DIpil Das
Metaverse Latest
Metaverse technologies and virtual gaming have surged in popularity during the Covid19 pandemic and are continuing to evolve, grow and converge each month. Coresight Research has identified the expanding metaverse as a key trend to watch in global retail in 2022 and beyond. Our Metaverse Latest series provides regular updates on metaverse developments, showing how key players and new entrants are seizing opportunities in the space. We also discuss metaverse trends we have seen recently. In this report, we present developments as of April 19, 2022.Recent Metaverse Developments
Virtual Worlds and Platforms- On April 7, 2022, metaverse platform provider Improbable received a $150 million investment to build a “network of interoperable Web 3 metaverses,” named M2.
- On April 11, 2022, Epic Games announced a $2 billion round of funding, one week after forming a partnership with Lego to create a new family-friendly virtual world. Sony and KIRKBI, an investment group operated by Lego’s founding family, provided the funds.
- On April 11, 2022, Meta published a blog post announcing that it would begin giving creators tools to sell virtual assets created within its Horizon Worlds virtual game, eventually leading to the sale of NFTs (non-fungible tokens). CNBC reported that Meta will charge roughly 50% on virtual asset sales. Meta is also working on a virtual currency, similar to Roblox’s Robux.
- On April 12, 2022, the Council of Fashion Designers of America partnered with creative consultancy 5Crypto and will work alongside Polygon Studios and The Sandbox to develop a blueprint for the future of Web 3.0 fashion.
- On April 13, 2022, blockchain game Somnium Space revealed plans to release a “live forever” mode that allows users to record their conversations and movements, which AI (artificial intelligence) then recreates as an avatar that will continue to live on after the user passes away in reality.
- On April 14, 2022, Amazon India revealed an unboxing experience for the OnePlus 10 Pro smartphone in Decentraland. After navigating to the unboxing venue’s coordinates, users can examine a 3D, 360-degree model of the phone, as well as its features. Amazon hopes to generate interest before users see the product in real life.
- On April 14, 2022, UK-based architecture firm Grimshaw reported that it had been tapped to design metaverse spaces for an upcoming project, pax.world, which will ultimately contain 20,000 land parcels. Landowners can create their own completely customizable experiences in a hyper-realistic setting.
- On April 14, 2022, Meta revealed that it is working on a web-based version of Horizon Worlds. Currently, the game is only available through Oculus, which is one of its biggest limitations. Meta also announced that it is working on a mobile version of the game, significantly increasing access and its potential user base.
- On April 16, 2022, the National Basketball Association (NBA) announced a series of Web 3.0 initiatives, including a partnership with Google to create a basketball metaverse accessible through smartphones. The platform will provide immersive experiences for fans between games and during halftimes.
- On April 18, 2022, metaverse services provider and platform, MudAi introduced a new metaverse project, Innovative Metaverse System, which will support a globally interoperable metaverse. The platform, powered by Unreal Engine 5, will support tokens from Ethereum, Solana, Binance Smart Chain and more.
- On April 18, 2022, in a key step toward metaverse interoperability, The Sandbox announced a partnership with gaming company FlickPlay, which will allow players to use blockchain assets on both platforms.
- On April 6, 2022, Netherlands-based hotel chain CitizenM reported that it purchased a plot of land in The Sandbox, where it intends to connect with global customers and explore immersive marketing opportunities.
- On April 6, 2022, supercar manufacturer Lamborghini reported that its last V12 vehicle—before the company switches to hybrids and full-electric engines—would be sold with an NFT designed by digital artist Krista Kim and featuring music by DJ Steve Aoki.
- On April 8, 2022, Netherlands-based blockchain fashion house The Fabricant—which has created 3D clothing designs for Adidas—reported that it received $14 million in funding to develop technologies to dress metaverse avatars. Sebastian Borget, COO of The Sandbox, participated in the funding as an angel investor.
- On April 8, 2022, beverage brand Heineken, which launched a metaverse-only flavor, Heineken Silver, in March, reported that the flavor would be making its debut in the real world. The original launch was held in Decentraland and featured collectible pieces of art, dubbed “For Real Tokens.”
- On April 11, 2022, Absolut Vodka announced that it would launch a three-floor metaverse pop-up, “Absolut.Land,” in Decentraland to celebrate the return of music festival Coachella. The virtual bar will feature games, virtual cocktails, prizes and wearables for avatars.
- On April 11, 2022, business magazine Forbes entered the metaverse with an NFT collection of fictional billionaires, debuting the collection on cryptocurrency exchange FTX. Each billionaire contains an impressive virtual portfolio and a net worth determined by live stock prices.
- On April 12, 2022, China-based computer giant Lenovo revealed plans to invest billions of dollars over the next five years in metaverse technologies that help capitalize on virtual business opportunities.
- On April 12, 2022, Snoop Dogg launched an NFT collection on Ethereum rival, Cardano, featuring unreleased music. Snoop Dogg has remained active in the metaverse, including owning a virtual world within The Sandbox where he hosts concerts and interacts with fans.
- · On April 14, 2022, Vogue Business reported that luxury brand Louis Vuitton will release new NFTs for its digital game, Louis: The Game, incentivizing players to learn about the brand’s history.
- On April 14, 2022, luxury brand Marni unveiled an immersive, digital experience dubbed “Wearware,” which brings its Spring Summer 2022 collection into the virtual world.
- On April 14, 2022, Spain-based fashion retailer Zara announced the launch of its Lime-Glam Spring Summer Collection, the first solo metaverse collection to be worn by avatars in both the virtual platform Zepeto and the real world. The project aims to empower self-expression and creativity in virtual settings with items that translate to the real world.
- On April 17, 2022, South Korean-based carmaker Hyundai announced a collaboration with NFT brand Meta Kongz, which includes launching an NFT community via Discord and Twitter. The collaboration will support Hyundai’s larger vision of the metaverse, Metamobility, which the company says will bridge the physical and virtual worlds with robotics.
- On April 18, 2022, the Union of European Football Associations (UEFA)—one of the largest professional sports leagues in the world—announced a partnership with Roblox, unveiling virtual mascots meant to increase interest in soccer.
- On April 18, 2022, retailer Urban Outfitters announced a new NFT collection to celebrate its 50th anniversary. The “Smiley Collectors” NFTs are collectible pieces of art that serve as tokens that unlock prizes and rewards.
- On April 19, 2022, the NBA, through its NFT marketplace NBA TopShot, announced a new collection of 18,000 NFTs to celebrate the start of the NBA playoffs. The NFTs will be free to mint, apart from the cost of gas on Ethereum.
- On April 19, 2022, beauty and clothing retailer Victoria’s Secret debuted a digital-only collection aimed at tweens dubbed “Happy Nation.” The clothing is non-gender-specific and will “activate in the metaverse” later this summer.
- On April 5, 2022, Epic Games launched Unreal Engine 5, a gaming engine that aims to push the boundaries of what is visually possible in gaming environments.
- On April 6, 2022, OpenSea, the largest NFT marketplace (by volume), announced beta, “limited collection coverage” of Solana NFTs—starting with 165 collections—allowing users to trade Solana NFTs. This is a significant development for Solana, a primary Ethereum rival, on which many up-and-coming metaverse projects are based.
- On April 6, 2022, Xmov, a China-based metaverse infrastructure startup, received a $130 million investment. Xmov has developed virtual idols for many large companies, including Tencent, Alibaba and L’Oréal, which use them for targeted campaigns.
- On April 12, 2022, digital avatar platform Genies announced that it raised $150 million, with the round valuing the startup at $1 billion. Although Genies avatars are not yet available in virtual games, the investment will go toward developing creator tools and expanding avatar features and accessories.
- On April 12, 2022, US hedge fund Pantera Capital announced that it had accumulated $1.3 billion—double its target—for the Pantera Blockchain Fund. The company plans to invest in new blockchain projects and metaverse infrastructure.
- On April 12, 2022, short-video platform TikTok released its augmented reality (AR) tool, which had been in beta since fall 2021, to all users. The tool allows creators to make their own AR effects for other users, developers and designers to use.
- On April 13, 2022, The Verge reported that Meta Platforms plans to release AR smart glasses in 2024 and is already working on a lighter design scheduled for release in 2026, with a third version planned for 2028.
- On April 18, 2022, MetaVRse, a platform and game engine working to build metaverse infrastructure, reported that it has started working on a virtual mall set to open in the fourth quarter of 2022. The mall will feature 100 floors with 100 million total square feet of virtual space.
- On April 19, 2022, according to a report from Bloomberg, The Sandbox announced that it is seeking to raise $400 million at a $4 billion valuation.
Trends We’ve Seen Recently
1. Companies Race To Build IoT Digital Twins The Internet of Things (IoT) describes objects with software and sensors that connect them to the Internet. The usage of IoT has steadily increased over the past few years, rapidly changing everyday life. Because of the connection to the Internet, ordinary devices of all types—in addition to typical Internet-connected technologies such as computers and smartphones—can collect massive amounts of data and help people live and work smarter by providing real-time insights. Some examples of common IoT devices include smart appliances (stoves, refrigerators, etc.), intelligent security systems, wearable trackers, smart shelves and even smart assistants (Amazon’s Alexa, Apple’s Siri, etc.). There are set to be around 25 billion IoT-connected devices worldwide by 2030—up from less than 12 billion today—according to Transforma Insights. Digital twins represent an emerging field of IoT with a strong connection to the metaverse—linking virtual copies of physical objects to their real-world counterparts. Any object or device fitted with smart sensors could theoretically be perfectly replicated in the metaverse, as the sensors provide real-time data about performance, design and condition. Many applications and tools already exist to scan objects and create 3D versions of them; however, these are just digital copies. IoT digital twins linked to real-world objects allow brands and retailers to create complex and detailed simulations of real-world shopping experiences—complete with comprehensive product information—for customers worldwide to enjoy from the comfort of their homes. Digital twins also allow retailers to run simulations of new storefront, warehousing and supply chain concepts, saving costs and increasing efficiency. One of the most popular tools for creating digital twins is NVIDIA’s Omniverse, which is not a metaverse but a tool that allows companies to develop small, collaborative virtual environments for use in production and manufacturing. Today, many brands and retailers—including BMW and Lowe’s, discussed in more detail below—have used Omniverse’s tools to construct and model assets and strategies in 3D.- BMW Group
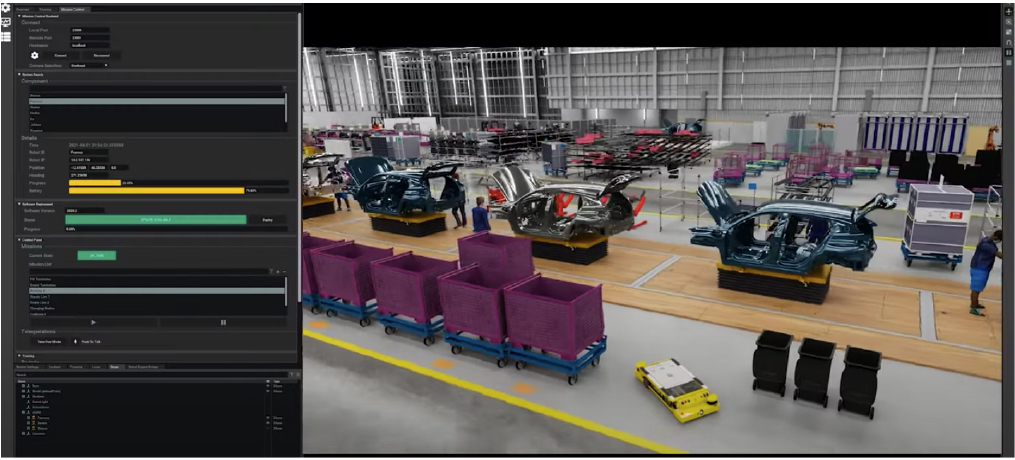 BMW Group modeling production with Omniverse
BMW Group modeling production with Omniverse Source: NVIDIA [/caption]
- Lowe’s
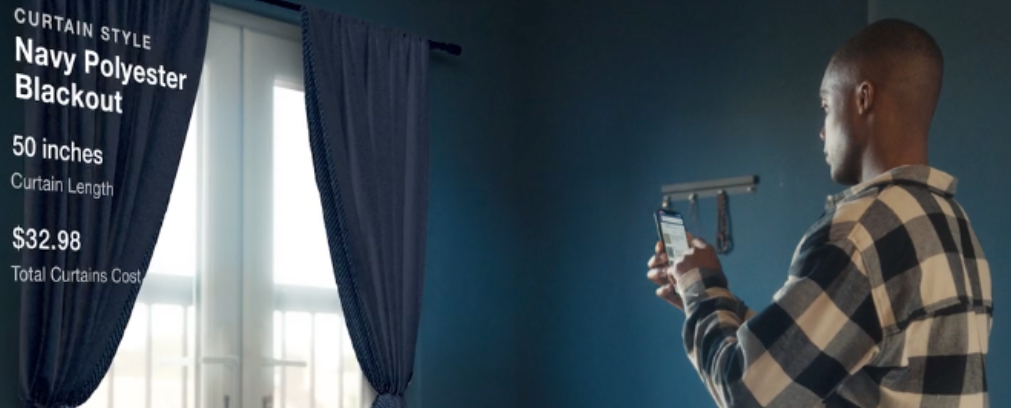 Lowe’s home-improvement application utilizing digital twins
Lowe’s home-improvement application utilizing digital twins Source: Lowe’s [/caption] 2. The Power of 3D Game Engines Is Increasing To effectively power graphics, resolution and speed—significant factors in the quality of a virtual experience—developers utilize 3D game engines, the software framework for building virtual environments. Game engines house the features that determine the quality of a virtual experience, from animation and sound to memory management and AI. Game engines empower developers to create environments more efficiently and with less effort than building from scratch, as the engines use pre-existing models and tools. Likewise, engines allow those looking to establish virtual experiences to focus on the idea and feel of the experience, rather than the complexity of the development. Unity Technologies’ Unity Engine and Epic Games’ Unreal Engine are two engines that are helping to push the boundaries of what metaverse platforms—and businesses operating within them—can provide for users in virtual experiences and interactions. [caption id="attachment_146395" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
 Fall Guys, powered by Unity Engine (Left); Fortnite, powered by Unreal Engine (right)
Fall Guys, powered by Unity Engine (Left); Fortnite, powered by Unreal Engine (right) Source: Fall Guys/Unreal Engine [/caption] Although the Unity and Unreal game engines compete, each has specialized features that may be best suited for different experiences (see Figure 1).
Figure 1. Unity Engine vs. Unreal Engine [wpdatatable id=1930 table_view=regular]
Source: Hackr.io/Coresight Research We expect more and more metaverse platforms, including those constructed off blockchain technology, will use Epic Games’ Unreal Engine 5, which launched on April 5, 2022, arguably the most powerful game engine on the market. As game engines continue to improve, so will the quality and immersion-level of both games and the metaverse. One of the metaverse’s most significant hurdles is that virtual experiences are not immersive enough. However, as game engines continue to develop rapidly—thanks in part to increased interest in blockchain gaming—the average person, not just gamers, may soon spend hours at a time in virtual worlds.