
albert Chan
Farfetch Limited
Sector: Luxury Country of operation: Operates stores in France, Italy, Japan, the UK and the US and sells through franchises and outlet stores; Sells online through its marketplace in over 190 countries Key product categories: Accessories, apparel, bags, footwear and jewelry Annual Metrics [caption id="attachment_138611" align="aligncenter" width="700"]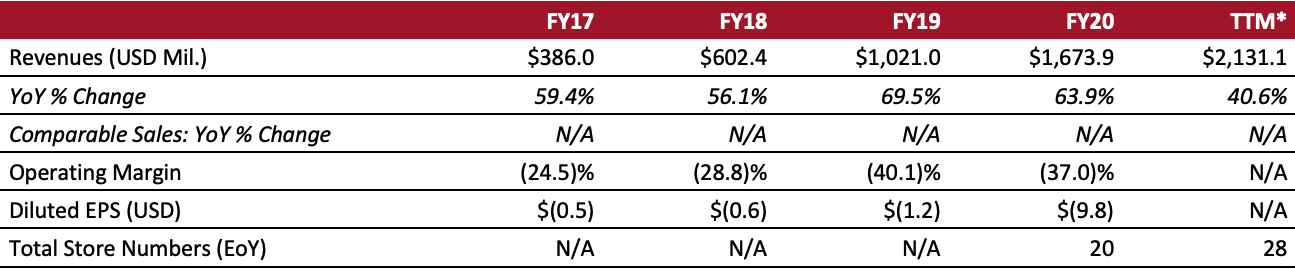 Last fiscal year end: December 31, 2020.
Last fiscal year end: December 31, 2020.*Trailing 12 months ended September 30, 2021.[/caption] Summary Founded in 2007 and headquartered in London, the UK, Farfetch is a technology platform dedicated to luxury fashion. Its key businesses are listed below.
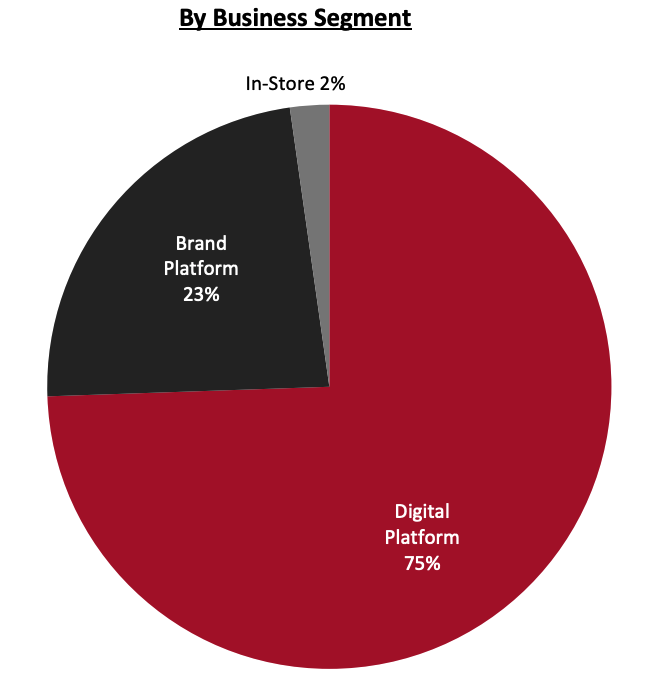
- Farfetch Marketplace: A global luxury marketplace offering consumers in over 190 countries more than 3,550 brands from more than 1,400 sellers, as of November 18, 2021—many of which are offline or have limited online presence.
- Farfetch Platform Solutions (FPS): A white-label enterprise offering, which builds and operates e-commerce and technology platforms for luxury brands and retailers, based on the proprietary Farfetch platform. FPS offers luxury sellers additional services, such as customer services, digital marketing and production.
- Farfetch Store of the Future: The company’s retail innovation arm which builds technology offerings to help luxury sellers merge digital platforms and physical stores, and create a blended customer experience.
- Browns: A British fashion and luxury goods retailer.
- Stadium Goods: A US-based retailer of premium sneakers and streetwear that Farfetch acquired in January 2019.
- New Guards: A fashion production and distribution business, which incubates emerging luxury brands and helps them to grow. Farfetch acquired the company in August 2019.
| Tailwinds | Headwinds |
|
|
- Grow GMV by 30%–35% in fiscal 2021 to drive profitability—current industry growth is at 20%–25%, according to the company.
- Expand its partnerships and increase offerings in the accessories, childrenswear, fine jewelry and watches categories, aiming to drive GMV growth. Additionally, the company plans to launch beauty as a new category in 2022.
- Improve offerings for its private VIP clients, which account for 1% of its customer base but 25%–30% of its overall GMV, according to the company. It also plans to elevate the customer experience for the other 99% of its customer base.
- Leverage its partnership with Alibaba’s Tmall Luxury Pavilion to grow its visibility and customer base in the robust China luxury market.
- Develop its own brands, including New Guards, and create exclusive offerings for its platform.
 Company Developments
Company Developments
| Date | Development |
| November 16, 2021 | Farfetch will stop selling products made of angora wool by April 2022, according to an announcement made by animal rights organization PETA. |
| November 12, 2021 | Farfetch and Richemont confirm that they are in discussions related to several new initiatives, including Richemont leveraging FPS to power its Maisons and Yoox Net-A-Porter, adding Richemont Maisons to the Farfetch marketplace, and Farfetch investing in Yoox Net-A-Porter as a minority shareholder. |
| October 19, 2021 | Farfetch launches its own ethical fashion brand “There Was One.” |
| February 26, 2021 | Farfetch and Chinese mobile developer service Aurora announce a partnership. Aurora will use its artificial intelligence-driven technology, machine learning-based push notification services and intelligent operational analytics to enable Farfetch to personalize smart retail experiences and deliver more targeted services to its customers. |
- Jose Neves—Chairman and CEO
- Elliot Jordan—CFO
- Luis Teixeira—COO
- Cipriano Sousa—CTO
Source: Company reports/S&P Capital IQ