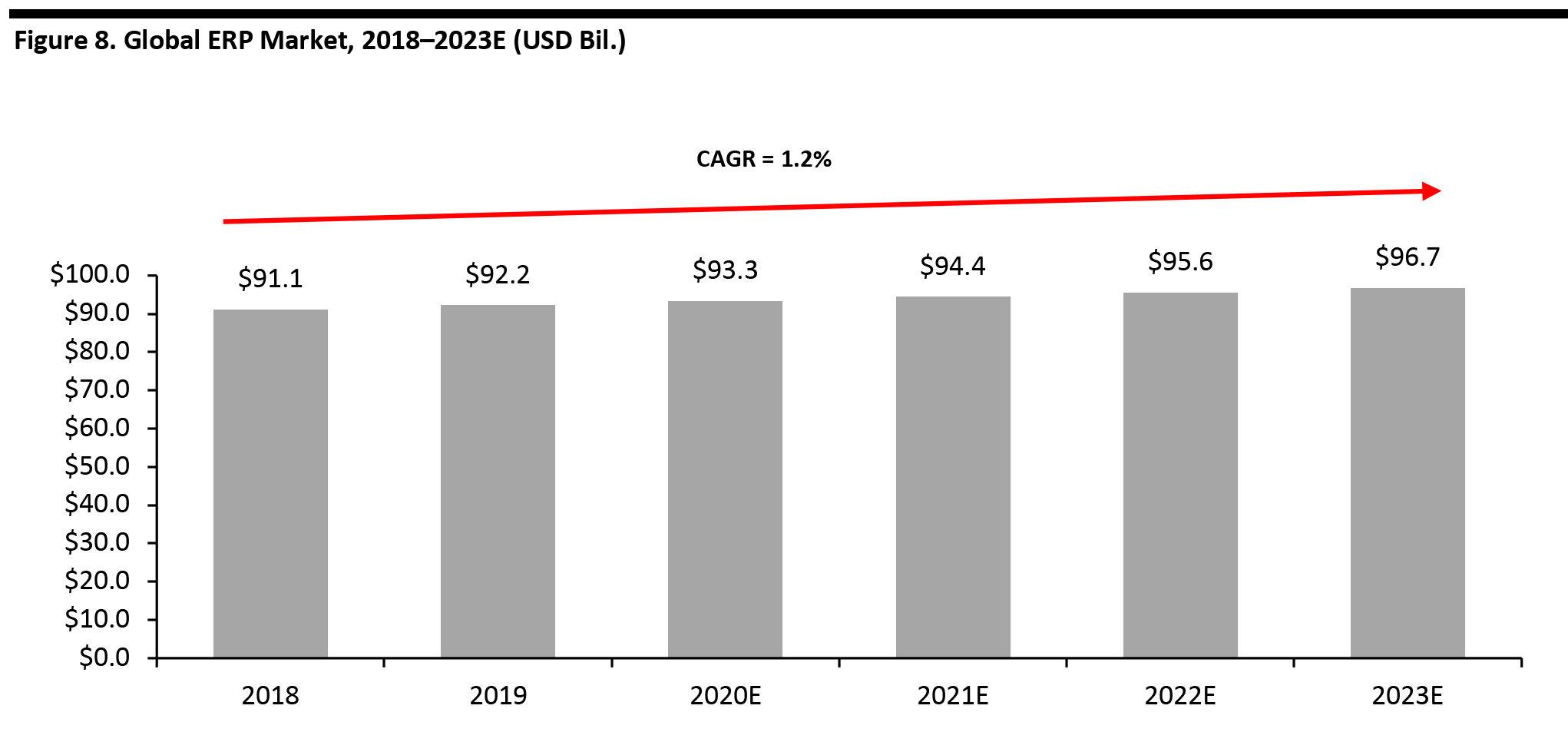 Source: Apps Run the World[/caption]
The US ERP market was estimated to be worth $16.4 billion in 2019 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.2% during 2016–2021, according to Statista.
According to the most recent available data, Oracle ranks second in the global market, with 4% share in 2017 (see Figure 9).
[caption id="attachment_110798" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
Source: Apps Run the World[/caption]
The US ERP market was estimated to be worth $16.4 billion in 2019 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.2% during 2016–2021, according to Statista.
According to the most recent available data, Oracle ranks second in the global market, with 4% share in 2017 (see Figure 9).
[caption id="attachment_110798" align="aligncenter" width="700"]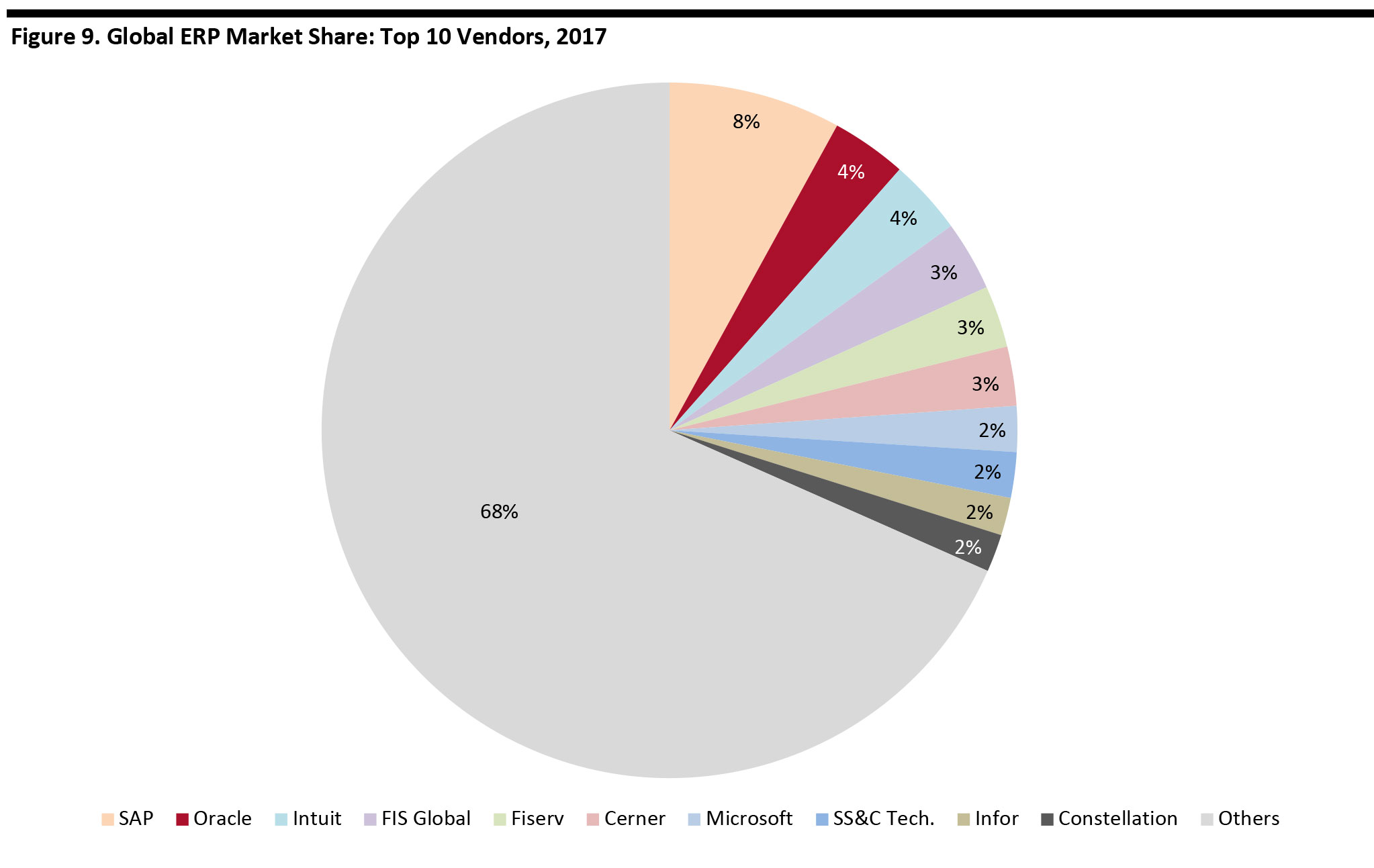 Source: Apps Run the World[/caption]
Source: Apps Run the World[/caption]
Customers
Oracle’s customers in retail and consumer goods include the following companies:| · Chico’s FAS · Coach · De Beers Jewelers · GAP · HBC · Keurig Dr. Pepper | · Kohl’s · Laura Ashley · Macy’s · National Pen · Office Depot/OfficeMax · Sainsbury’s | · Sportina Group · Tesco · Tiffany & Co. · Tom’s · UNFI · Williams-Sonoma |