
DIpil Das
Grocery retail remains a low-margin, predominantly offline business. Yet, across the US, grocery retailers are pouring investments into digitalization efforts to cater to shopper expectations for e-commerce and help see off the threat from digital-first rivals such as Amazon. Technology isn’t just facilitating e-commerce; increasingly, advanced technologies are being deployed to mitigate the unfavorable economics that come with selling online. We expect more and more retailers to seek solutions to the challenge of e-commerce’s variable costs, which threatens to erode or even eliminate margins. All the time, grocery retailers are turning to technologies to give them a competitive advantage in marketing communications and mitigate the impact of rising labor costs.
Numerous technologies promise to assist grocery retailers in their search for these solutions—and one common thread across many of these is AI. As we discuss in this report, AI offers the promise of smarter customer engagement, better communication with customers, improved operational efficiency, the removal of friction from the shopping process, and helping grocery retailers push further—and more profitably—into e-commerce and omnichannel retailing.
Together, these five components form our SCORE framework for AI in grocery retail. This framework is designed to help retailers focus on the core, high-value use cases of AI in their businesses.
[caption id="attachment_96438" align="aligncenter" width="700"]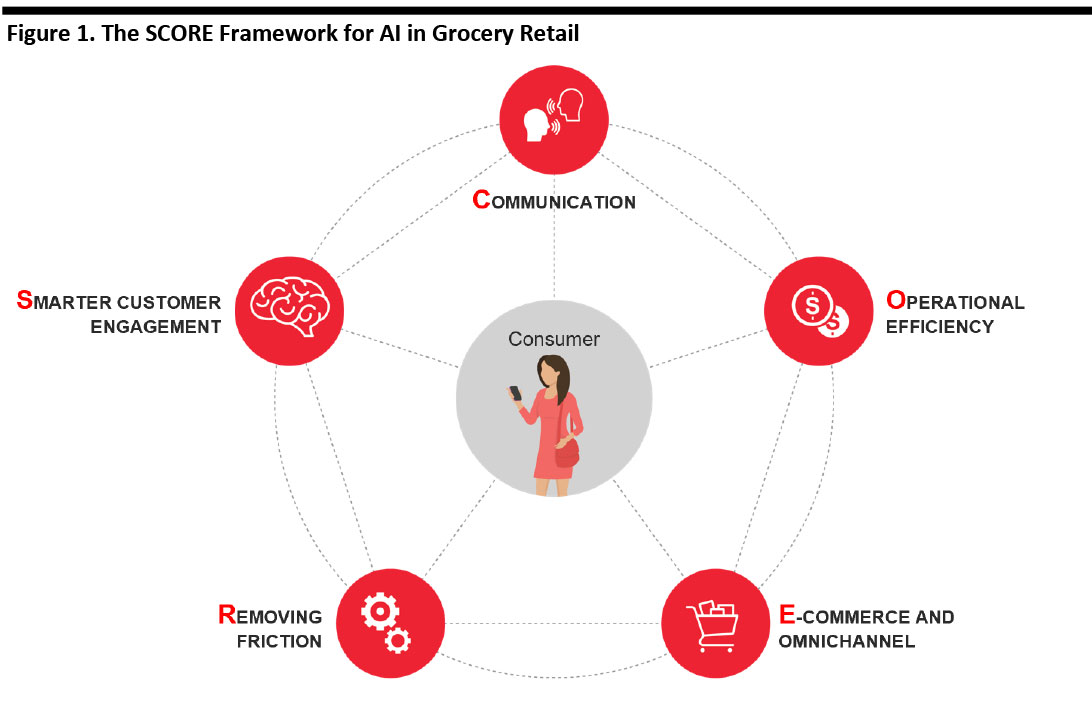 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Smarter Customer Engagement
In a digital world where consumers are bombarded with information and have the ability to search out innumerable deals, nontargeted offers and recommendations are becoming increasingly insufficient to cut through to consumers.
The growth in grocery e-commerce is the fuel for personalized offers and adaptive targeting: While stores have previously been a “black hole” for shopper data, e-commerce provides retailers with an abundance of information on their customers.
AI’s algorithms can turn this surfeit of data into more focused marketing that surfaces the most relevant content, product recommendations and promotions, thereby driving loyalty, repeat custom and incremental spending. The technology can also support adaptive targeting, to dynamically refine customer segments as shopping behaviors change.
[caption id="attachment_96439" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Smarter Customer Engagement
In a digital world where consumers are bombarded with information and have the ability to search out innumerable deals, nontargeted offers and recommendations are becoming increasingly insufficient to cut through to consumers.
The growth in grocery e-commerce is the fuel for personalized offers and adaptive targeting: While stores have previously been a “black hole” for shopper data, e-commerce provides retailers with an abundance of information on their customers.
AI’s algorithms can turn this surfeit of data into more focused marketing that surfaces the most relevant content, product recommendations and promotions, thereby driving loyalty, repeat custom and incremental spending. The technology can also support adaptive targeting, to dynamically refine customer segments as shopping behaviors change.
[caption id="attachment_96439" align="aligncenter" width="700"]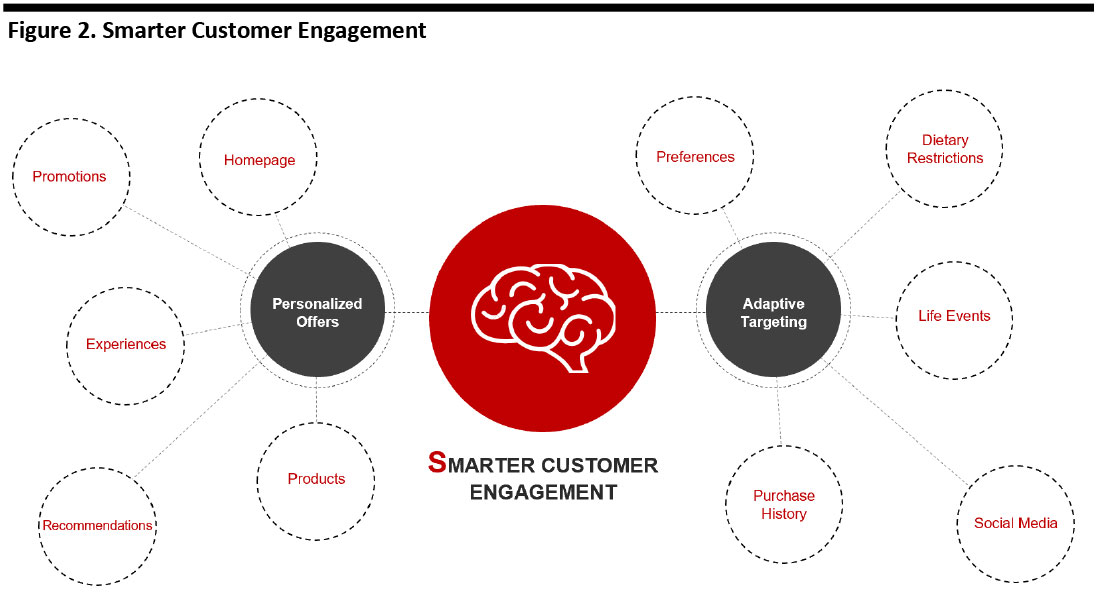 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Communication
For omnichannel grocery retailers, customer service extends well beyond a store’s four walls. Online, via mobile and voice devices, shoppers can benefit from automated support and virtual assistants. These include chatbots, whose increasing sophistication allows not just for responses catering to what is said, but how shoppers express themselves—in other words, mood sensitivity.
All the while, the universe of communications can be made more tailored than ever, from personalized communications across channels and devices to landing pages that are unique to each user.
[caption id="attachment_96440" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Communication
For omnichannel grocery retailers, customer service extends well beyond a store’s four walls. Online, via mobile and voice devices, shoppers can benefit from automated support and virtual assistants. These include chatbots, whose increasing sophistication allows not just for responses catering to what is said, but how shoppers express themselves—in other words, mood sensitivity.
All the while, the universe of communications can be made more tailored than ever, from personalized communications across channels and devices to landing pages that are unique to each user.
[caption id="attachment_96440" align="aligncenter" width="700"]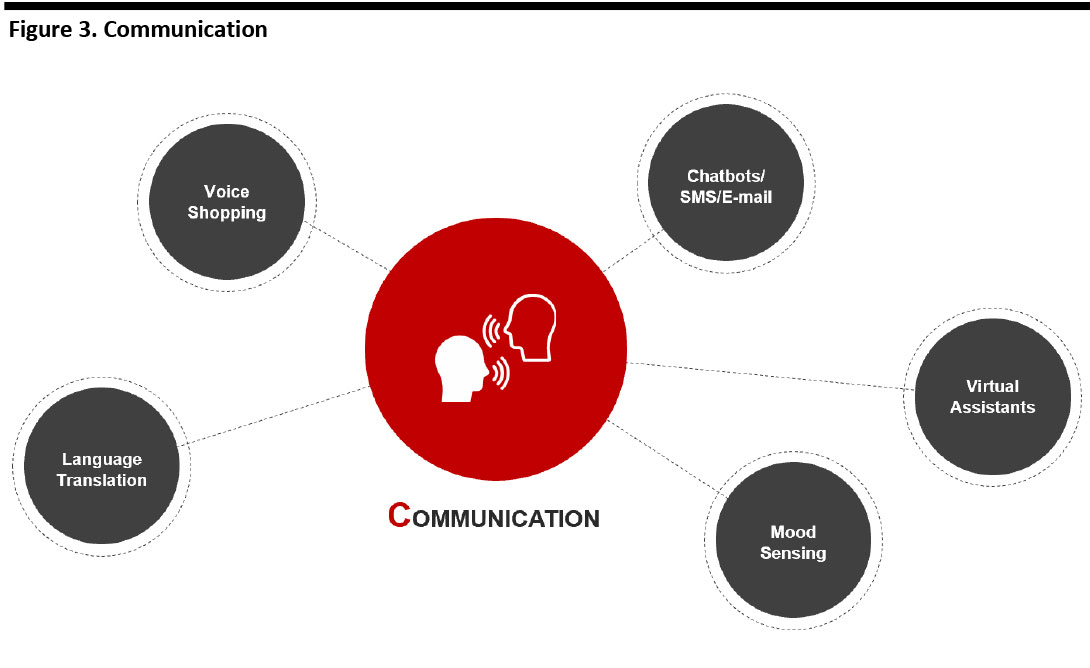 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Operational Efficiency
In the low-margin grocery business, major incumbents are pressured by rising costs (including labor) and the competitive pressures from high-growth, price-focused rivals such as Aldi and Grocery Outlet. At the same time, they face traditional sector demands such as getting perishable products in the right volumes to the right place at the right time.
AI can help retailers to increase operational efficiencies. It can optimize prices based on a mix of external and internal conditions; it can forecast demand, and manage and allocate inventory; and it can support the optimization of assortment.
In addition, AI can reduce labor costs in areas such as store maintenance, checkouts and automated distribution centers.
[caption id="attachment_96441" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Operational Efficiency
In the low-margin grocery business, major incumbents are pressured by rising costs (including labor) and the competitive pressures from high-growth, price-focused rivals such as Aldi and Grocery Outlet. At the same time, they face traditional sector demands such as getting perishable products in the right volumes to the right place at the right time.
AI can help retailers to increase operational efficiencies. It can optimize prices based on a mix of external and internal conditions; it can forecast demand, and manage and allocate inventory; and it can support the optimization of assortment.
In addition, AI can reduce labor costs in areas such as store maintenance, checkouts and automated distribution centers.
[caption id="attachment_96441" align="aligncenter" width="700"]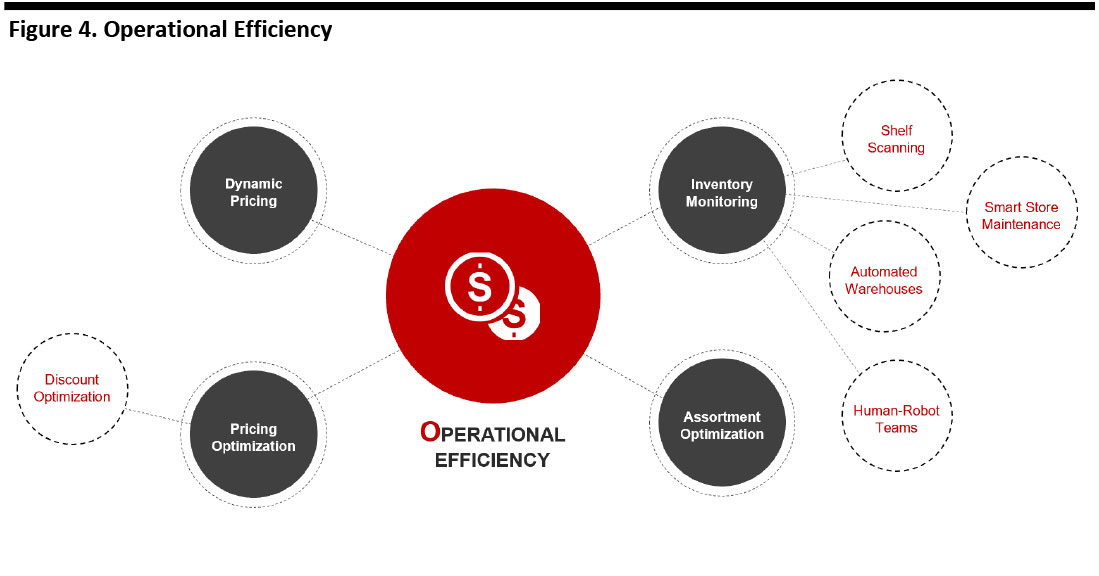 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Removing Friction
Grocery is a frequently purchased, nondiscretionary category, and that means shoppers are looking to minimize the time and effort spent buying groceries. More than in discretionary sectors, consumers are looking to reduce friction rather than seek out experiential shopping trips.
AI can streamline and automate the traditional pain point in grocery shopping—checkout—though Amazon is pretty much alone in deploying AI to eliminate checkouts entirely, in its Amazon Go stores. Elsewhere, retailers are deploying image recognition to streamline checkouts, and facial recognition can shave seconds off the payment process.
AI is able to support product discovery and shopper navigation too, with smart grocery lists, in-store route mapping and visual search capabilities—to help shoppers navigate around stores, find what they want and get out more quickly.
Robots and staffless stores can provide low-friction alternatives to traditional service-driven concepts, including where shopper numbers do not justify staffed equivalents.
[caption id="attachment_96442" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Removing Friction
Grocery is a frequently purchased, nondiscretionary category, and that means shoppers are looking to minimize the time and effort spent buying groceries. More than in discretionary sectors, consumers are looking to reduce friction rather than seek out experiential shopping trips.
AI can streamline and automate the traditional pain point in grocery shopping—checkout—though Amazon is pretty much alone in deploying AI to eliminate checkouts entirely, in its Amazon Go stores. Elsewhere, retailers are deploying image recognition to streamline checkouts, and facial recognition can shave seconds off the payment process.
AI is able to support product discovery and shopper navigation too, with smart grocery lists, in-store route mapping and visual search capabilities—to help shoppers navigate around stores, find what they want and get out more quickly.
Robots and staffless stores can provide low-friction alternatives to traditional service-driven concepts, including where shopper numbers do not justify staffed equivalents.
[caption id="attachment_96442" align="aligncenter" width="700"]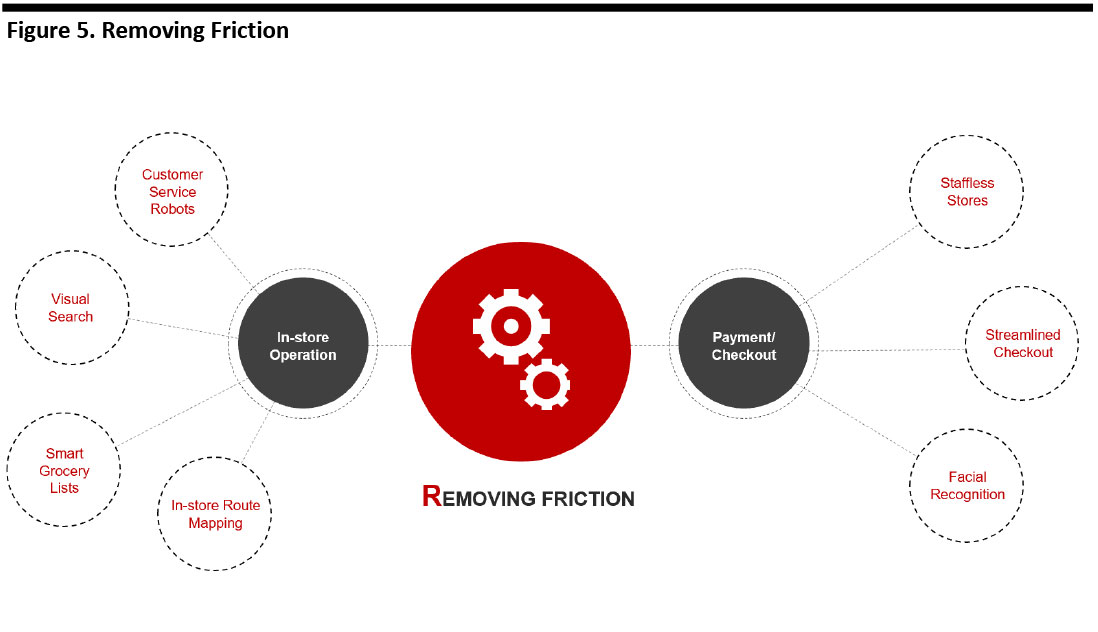 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
E-Commerce and Omnichannel
Grocery remains overwhelmingly an offline category: we estimate 2.6% of US food and beverage retail sales will be online in 2019, versus around 19.8% of all US nonfood retail sales. Yet, from this small base, online grocery sales are growing fast, fueled by legacy retailers pouring investments into delivery and collection capabilities.
AI can provide major support for these initiatives—and it may also support profitability as retailers move toward digital operations. The variable-cost nature of e-commerce, coupled with the uniquely complex picking and delivery methods required for groceries, make it tough to sell groceries online and still turn a profit. AI can help by automating distribution centers to reduce the time and cost taken to pick items (which is one reason why Kroger has partnered with Ocado to build a fleet of robot-equipped distribution centers in the US). Furthermore, AI can reduce last-mile delivery costs with smart routing for deliveries of online orders and autonomous vehicles or delivery robots.
[caption id="attachment_96443" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
E-Commerce and Omnichannel
Grocery remains overwhelmingly an offline category: we estimate 2.6% of US food and beverage retail sales will be online in 2019, versus around 19.8% of all US nonfood retail sales. Yet, from this small base, online grocery sales are growing fast, fueled by legacy retailers pouring investments into delivery and collection capabilities.
AI can provide major support for these initiatives—and it may also support profitability as retailers move toward digital operations. The variable-cost nature of e-commerce, coupled with the uniquely complex picking and delivery methods required for groceries, make it tough to sell groceries online and still turn a profit. AI can help by automating distribution centers to reduce the time and cost taken to pick items (which is one reason why Kroger has partnered with Ocado to build a fleet of robot-equipped distribution centers in the US). Furthermore, AI can reduce last-mile delivery costs with smart routing for deliveries of online orders and autonomous vehicles or delivery robots.
[caption id="attachment_96443" align="aligncenter" width="700"]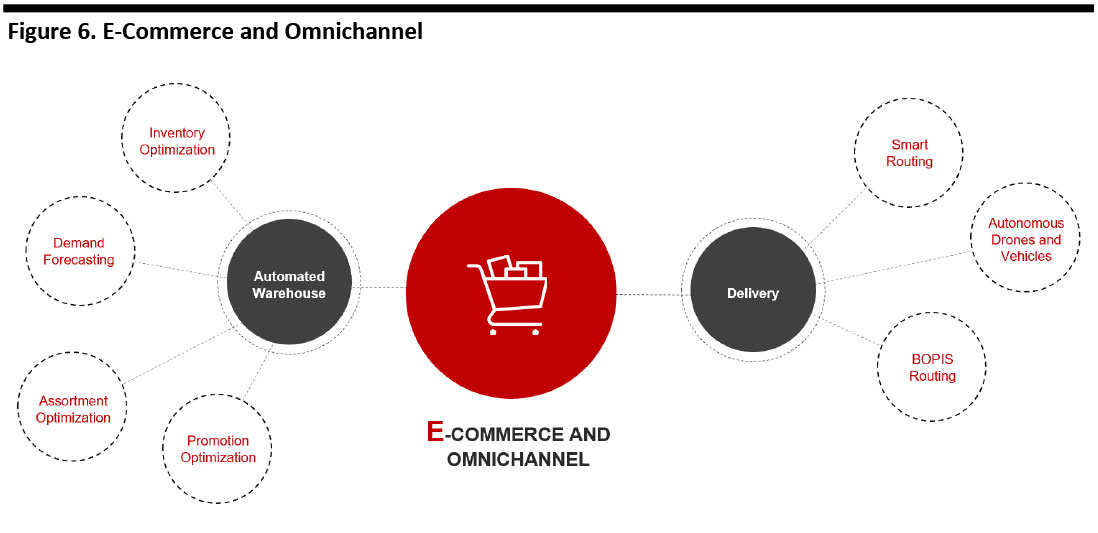 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Smarter Customer Engagement
In a digital world where consumers are bombarded with information and have the ability to search out innumerable deals, nontargeted offers and recommendations are becoming increasingly insufficient to cut through to consumers.
The growth in grocery e-commerce is the fuel for personalized offers and adaptive targeting: While stores have previously been a “black hole” for shopper data, e-commerce provides retailers with an abundance of information on their customers.
AI’s algorithms can turn this surfeit of data into more focused marketing that surfaces the most relevant content, product recommendations and promotions, thereby driving loyalty, repeat custom and incremental spending. The technology can also support adaptive targeting, to dynamically refine customer segments as shopping behaviors change.
[caption id="attachment_96439" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Smarter Customer Engagement
In a digital world where consumers are bombarded with information and have the ability to search out innumerable deals, nontargeted offers and recommendations are becoming increasingly insufficient to cut through to consumers.
The growth in grocery e-commerce is the fuel for personalized offers and adaptive targeting: While stores have previously been a “black hole” for shopper data, e-commerce provides retailers with an abundance of information on their customers.
AI’s algorithms can turn this surfeit of data into more focused marketing that surfaces the most relevant content, product recommendations and promotions, thereby driving loyalty, repeat custom and incremental spending. The technology can also support adaptive targeting, to dynamically refine customer segments as shopping behaviors change.
[caption id="attachment_96439" align="aligncenter" width="700"] Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Communication
For omnichannel grocery retailers, customer service extends well beyond a store’s four walls. Online, via mobile and voice devices, shoppers can benefit from automated support and virtual assistants. These include chatbots, whose increasing sophistication allows not just for responses catering to what is said, but how shoppers express themselves—in other words, mood sensitivity.
All the while, the universe of communications can be made more tailored than ever, from personalized communications across channels and devices to landing pages that are unique to each user.
[caption id="attachment_96440" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Communication
For omnichannel grocery retailers, customer service extends well beyond a store’s four walls. Online, via mobile and voice devices, shoppers can benefit from automated support and virtual assistants. These include chatbots, whose increasing sophistication allows not just for responses catering to what is said, but how shoppers express themselves—in other words, mood sensitivity.
All the while, the universe of communications can be made more tailored than ever, from personalized communications across channels and devices to landing pages that are unique to each user.
[caption id="attachment_96440" align="aligncenter" width="700"] Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Operational Efficiency
In the low-margin grocery business, major incumbents are pressured by rising costs (including labor) and the competitive pressures from high-growth, price-focused rivals such as Aldi and Grocery Outlet. At the same time, they face traditional sector demands such as getting perishable products in the right volumes to the right place at the right time.
AI can help retailers to increase operational efficiencies. It can optimize prices based on a mix of external and internal conditions; it can forecast demand, and manage and allocate inventory; and it can support the optimization of assortment.
In addition, AI can reduce labor costs in areas such as store maintenance, checkouts and automated distribution centers.
[caption id="attachment_96441" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Operational Efficiency
In the low-margin grocery business, major incumbents are pressured by rising costs (including labor) and the competitive pressures from high-growth, price-focused rivals such as Aldi and Grocery Outlet. At the same time, they face traditional sector demands such as getting perishable products in the right volumes to the right place at the right time.
AI can help retailers to increase operational efficiencies. It can optimize prices based on a mix of external and internal conditions; it can forecast demand, and manage and allocate inventory; and it can support the optimization of assortment.
In addition, AI can reduce labor costs in areas such as store maintenance, checkouts and automated distribution centers.
[caption id="attachment_96441" align="aligncenter" width="700"] Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Removing Friction
Grocery is a frequently purchased, nondiscretionary category, and that means shoppers are looking to minimize the time and effort spent buying groceries. More than in discretionary sectors, consumers are looking to reduce friction rather than seek out experiential shopping trips.
AI can streamline and automate the traditional pain point in grocery shopping—checkout—though Amazon is pretty much alone in deploying AI to eliminate checkouts entirely, in its Amazon Go stores. Elsewhere, retailers are deploying image recognition to streamline checkouts, and facial recognition can shave seconds off the payment process.
AI is able to support product discovery and shopper navigation too, with smart grocery lists, in-store route mapping and visual search capabilities—to help shoppers navigate around stores, find what they want and get out more quickly.
Robots and staffless stores can provide low-friction alternatives to traditional service-driven concepts, including where shopper numbers do not justify staffed equivalents.
[caption id="attachment_96442" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Removing Friction
Grocery is a frequently purchased, nondiscretionary category, and that means shoppers are looking to minimize the time and effort spent buying groceries. More than in discretionary sectors, consumers are looking to reduce friction rather than seek out experiential shopping trips.
AI can streamline and automate the traditional pain point in grocery shopping—checkout—though Amazon is pretty much alone in deploying AI to eliminate checkouts entirely, in its Amazon Go stores. Elsewhere, retailers are deploying image recognition to streamline checkouts, and facial recognition can shave seconds off the payment process.
AI is able to support product discovery and shopper navigation too, with smart grocery lists, in-store route mapping and visual search capabilities—to help shoppers navigate around stores, find what they want and get out more quickly.
Robots and staffless stores can provide low-friction alternatives to traditional service-driven concepts, including where shopper numbers do not justify staffed equivalents.
[caption id="attachment_96442" align="aligncenter" width="700"] Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
E-Commerce and Omnichannel
Grocery remains overwhelmingly an offline category: we estimate 2.6% of US food and beverage retail sales will be online in 2019, versus around 19.8% of all US nonfood retail sales. Yet, from this small base, online grocery sales are growing fast, fueled by legacy retailers pouring investments into delivery and collection capabilities.
AI can provide major support for these initiatives—and it may also support profitability as retailers move toward digital operations. The variable-cost nature of e-commerce, coupled with the uniquely complex picking and delivery methods required for groceries, make it tough to sell groceries online and still turn a profit. AI can help by automating distribution centers to reduce the time and cost taken to pick items (which is one reason why Kroger has partnered with Ocado to build a fleet of robot-equipped distribution centers in the US). Furthermore, AI can reduce last-mile delivery costs with smart routing for deliveries of online orders and autonomous vehicles or delivery robots.
[caption id="attachment_96443" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
E-Commerce and Omnichannel
Grocery remains overwhelmingly an offline category: we estimate 2.6% of US food and beverage retail sales will be online in 2019, versus around 19.8% of all US nonfood retail sales. Yet, from this small base, online grocery sales are growing fast, fueled by legacy retailers pouring investments into delivery and collection capabilities.
AI can provide major support for these initiatives—and it may also support profitability as retailers move toward digital operations. The variable-cost nature of e-commerce, coupled with the uniquely complex picking and delivery methods required for groceries, make it tough to sell groceries online and still turn a profit. AI can help by automating distribution centers to reduce the time and cost taken to pick items (which is one reason why Kroger has partnered with Ocado to build a fleet of robot-equipped distribution centers in the US). Furthermore, AI can reduce last-mile delivery costs with smart routing for deliveries of online orders and autonomous vehicles or delivery robots.
[caption id="attachment_96443" align="aligncenter" width="700"] Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]