
Nitheesh NH
What’s the Story?
Covid-19 has changed consumer behavior, and retailers and brands will need to actively respond to such changes. The crisis has also changed how firms operate, prompting them to be more agile and lean, as well as adopting new channels, services and ways of selling. In our Retail Reimagined series, we offer a thematic outlook to the post-crisis world, identifying and discussing key retail trends that are likely to prevail and exploring how retail may be reimagined in response to shifts in demand and supply. [caption id="attachment_114374" align="aligncenter" width="700"] Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
In our final Retail Reimagined report, we explore the innovative solutions that brands and retailers can employ to enable faster last-mile delivery for consumers.
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
In our final Retail Reimagined report, we explore the innovative solutions that brands and retailers can employ to enable faster last-mile delivery for consumers.
Why It Matters
Before Covid-19, US retailers had already been investing in efficient fulfillment options to compete with the likes of Amazon, with the e-commerce giant having set the bar for speedy deliveries. Meanwhile, Alibaba and JD.com have been developing their logistics networks for years; fast delivery is one of the key factors contributing to the success of e-commerce in China. However, with the pandemic causing consumers to turn to e-commerce as their preferred shopping channel, brands and retailers have been accelerating improvement in last-mile fulfillment—searching for ways to offer fast and efficient delivery while minimizing contact between humans in the delivery process. The online shopping trend is here to stay post pandemic: A Coresight Research survey of US consumers on July 22, 2020, revealed that 27.5% of respondents expect to retain the habit of shopping more online, less in stores after the crisis ends. As last-mile delivery continues to be a critical part of customers’ overall online shopping experience, we expect brands and retailers to continue upgrading their capabilities in this area by leveraging innovative technologies. Such solutions enable retailers to meet consumer demand for fast delivery; according to a January 2019 survey by Hanover Research and LaserShip, 63% of US online shoppers expect their orders to eb delivered within three days. [caption id="attachment_114375" align="aligncenter" width="700"]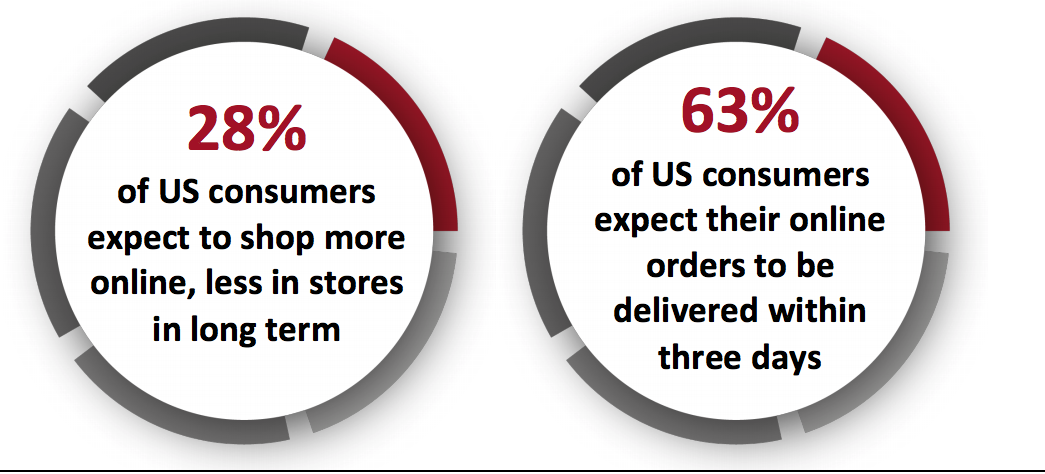 Source: Coresight Research/LaserShip[/caption]
Source: Coresight Research/LaserShip[/caption]
Looking Beyond the Crisis
We believe that Covid-19 will push brands and retailers to rethink their last-mile delivery strategy and take actions to improve efficiency and expedite delivery to customers by leveraging innovative technologies—such as employing drones and robots, installing smart parcel lockers and using stores as fulfillment centers. Increased Use of Autonomous Delivery Technologies We expect autonomous delivery technologies such as drones and robots to be more widely adopted post pandemic, as they are suitable for a contact-light retail environment. Automatic delivery technologies are expected to generate $33–48.4 billion in revenue by 2030, addressing roughly 20% of all parcel deliveries, according to research firm Lux Research. Covid-19 has fast-tracked trials of autonomous delivery technologies and turned businesses and consumers into eager early adopters. We are likely to see increasing investments into these technologies by brands and retailers in the coming years. Drones Drone deliveries are likely to become more commonplace as their potential applications expand. The rollout of 5G technology will also enable a more seamless and fully automated delivery process. Drones can move items quickly as they are able to bypass traffic or complex terrain. We have seen multiple tests of drone delivery services for food and other products in many countries, including in the US. Big companies such as Amazon and Walmart both have their own drone delivery service. Other brands and retailers can seek partnership with third-party tech companies:- CVS worked with UPS to begin delivering prescriptions by drone in Florida from May 2020.
- Grocery chain Rouses Markets announced on July 7, 2020 that it would test grocery drone delivery this fall, through its partnership with tech startup Deuce Drone.
- In July 2020, Amazon announced the expansion of its Scout six-wheeled, self-driving delivery robot to two more cities in Georgia and Tennessee.
- Starship Technologies, which mainly uses robots to deliver groceries and food on college campuses, has extended its reach to several new areas in Arizona, California and Washington, D.C.. The company said it has more than tripled its robot delivery fleet in the last year.
 Alphabet’s Wing drone (Left); JD.com’s autonomous delivery robot (right)
Alphabet’s Wing drone (Left); JD.com’s autonomous delivery robot (right)Source: Wing.com/JD Corporate Blog[/caption] Smart Parcel Lockers Will Gain Traction We expect smart parcel lockers to gain traction and solution providers will continue to add innovative functions that increase convenience for consumers. Parcel lockers were originally created to help retailers manage the surging volume of package deliveries and enable consumers to easily pick up or drop off their packages at any time of day. Lockers improve convenience and reduce the risk of theft for customers while increasing delivery efficiency and lowering the costs of last-mile delivery for brands and retailers. We are seeing parcel locker providers make efforts to offer a completely contactless parcel-pickup experience by applying barcodes, facial recognition and Bluetooth Low Energy (wireless personal area network technology) to enable customers to open locker doors without using touchscreens. Smart parcel locker provider Smiota also plans to equip lockers with sterilization tools such as ultraviolet LEDs and disinfectant spray—which would be particularly appealing to health and safety-conscious consumers in the wake of the coronavirus crisis. Smart parcel lockers are ubiquitous in China, with more than 406,000 installed in 2019, up 46% from 2018, according to China’s State Post Bureau. We expect that number to grow at the same rate to 600,000 in 2020. Logistics players in China are continuing to optimize parcel locker solutions by implementing new technologies. Alibaba’s logistics arm Cainiao has developed a new generation of AI-powered pickup lockers that can automatically shift their storage space based on the size of parcels—meaning that they can accommodate up to 60% more parcels in the same space than previous lockers. Furthermore, consumers can simply scan a code or use facial recognition to have their packages be automatically brought to them, without having to find the designated locker. Effective Route Optimization To Become More Crucial We will see more brands and retailers embrace more sophisticated and effective route planning and optimization solutions. Automatic route planning, which leverages machine learning and analytics, has significant benefits over manual inputs, as the software can re-route in real time based on constantly changing parameters such as traffic congestion, weather conditions and road restrictions. Covid-19 further underscores the need for dynamic route-optimization software, to ensure a more agile and efficient delivery process. During the pandemic, last-mile delivery has been heavily disrupted amid a sudden spike in online orders, especially for food and grocery. In China, logistics providers also faced roadblocks due to strict lockdowns, delaying deliveries. An optimized delivery route can expedite delivery for consumers, while providing more precise and accurate estimated arrival time and real-time tracking, which is highly desired by consumers. According to a 2020 survey from Dassault Systèmes, real-time updates on delivery is the second-most important consumer need for last-mile delivery. Physical Stores Will Play a Bigger Role in Fulfilling Online Orders We anticipate that more brick-and-mortar stores, especially those in densely populated areas, will serve as mini fulfillment centers, in response to consumer demand of faster delivery of online orders. Brands and retailers that start shipping from stores can realize the benefits of having a larger base of inventory closer to consumers, thus the ability to deliver products in shorter lead times. According to a 2019 survey from Zebra Technologies, 76% of global retailers use store inventory to fulfill online orders, and 68% expect the trend to continue growing in the next five years. The survey was conducted before the pandemic, and we expect that the numbers would be higher post crisis: Major retailers have been ramping up their ship-from-store capabilities to handle the spike in e-commerce volumes. We are also likely to see retailers convert underperforming stores into fulfillment centers, or “dark stores,” as demand for in-store shopping may remain muted. According to commercial real-estate firm JLL, US retailers will need an additional 1 billion square feet of industrial real estate by 2025 as fulfillment space for e-commerce distribution.
Innovation in Last-Mile Delivery amid the Crisis
Below, we discuss recent examples of innovative approaches in last-mile delivery adopted by brands and retailers to cope with lockdown restrictions and a boom in online orders. Deploying Autonomous Robots for Delivery Leading Chinese retailer Suning.com started deploying delivery robots to complete contactless door-to-door deliveries in the city of Nanjing, which implemented strict measures to prohibit the entry of any courier during lockdowns. The 1.25m-tall robots have a maximum capacity of 145 liters and can operate for up to 10 hours. They are disinfected after each delivery to prevent the potential spread of the virus. Using technologies such as big data and AI, the robots can map out delivery routes and avoid obstacles. [caption id="attachment_114377" align="aligncenter" width="700"]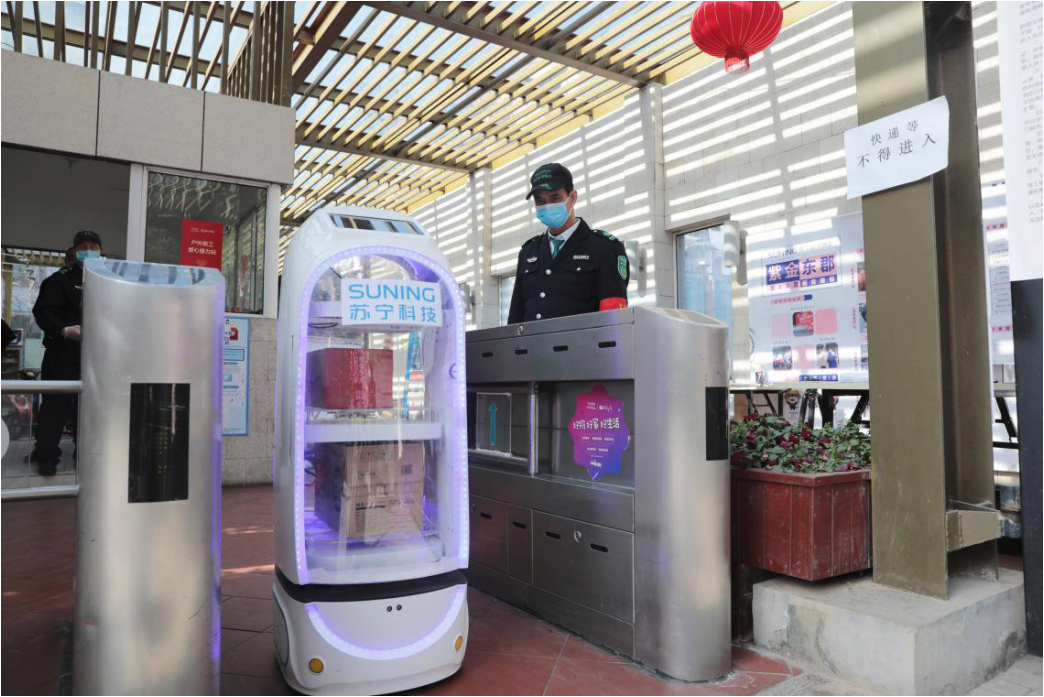 Source: Suning.com[/caption]
Delivering Products to Remote Areas by Drone
Delivery of consumer products to China’s rural areas requires two to three modes of transport, and that became challenging during the pandemic. At the beginning of February, JD.com completed its first drone delivery to a village near Baiyang Lake in Hebei province. The original delivery route was facilitated by ferry, which was suspended due to Covid-19. Additional land-based routes could take more than two hours of driving. With JD.com’s drone, it only took around 10 minutes to fly the two kilometers (around 1.2 miles) from the lake to the village. Consumers could then receive the products without any human-to-human contact.
Source: Suning.com[/caption]
Delivering Products to Remote Areas by Drone
Delivery of consumer products to China’s rural areas requires two to three modes of transport, and that became challenging during the pandemic. At the beginning of February, JD.com completed its first drone delivery to a village near Baiyang Lake in Hebei province. The original delivery route was facilitated by ferry, which was suspended due to Covid-19. Additional land-based routes could take more than two hours of driving. With JD.com’s drone, it only took around 10 minutes to fly the two kilometers (around 1.2 miles) from the lake to the village. Consumers could then receive the products without any human-to-human contact.
What We Think
With soaring e-commerce fueled by the pandemic, the need to deliver parcels rapidly and efficiently to meet consumer expectations is pushing brands and retailers to focus on making improvements to last-mile delivery. Implications for Brands and Retailers- In e-commerce, brands and retailers will need to work more closely with couriers to offer faster delivery services in order to compete with the capabilities of major e-commerce players such as Amazon. They should consider partnering with third-party technology vendors to gain access to their last-mile delivery solutions and expertise. Solutions can include autonomous delivery technologies that utilize route-optimization software.
- In physical retail, retailers should consider adding more delivery capabilities to their store fleets by turning them into partial mini fulfillment centers or dark stores. They can also add smart pickup facilities such as lockers. It is important for retailers to have clear visibility of their inventory levels to minimize the risk of out-of-stocks. Brands and retailers can leverage technologies such as inventory management and even robotics to access real-time inventory updates.
- AI, sensors, GPS and computer vision in autonomous robots and drones.
- AI, scanners and Bluetooth Low Energy in parcel lockers.
- AI, machine learning, IoT sensors and analytics to optimize and streamline delivery.
- In-store inventory management and AI-driven shelf-monitoring to track stocks in real time for online fulfillment.