
DIpil Das
Introduction
What’s the Story? The Coresight Research Playbook series provides recommendations for brands, retailers and marketplaces seeking to tap growth segments and emerging trends. Coresight Research has identified the expanding metaverse as a key trend to watch in retail and a component trend of Coresight Research’s RESET framework for change. That framework provides retailers with a model for adapting to a new world marked by consumer-centricity, in 2022 and beyond (see the end of this report for more details). We are seeing brands and retailers begin to turn to the metaverse (a computer-generated augmented and virtual reality where users can interact with one another in a 3D, immersive world) to realize opportunities in consumer engagement and alternative revenue streams. In this Playbook, we present four strategies for retailers to begin capitalizing on the benefits of metaverse-related technologies. We discuss notable recent examples of each strategy as well as key considerations and potential use cases. Why It Matters The metaverse universe is in its infancy but could eventually have as many users as the real world, and businesses of all types are looking to stake a claim. Because virtual worlds do not come with any pre-existing land, avatars or environment specifications, retailers have the opportunity to reach more consumers and monetize the space, providing customers with stunning imagery and immersive visuals to reinforce their brand. Economies within virtual worlds are growing rapidly, and businesses are now able to give customers around the world the same immersive experience. Although the enabling technologies of the metaverse—such as 5G, AR/VR (augmented and virtual reality) and blockchain—have been in development for decades, the prospect of conducting commerce in virtual worlds can be daunting. However, as user bases increase in size, brands and retailers should begin to explore such technologies further, to capitalize on commercial opportunities in the metaverse. In China, where businesses have been engaged in strategies involving metaverse technologies for over a decade, is seeing highly innovative applications—with related trademark filings recently surpassing 16,000, according to the South China Morning Post. Given political tension, it is unclear whether China’s metaverse will exist separately from the rest of the world’s, but it is providing examples and setting trends for businesses to follow.- Revenues generated in virtual worlds could reach $400 billion by 2025, up from $180 billion in 2020, according to asset manager Ark Invest.
- The initial addressable metaverse market in China totals around $4 trillion currently but could balloon to $8 trillion in the near future, according to Morgan Stanley.
- Video-game developers polled in late 2021 expect the metaverse to have a variety of features relevant to economic activities, according to metaverse platform-developer Improbable (see Figure 1).
Figure 1. Video-Game Developers: Expected Features and Use Cases of the Metaverse (% of Respondents) [caption id="attachment_143142" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
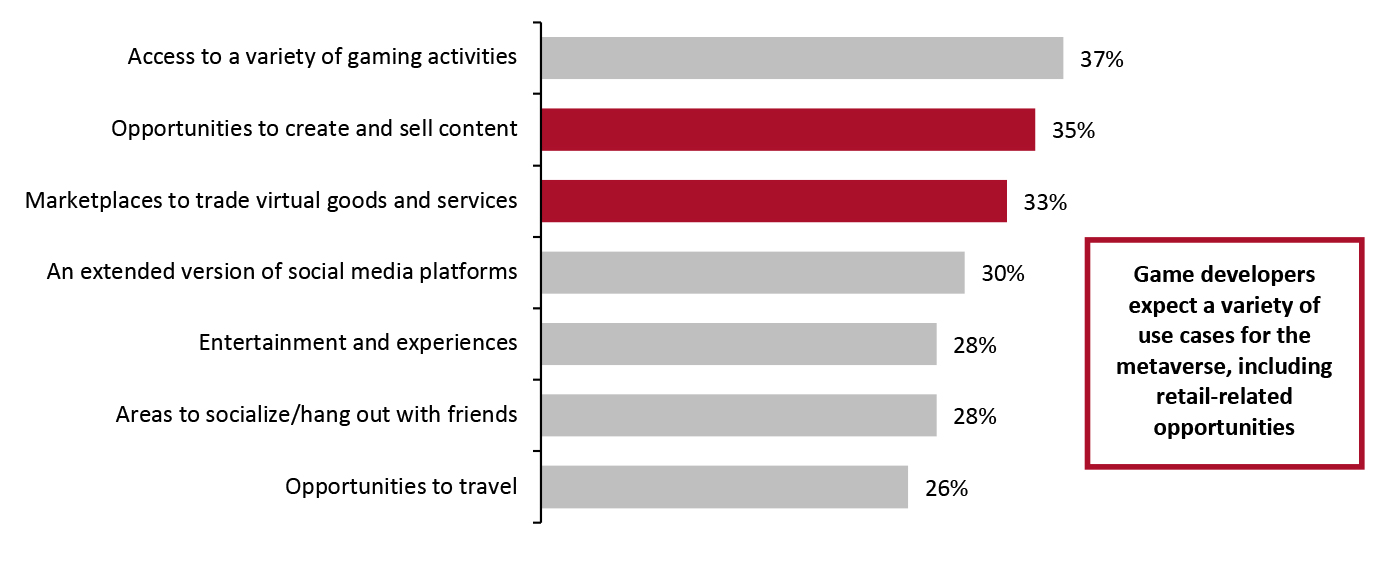 Base: Video-game developers polled in late 2021
Base: Video-game developers polled in late 2021 Source: Improbable [/caption]
Strategies for Retailers To Monetize the Metaverse: A Playbook
In Figure 2, we summarize four strategies that organizations globally can employ to establish a presence in the metaverse in its early days—and we explore each in detail below, with examples of success and the benefits for retailers.Figure 2. Strategies for Brands and Retailers To Monetize the Metaverse, Based on Current Trends [caption id="attachment_143178" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
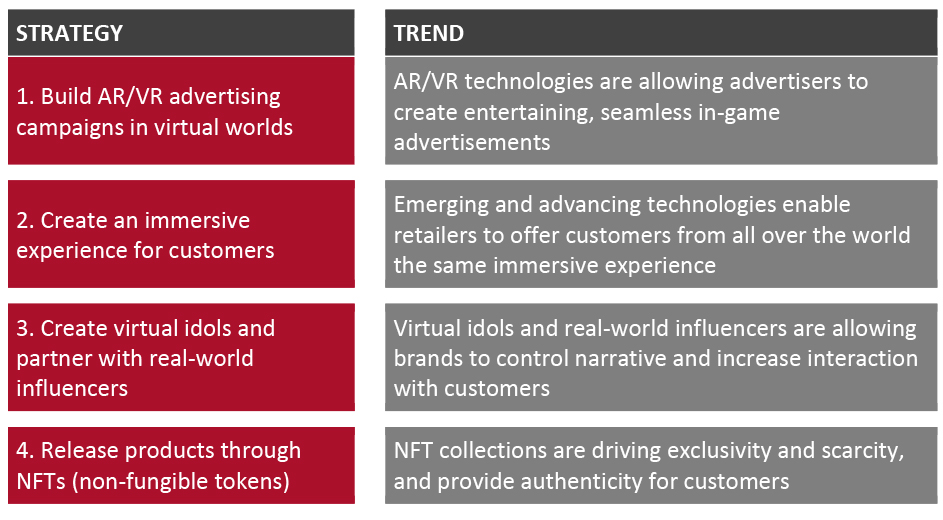 Source: Coresight Research [/caption]
1. Build AR/VR Advertising Campaigns in Virtual Worlds
Advertising in the metaverse is essential to making gains from increasing digital traffic in the metaverse. Many brands have partnered with in-game and extended-reality (XR) advertising platforms to introduce virtual billboards and launch commercials in the metaverse to target specific audiences. Advertisers can also make use of in-game features to advertise events and digital objects. Brands could also curate sponsored content in social communities and strategically place products.
Using In-World Billboards and Media Outlets
With the visually stunning displays available in the metaverse, advertisers can create immersive advertisements on billboards that are not possible in the real world. As digital traffic increases and user bases grow, virtual spaces—such as Decentraland’s Shopping District or The Sandbox’s adiVerse (Adidas)—will become highly coveted for themed advertising. In virtual games based on the blockchain, advertisers may purchase land space as NFTs to advertise on, or rent the space from landowners.
Other platforms are partnering with advertising firms to improve gameplay. For example, Subway enlisted marketing agency Cadreon (in Turkey) to partner with digital marketing firm Bidstack, bringing in-game advertisements to Football Manager 2019, much like they exist in an actual sports stadium. Bidstack is also partnered with UK-based gaming company Sports Interactive, which developed Football Manager. Coca-Cola, McDonald’s and Volkswagen have all engaged in similar strategies, which have improved gameplay realism by 95% and increased intent to purchase by 12%, on average, according to Bidstack.
[caption id="attachment_143143" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
Source: Coresight Research [/caption]
1. Build AR/VR Advertising Campaigns in Virtual Worlds
Advertising in the metaverse is essential to making gains from increasing digital traffic in the metaverse. Many brands have partnered with in-game and extended-reality (XR) advertising platforms to introduce virtual billboards and launch commercials in the metaverse to target specific audiences. Advertisers can also make use of in-game features to advertise events and digital objects. Brands could also curate sponsored content in social communities and strategically place products.
Using In-World Billboards and Media Outlets
With the visually stunning displays available in the metaverse, advertisers can create immersive advertisements on billboards that are not possible in the real world. As digital traffic increases and user bases grow, virtual spaces—such as Decentraland’s Shopping District or The Sandbox’s adiVerse (Adidas)—will become highly coveted for themed advertising. In virtual games based on the blockchain, advertisers may purchase land space as NFTs to advertise on, or rent the space from landowners.
Other platforms are partnering with advertising firms to improve gameplay. For example, Subway enlisted marketing agency Cadreon (in Turkey) to partner with digital marketing firm Bidstack, bringing in-game advertisements to Football Manager 2019, much like they exist in an actual sports stadium. Bidstack is also partnered with UK-based gaming company Sports Interactive, which developed Football Manager. Coca-Cola, McDonald’s and Volkswagen have all engaged in similar strategies, which have improved gameplay realism by 95% and increased intent to purchase by 12%, on average, according to Bidstack.
[caption id="attachment_143143" align="aligncenter" width="700"] Subway’s advertising campaign in Football Manager
Subway’s advertising campaign in Football Manager Source: Bidstack [/caption] We expect game providers to launch new ways to distribute information to users, such as live news. For example, Bloktopia (a blockchain game set to launch in beta version in March 2022), will feature a radio with themed stations and curated content. “Bloktopians” will tune into these stations to receive general and targeted news, presenting an opportunity for brands to advertise their metaverse events and offerings. Strategically Placing Products and Sponsoring Curated Content Many virtual gaming platforms give developers and creators opportunities to build and play their own games within the environments. Such fully immersive games enable advertisers to seamlessly reach their target demographics with strategically placed products. In this manner, advertisements will be less intrusive and can contribute to improved gameplay.
- Roblox’s most popular games include “Piggy” and “Arsenal.”
- The Sandbox offers many in-world games, such as The Smurfs’ Village game.
- Gatorade bottles were featured in unskippable “press conferences” in NBA 2K. Players also have their own Gatorade bottles, which can be customized.
- Logitech has begun placing product advertisements for its gaming mice within first-person shooter game Battlefield 2042(released October 2021).
- Beer brand Miller Lite debuted a Super Bowl commercial hosted by an avatar spokesperson with stunning simulated outdoor scenery in a Decentraland bar.
 “Meta Lite” bar in Decentraland
“Meta Lite” bar in Decentraland Source: Decentraland [/caption] Partnering with AR/VR Advertising and Infrastructure Agencies As metaverse offerings are still complex and difficult to understand, it will be important for brands and retailers wanting to create a digital presence to collaborate with XR and in-game advertising firms such as Bidstack and Trivver, as they are partnered with multiple game developers and can offer smooth integration processes.
- Bidstack is aiming to bridge the gap between interactive/entertainment platforms and advertisers by enhancing the gaming experience with immersive advertisements, enabling in-game monetization opportunities.
- Trivver offers a product portal with a fully immersive display, compatible with VR environments as well as 2D applications. Using the portal, customers are able to see and learn about brands in 3D and AR, and receive discounts and promotions.
Figure 3. Game Developers: Whether They Are Looking To Create Content for Massive Multiplayer and Virtual Game Experiences (% of Respondents) [caption id="attachment_143145" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
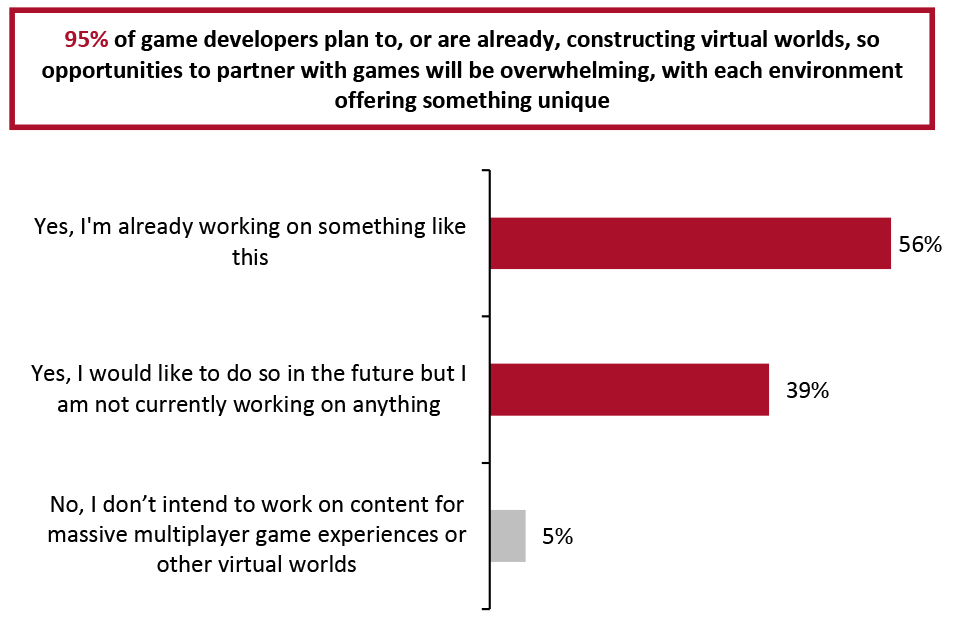 Source: Improbable[/caption]
Businesses can partner directly with virtual worlds and games, through which they are given land to bring their experiences to those platforms in a mutually beneficial partnership, where the developers receive a portion of revenues generated in the virtual space. Such collaborations enable developers to provide guidance and assistance to the retailers in constructing their virtual environments.
There are also opportunities to partner with platforms that create the experience for users either in a number of different virtual worlds or as an independent experience. For example, Obsess is a VR shopping platform that works with retailers and brands to create accurate and realistic virtual versions of real stores to expand customer base globally; virtual stores with experiences and visuals not possible in the physical world; and metaverse shopping stores in worlds such as Fortnite and Roblox, and accessible through Oculus. Clients of Obsess include Coach, General Mills, Nars, Ralph Lauren, Tommy Hilfiger and Universal Music Group.
Choosing a World with Smooth Payment Channels
Many virtual worlds are built on blockchain, but there are also games (such as Fortnite and Roblox) that are not but have similar systems to support NFTs and in-game transactions (V-Bucks and Robux, respectively). Blockchain payment systems offer instant payments and transactions, security, transparency, authenticity and smart contracts (lines of code written into the blockchain that automatically execute contracts when pre-existing conditions are met). Without delays from third parties, virtual economies are free to thrive, unlike in the physical world.
One payment channel that virtual worlds based on blockchains could soon feature are “hashed timelock contract” (HTLC) networks, through which users receiving funds will have to enter a passphrase and claim funds within a certain time period. The Lightning Network, which is a payment protocol for blockchains that provides instant and scalable transactions, is an example of an HTLC network. In this network, various individual payment channels between different parties combine to form a network of “lightning nodes” that route transactions.
All payment channels in blockchain-based games will use crypto wallets, as transactions between users and businesses in blockchain worlds are conducted directly with one another in the world’s specific currency. Examples of wallets include Alpha, Coinbase, Enjin, Math and MetaMask. Both users and businesses will need to set up wallets that are compatible with whichever token the virtual world uses. MetaMask supports multiple tokens (opening the door for interoperability).
[caption id="attachment_143146" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
Source: Improbable[/caption]
Businesses can partner directly with virtual worlds and games, through which they are given land to bring their experiences to those platforms in a mutually beneficial partnership, where the developers receive a portion of revenues generated in the virtual space. Such collaborations enable developers to provide guidance and assistance to the retailers in constructing their virtual environments.
There are also opportunities to partner with platforms that create the experience for users either in a number of different virtual worlds or as an independent experience. For example, Obsess is a VR shopping platform that works with retailers and brands to create accurate and realistic virtual versions of real stores to expand customer base globally; virtual stores with experiences and visuals not possible in the physical world; and metaverse shopping stores in worlds such as Fortnite and Roblox, and accessible through Oculus. Clients of Obsess include Coach, General Mills, Nars, Ralph Lauren, Tommy Hilfiger and Universal Music Group.
Choosing a World with Smooth Payment Channels
Many virtual worlds are built on blockchain, but there are also games (such as Fortnite and Roblox) that are not but have similar systems to support NFTs and in-game transactions (V-Bucks and Robux, respectively). Blockchain payment systems offer instant payments and transactions, security, transparency, authenticity and smart contracts (lines of code written into the blockchain that automatically execute contracts when pre-existing conditions are met). Without delays from third parties, virtual economies are free to thrive, unlike in the physical world.
One payment channel that virtual worlds based on blockchains could soon feature are “hashed timelock contract” (HTLC) networks, through which users receiving funds will have to enter a passphrase and claim funds within a certain time period. The Lightning Network, which is a payment protocol for blockchains that provides instant and scalable transactions, is an example of an HTLC network. In this network, various individual payment channels between different parties combine to form a network of “lightning nodes” that route transactions.
All payment channels in blockchain-based games will use crypto wallets, as transactions between users and businesses in blockchain worlds are conducted directly with one another in the world’s specific currency. Examples of wallets include Alpha, Coinbase, Enjin, Math and MetaMask. Both users and businesses will need to set up wallets that are compatible with whichever token the virtual world uses. MetaMask supports multiple tokens (opening the door for interoperability).
[caption id="attachment_143146" align="aligncenter" width="700"] Source: MetaMask[/caption]
As wallets are compatible with different tokens, choosing one will be dependent on whether it supports a particular token. Users can still explore environments without wallets, but they will not be able to participate in transactions or events, or claim in-game rewards.
Non-blockchain games may still operate under fiat currencies, or use other virtual currencies not based on a blockchain (such as Roblox’s Robux). If brands and retailers entering the metaverse are planning to do digital commerce with customers, they should consider a platform built on a blockchain or similar type of system. Many worlds may be interoperable with blockchain-based games but are not built on the blockchain or any similar system, diminishing the benefits of conducting commerce in a decentralized setting.
Providing Stunning Visuals and Immersiveness
Because metaverse environments are virtual, there is theoretically no limit to what brands are able to provide for customers. Brands and retailers have the opportunity to create immersive experiences for customers to interact in and learn more about the brand, as well as establish a community for people to spend hours in. Avatars from all parts of the virtual world have access to virtual marketing spectacles—whereas in the physical world, one would have to travel to Las Vegas or Times Square in New York City, for example, to see amazing displays.
Consumer electronics company Samsung recently created a virtual experience by purchasing a plot of land in Decentraland and opening a virtual store where users learn about its sustainability practices and donate to plant physical trees, have dance parties with DJs and learn about the latest consumer electronics news. Samsung also recently hosted “Galaxy Unpacked 2022” in Decentraland to launch the S22 smartphone.
As advances in communications technology, such as 5G, improve the speed and performance of headset technology, brands will be able to create fully immersive, physics-defying environments not possible in the real world that help users to feel as though they are truly living in the virtual world. The longer users spend in the metaverse, the more opportunity there is for economic activity and interaction with brands.
Exploring Interoperability
Many existing platforms will allow for interoperability because they are built on the same blockchain, Ethereum. However, in the near future, we are likely to see cross-chain implementation, which will allow for blockchains to communicate and share data with one another, meaning that NFTs and digital avatars may be transferred from one environment to another. Without this feature, customers are forced to stick with one environment, and could end up becoming bored with the offerings or graphics. If they cannot take their customized assets and digital avatar with them, they may even abandon the game altogether.
Currently, however, worlds mostly exist separate from one another, with a few exceptions. South Korean metaverse Zepeto, for example, has formed a partnership with The Sandbox; the two games are offering parallel 3D virtual environments for avatars from both platforms to interact, socialize and play games in. Businesses may also look to enter the metaverse with one of more than 260 applications partnered with Estonia-based startup Wolf 3D’s Ready Player Me, which provides cross-platform avatars that traverse the metaverse.
[caption id="attachment_143147" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
Source: MetaMask[/caption]
As wallets are compatible with different tokens, choosing one will be dependent on whether it supports a particular token. Users can still explore environments without wallets, but they will not be able to participate in transactions or events, or claim in-game rewards.
Non-blockchain games may still operate under fiat currencies, or use other virtual currencies not based on a blockchain (such as Roblox’s Robux). If brands and retailers entering the metaverse are planning to do digital commerce with customers, they should consider a platform built on a blockchain or similar type of system. Many worlds may be interoperable with blockchain-based games but are not built on the blockchain or any similar system, diminishing the benefits of conducting commerce in a decentralized setting.
Providing Stunning Visuals and Immersiveness
Because metaverse environments are virtual, there is theoretically no limit to what brands are able to provide for customers. Brands and retailers have the opportunity to create immersive experiences for customers to interact in and learn more about the brand, as well as establish a community for people to spend hours in. Avatars from all parts of the virtual world have access to virtual marketing spectacles—whereas in the physical world, one would have to travel to Las Vegas or Times Square in New York City, for example, to see amazing displays.
Consumer electronics company Samsung recently created a virtual experience by purchasing a plot of land in Decentraland and opening a virtual store where users learn about its sustainability practices and donate to plant physical trees, have dance parties with DJs and learn about the latest consumer electronics news. Samsung also recently hosted “Galaxy Unpacked 2022” in Decentraland to launch the S22 smartphone.
As advances in communications technology, such as 5G, improve the speed and performance of headset technology, brands will be able to create fully immersive, physics-defying environments not possible in the real world that help users to feel as though they are truly living in the virtual world. The longer users spend in the metaverse, the more opportunity there is for economic activity and interaction with brands.
Exploring Interoperability
Many existing platforms will allow for interoperability because they are built on the same blockchain, Ethereum. However, in the near future, we are likely to see cross-chain implementation, which will allow for blockchains to communicate and share data with one another, meaning that NFTs and digital avatars may be transferred from one environment to another. Without this feature, customers are forced to stick with one environment, and could end up becoming bored with the offerings or graphics. If they cannot take their customized assets and digital avatar with them, they may even abandon the game altogether.
Currently, however, worlds mostly exist separate from one another, with a few exceptions. South Korean metaverse Zepeto, for example, has formed a partnership with The Sandbox; the two games are offering parallel 3D virtual environments for avatars from both platforms to interact, socialize and play games in. Businesses may also look to enter the metaverse with one of more than 260 applications partnered with Estonia-based startup Wolf 3D’s Ready Player Me, which provides cross-platform avatars that traverse the metaverse.
[caption id="attachment_143147" align="aligncenter" width="700"] Source: Ready Player Me[/caption]
Brands and retailers may want to consider how a platform is addressing interoperability, as it opens the door for a larger pool of customers as well as freedom and personalization for users throughout the metaverse.
3. Create Virtual Idols and Partner with Real-World Influencers
Brands are beginning to create virtual idols (computer-generated models and avatars) to promote their brands and advertise their products in digital campaigns such as short films, commercials, social media advertisements and short videos on platforms such as Instagram, TikTok and YouTube. Many brands are also partnering with celebrities and real-world influencers by creating digital avatars of them and offering interactive experiences to metaverse users. Virtual influencers are growing elements of the overall influencer market, and are actually in competition with one another.
Top celebrities on Instagram have the chance to earn staggering figures: On average, Instagram influencers with 1,000,000 followers can expect to make up to $670 per post; users with 100,000 followers can possibly earn $200 per post; and those with 10,000 followers can see $88 per post, according to Search Engine Journal, an SEO news provider.
Although there are only just over 200 notable virtual idols in existence, as of February 2022 (according to VirtualHumans.org), that number is growing on a weekly basis and the top idols are set to bring in impressive amounts this year. For example, Lu Do Magalu, a virtual human with 5.8 million Instagram followers, was created in 2003 by Brazil-based Magazine Luiza, a retailer with many consumer-facing brands; she is set to earn more than $17.3 million in 2022, per UK-based marketplace OnBuy. Less popular idols are still set to earn high figures. Idol Imma Gram, who has worked with retailers such as IKEA and ice-cream brand Magnum China, has just over 350,000 Instagram followers, but is set to earn more than $200,000 in 2022, according to OnBuy. These sources of income would be from more than just social media and Instagram; because these influencers are computer-generated, they can be controlled for specific marketing campaigns with a wider range of use than celebrity sponsors and real-world influencers have.
Brands and retailers operating in China have been employing virtual idol technologies for several years, but they have recently gained more steam due to the improving graphics of AR and VR. Idols can adjust their personalities, appearance and traits to adapt to changing consumer tastes. In China alone, virtual idols are set to drive $52.6 billion in additional sales by 2023, according to China-based data miner iiMedia Consulting—up from $2.0 billion in 2018 (see Figure 4).
Source: Ready Player Me[/caption]
Brands and retailers may want to consider how a platform is addressing interoperability, as it opens the door for a larger pool of customers as well as freedom and personalization for users throughout the metaverse.
3. Create Virtual Idols and Partner with Real-World Influencers
Brands are beginning to create virtual idols (computer-generated models and avatars) to promote their brands and advertise their products in digital campaigns such as short films, commercials, social media advertisements and short videos on platforms such as Instagram, TikTok and YouTube. Many brands are also partnering with celebrities and real-world influencers by creating digital avatars of them and offering interactive experiences to metaverse users. Virtual influencers are growing elements of the overall influencer market, and are actually in competition with one another.
Top celebrities on Instagram have the chance to earn staggering figures: On average, Instagram influencers with 1,000,000 followers can expect to make up to $670 per post; users with 100,000 followers can possibly earn $200 per post; and those with 10,000 followers can see $88 per post, according to Search Engine Journal, an SEO news provider.
Although there are only just over 200 notable virtual idols in existence, as of February 2022 (according to VirtualHumans.org), that number is growing on a weekly basis and the top idols are set to bring in impressive amounts this year. For example, Lu Do Magalu, a virtual human with 5.8 million Instagram followers, was created in 2003 by Brazil-based Magazine Luiza, a retailer with many consumer-facing brands; she is set to earn more than $17.3 million in 2022, per UK-based marketplace OnBuy. Less popular idols are still set to earn high figures. Idol Imma Gram, who has worked with retailers such as IKEA and ice-cream brand Magnum China, has just over 350,000 Instagram followers, but is set to earn more than $200,000 in 2022, according to OnBuy. These sources of income would be from more than just social media and Instagram; because these influencers are computer-generated, they can be controlled for specific marketing campaigns with a wider range of use than celebrity sponsors and real-world influencers have.
Brands and retailers operating in China have been employing virtual idol technologies for several years, but they have recently gained more steam due to the improving graphics of AR and VR. Idols can adjust their personalities, appearance and traits to adapt to changing consumer tastes. In China alone, virtual idols are set to drive $52.6 billion in additional sales by 2023, according to China-based data miner iiMedia Consulting—up from $2.0 billion in 2018 (see Figure 4).
Figure 4. China: Estimated Virtual Idol-Driven Retail Sales (USD Bil.) [caption id="attachment_143148" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
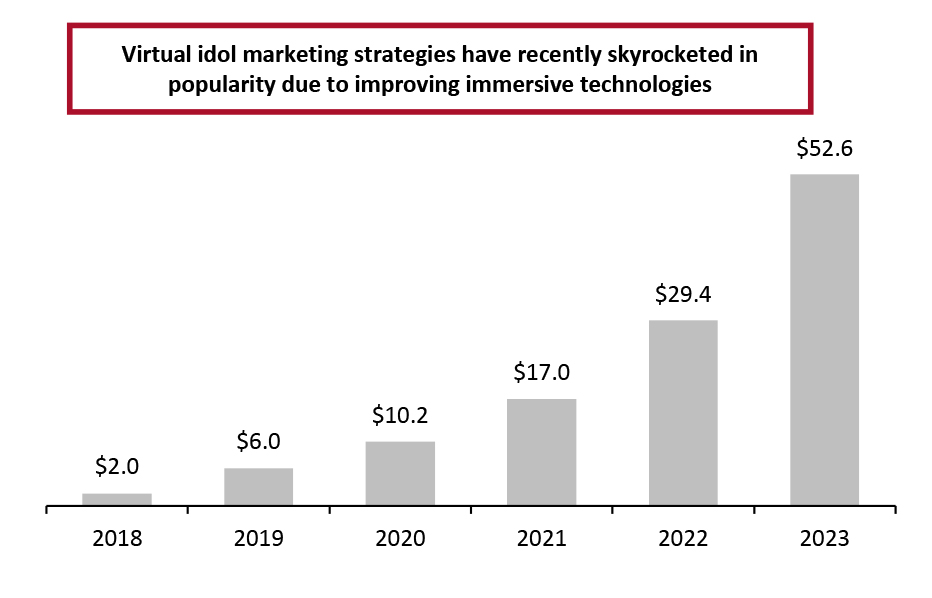 Source: iiMedia Consulting[/caption]
Controlling Brand Narrative
Rather than partnering with celebrities and social media influencers, brands are able to maintain better control of their brand narrative and adjust idol characteristics to match shifting consumer tastes and company values. Because the virtual human can be controlled, appearance, dialogue, timing of posts and number of posts can all be regulated to whatever the brand or retailer believes is the optimal strategy to engage the most customers—whether that be a short film campaign, social media posts or YouTube content.
Increasing Interaction with Customers
Despite the buzz surrounding virtual idols (in China in particular), real-world Instagram influencers and celebrities are still much more popular. If brands do not wish to create virtual idols to support their products, they can partner with an immersive-technologies firm to create digital avatars for celebrities to interact with fans in the metaverse.
Haptic technology is making it possible for humans to feel virtual objects within the metaverse, and full-body suits allow users to control their avatars. Facial tracking in headsets also allows for deeper levels of interaction and immersion for fans with the digital avatar of the celebrity, as their avatars are able to mimic facial expressions.
Singer Justin Bieber partnered with XR entertainment platform Wave to create and control a digital avatar through a motion-capture suit for a virtual concert, which drew an audience of 10 million listeners, according to MusicTech. Many other musical artists, including John Legend, Travis Scott and The Weeknd have used Wave or other platforms to create digital avatars of themselves and host virtual concerts with immersive visuals.
4. Release Products Through NFTs
An NFT is a non-exchangeable unit of data represented by a mathematical formula known as a cryptographic hash, which is stored on the blockchain. Many brands have started to partner with NFT platforms to mint and sell customized collections, raising brand awareness and teaching customers and users about products and the company’s history. Apparel retailers are beginning to file trademarks and patents to pair digital objects as NFTs with physical items in the real world, driving exclusivity and scarcity, as well as ensuring authenticity.
A variety of different brands and retailers, such as gaming giant Atari, the NBA (National Basketball Association), Adidas, digital apparel company RTFKT (acquired by NIKE), have already generated millions of dollars through NFT collections. We present the metrics for selected examples in Figure 5, according to NFT data aggregator CryptoSlam.
Source: iiMedia Consulting[/caption]
Controlling Brand Narrative
Rather than partnering with celebrities and social media influencers, brands are able to maintain better control of their brand narrative and adjust idol characteristics to match shifting consumer tastes and company values. Because the virtual human can be controlled, appearance, dialogue, timing of posts and number of posts can all be regulated to whatever the brand or retailer believes is the optimal strategy to engage the most customers—whether that be a short film campaign, social media posts or YouTube content.
Increasing Interaction with Customers
Despite the buzz surrounding virtual idols (in China in particular), real-world Instagram influencers and celebrities are still much more popular. If brands do not wish to create virtual idols to support their products, they can partner with an immersive-technologies firm to create digital avatars for celebrities to interact with fans in the metaverse.
Haptic technology is making it possible for humans to feel virtual objects within the metaverse, and full-body suits allow users to control their avatars. Facial tracking in headsets also allows for deeper levels of interaction and immersion for fans with the digital avatar of the celebrity, as their avatars are able to mimic facial expressions.
Singer Justin Bieber partnered with XR entertainment platform Wave to create and control a digital avatar through a motion-capture suit for a virtual concert, which drew an audience of 10 million listeners, according to MusicTech. Many other musical artists, including John Legend, Travis Scott and The Weeknd have used Wave or other platforms to create digital avatars of themselves and host virtual concerts with immersive visuals.
4. Release Products Through NFTs
An NFT is a non-exchangeable unit of data represented by a mathematical formula known as a cryptographic hash, which is stored on the blockchain. Many brands have started to partner with NFT platforms to mint and sell customized collections, raising brand awareness and teaching customers and users about products and the company’s history. Apparel retailers are beginning to file trademarks and patents to pair digital objects as NFTs with physical items in the real world, driving exclusivity and scarcity, as well as ensuring authenticity.
A variety of different brands and retailers, such as gaming giant Atari, the NBA (National Basketball Association), Adidas, digital apparel company RTFKT (acquired by NIKE), have already generated millions of dollars through NFT collections. We present the metrics for selected examples in Figure 5, according to NFT data aggregator CryptoSlam.
Figure 5. Selected Brand NFT Collections: Key Metrics [wpdatatable id=1809]
Metrics are ballpark figures Source: CryptoSlam Partnering with Existing Digital Brands, Marketplaces and Worlds To Mint NFTs Businesses wanting to mint NFTs, including the ones listed in Figure 5 above, have started to collaborate with NFT marketplaces and existing digital brands to design and distribute virtual goods. Some of the popular marketplaces (and blockchains) to sell NFTs are Axie Marketplace (Ethereum), BloctoBay (Flow), Magic Eden (Solana), NBA TopShot (Flow), OpenSea (Ethereum) and Rarible (Ethereum, Tezos). Notable examples of retailers creating partnerships for mint NFT collections include the following:
- Adidas recently collaborated with NFT brands Bored Ape Yacht Club and PUNKS comic to bring limited-edition digital clothing to the metaverse, also available in the OpenSea marketplace.
- Gucci, which recently purchased a plot of land in The Sandbox, is having its designers utilize in-game tool VoxEdit to design unique items and mint them as NFTs in The Sandboxmarketplace, available on OpenSea.
- Gap Inc. partnered with New York-based artist Brandon Sines and blockchain Tezos to release its first NFT collection on the Tezos marketplace.
- Burberry announced a collaboration with Mythical Games in August 2021 to bring fashion NFTs to the gaming company’s flagship, Blankos Block Party.
- Consumer goods corporation Procter & Gamble commissioned artists to create digital artwork toilet paper, then formed a partnership with NFT marketplace Rarible to mint and sell the product.
- NIKE acquired NFT apparel and accessory company RTFKT to pair NFTs with physical goods; RTFKT has NFTs listed on multiple marketplaces.
- Luxury retailer Dolce & Gabbana minted its Collezione Genesi NFT collection, which sold for $5.6 million.
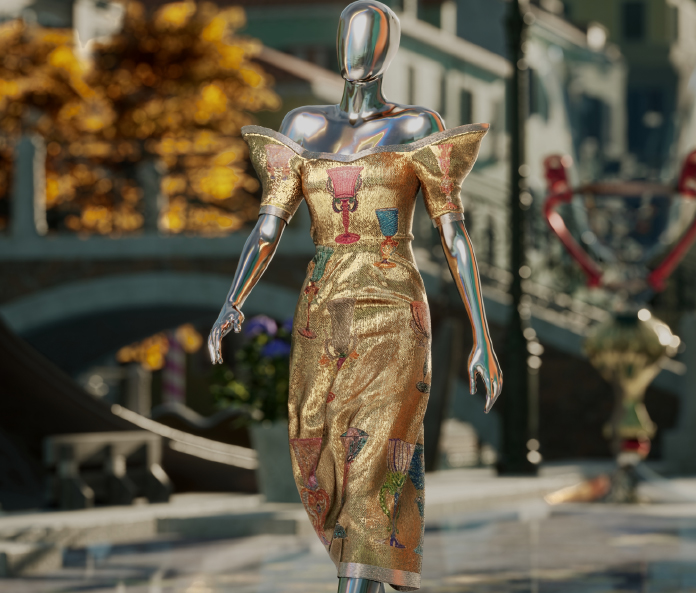 A piece from Dolce & Gabbana’s digital Collezione Genesi collection
A piece from Dolce & Gabbana’s digital Collezione Genesi collection Source: Dolce & Gabbana [/caption] Non-luxury retailers should also be interested in NFTs for authentication in virtual worlds. As digital assets can be created quite easily (with no restriction on features), and as users spend more hours in the metaverse and become more invested in their digital avatars, they will want to protect their uniqueness and personal features. Several brands and retailers, such as Victoria’s Secret, NIKE and Walmart, have begun to file patents to sell virtual goods in the metaverse. NFTs offer a verified way to transfer digital assets secured across the blockchain, allowing users to maintain exclusive ownership of their items, transferring them and selling them as they would in the real world. This authentication can also be applied to physical items. This allows for brands to exclusively pair physical products with a digital copy, or “digital twin”. One of NIKE’s virtual patents, for example, specifies pairing a physical sneaker with an NFT version, allowing the customer to see the transaction history of what they are purchasing. This also means that customers can ensure that what they are purchasing is authentic.
What We Think
The metaverse is still in its infancy, but commercial opportunities are starting to present themselves. As immersive technologies improve, user bases will grow globally and people will be more likely to spend hours of their time in the metaverse as their digital avatars. The opportunity to reach such a large pool of customers with stunning visual offerings not hindered by the laws of physics is an exciting prospect for brands and retailers. China is a leader in the metaverse, with businesses having filed over 16,000 patents for virtual goods. Virtual idols have been soaring in popularity as immersive technologies improve virtual and augmented graphics. Brands and retailers are leveraging metaverse technologies to transform their businesses, setting precedents and demonstrating which trends have longevity. However, it remains to be seen how interconnected China’s metaverse will be with the rest of the world’s. Organizations with a virtual presence must continue to innovate and provide unique offerings to stay ahead of stiff competition, but it will be equally as important to decide which digital strategies to employ, depending on what the business wants their customer experience to entail. Digital advertising, immersive experiences, virtual idols and NFTs are all examples of unique strategies that brands have employed to establish their virtual presence. The ones that continue to build on these strategies and identify trends with staying power in a timely matter will be able to successfully monetize the metaverse. Implications for Retailers and Brands- Opportunities to monetize blockchain games will become increasingly expensive for retailers. Although there are many virtual worlds forming, each with their own opportunities, they will have limited land and token supply to drive scarcity and demand. This means that opportunities to become involved in some of the higher trafficked worlds of the metaverse will increasingly become more expensive.
- Offering an immersive environment will keep customers engaged and increase interaction. Immersive technologies are allowing for levels of customization and interaction with products that customers have never experienced before. Environments with stunning visuals not possible in the real world will customers users engaged and entertained for long periods of time, increasing opportunities for digital commerce. Customers at traditional brick-and-mortar stores typically do not shop for more than an hour (depending on the store), but as technologies such as 5G and haptic sensors improve headset frame rates and increase interaction with virtual environments, the overall metaverse user base will continue to grow and users are likely to become more invested in their virtual lives, spending hours at a time in immersive environments.
- Virtual idols and influencers are growing in popularity and allow fans to interact with brands like never before. Retailers are beginning to partner with companies that have created virtual personas (not tied to any particular person) to market their products and appear in ad campaigns. These idols have developed their own followings and are contracted by different companies to promote products. In doing so, brands can control their narrative and adjust their idols to align with their values and vision, making them powerful marketing tools. If retailers can dictate exactly what the idol does, says and how it acts, they can maintain total control over the product narrative. Retailers are also partnering with avatar companies to create digital versions of real-world celebrities to increase digital foot traffic. With facial tracking technology, fans are able to interact with celebrities and feel as though they are truly enjoying the celebrity’s presence.
- Brands are creating NFT collections to sell digital products. NFTs, whether they represent only a digital asset or they are paired with a physical item, provide verified ownership and ensure authenticity of a product across the blockchain, something not possible under centralized finance. They are also driving scarcity as they are released in limited editions and secured by cryptographic hashes, which make them non-exchangeable. Incorporating digital strategies including NFTs and their features is allowing brands to provide authenticity of products, drive scarcity, protect uniqueness in a digital setting and raise brand awareness.
- Retailers and brands will have to develop a metaverse advertisement strategy. In-world media outlets, such as billboards and radios, are providing advertisers with means to reach a large pool of customers (avatars). Metaverse users from all corners of the globe can experience the same stunning displays from the comfort of their own home. With no limits to visuals, ads are becoming more immersive and less intrusive, as they can be featured within virtual environments and video games in entertaining ways. XR and in-game advertising agencies are also offering specialized expertise and partnering with retailers to build digital and in-game advertising campaigns. Through such a digital advertising strategy, retailers can target markets more precisely than in a real-world setting.
Figure 6. RESET Framework [caption id="attachment_143173" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
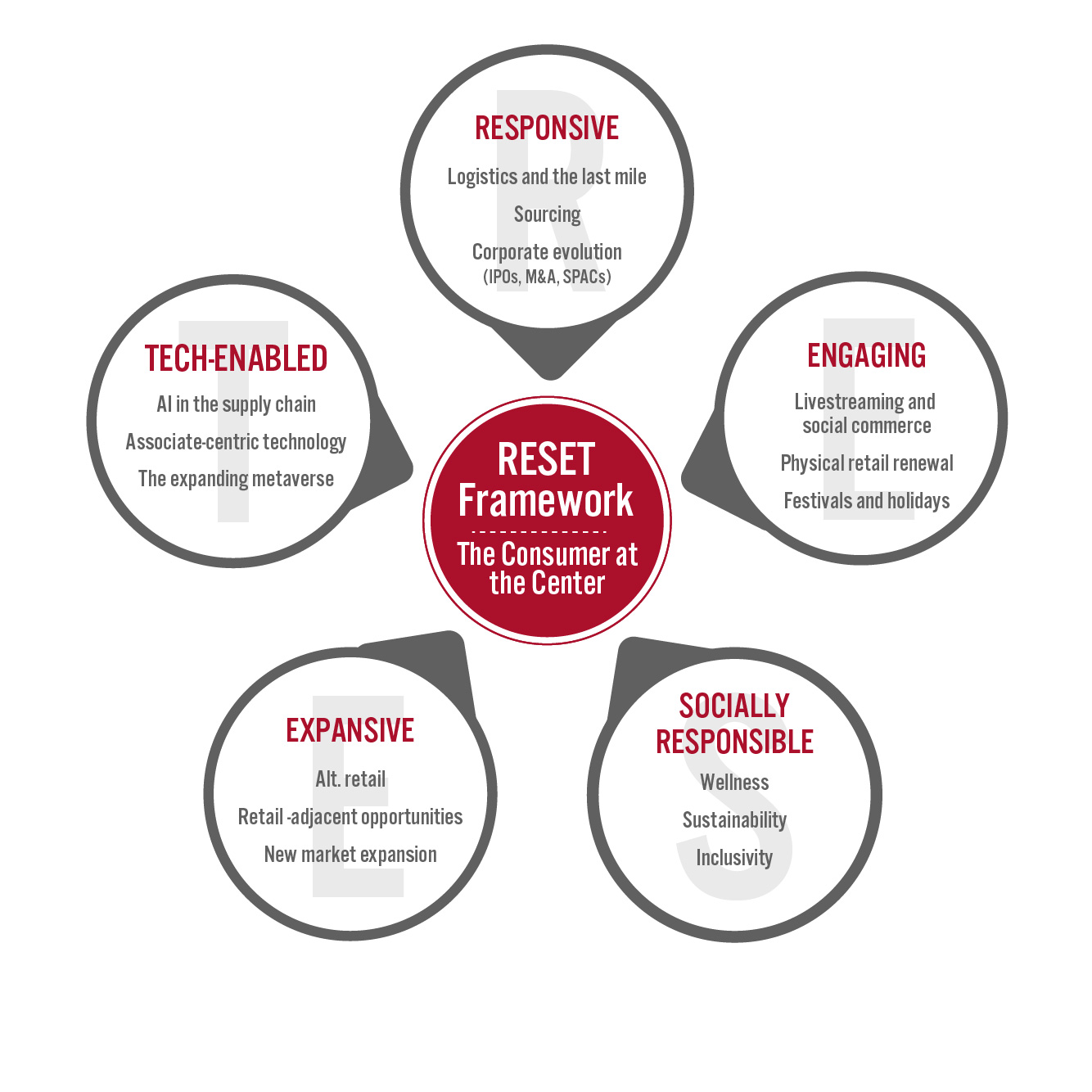 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]