Executive Summary
We believe JD.com is well positioned to benefit from the structural growth of China’s online retail industry and the continual shift in consumers’ preference toward online shopping. JD.com not only possesses best-in-class, in-house fulfillment capabilities that are critical to maintaining quality in the hyper-competitive e-commerce market, but it is also renowned for its business operation execution. Furthermore, for the first time ever, the company reported a GAAP net profit, in the first quarter of 2017, which further reinforces our confidence in the e-commerce giant.
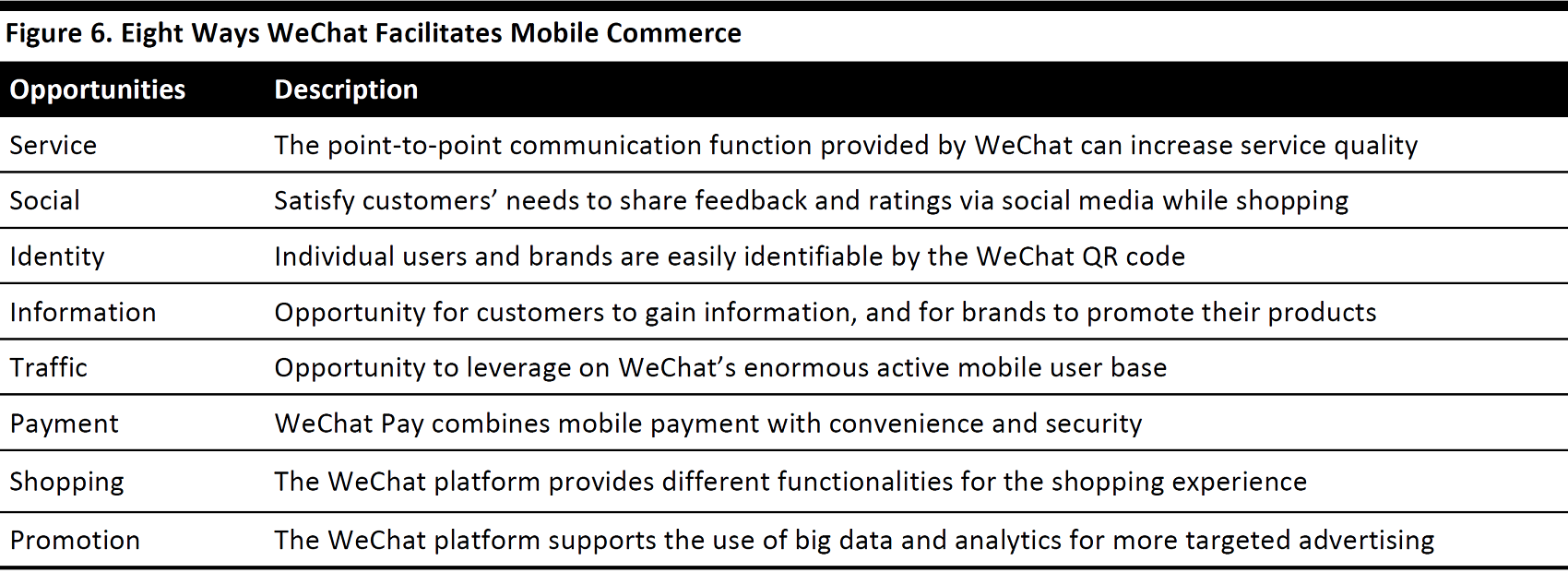
JD.com has formed strategic alliances with other e-commerce and retail giants, which we view as crucial to its continued growth. The partnership with China tech heavyweight Tencent, beginning in 2014, gave JD.com an entry point into mobile commerce that has since spread across China. At the same time, its partnership with US retailer Walmart allows JD.com to source quality overseas products and also expand the reach of its logistics network.
JD.com has come a long way from its origins as a retailer of 3C products (computers, communications, and consumer) to becoming one of China’s all-in-one e-commerce leaders. Its business-to-consumer (B2C) direct sales platform has been the driver of the business, accounting for 56.6% of total gross merchandise volume (GMV) in 2016, giving it a solid foundation from which it can expand into the online marketplace arena to compete head-on with Alibaba.
Source: JD.com
Building an ecosystem with valued-added services in order to retain customers and increase competitiveness has always been a priority for the firm. With the buyers and sellers of its e-commerce business at its core, this ecosystem now spans across Internet finance, logistics service, online-to-offline (O2O), technology, etc.
In this report, we discuss the key drivers behind JD.com’s continual growth and how its different segments are performing. We also look at various industry trends that are shaping the e-commerce market in China and how JD.com stands to benefit.
Growth Drivers
JD.com aims to become China’s go-to, one-stop online shopping platform, offering a comprehensive array of products and best-in-class fulfillment capabilities. Future growth will be driven primarily by further expansion of product categories and its marketplace platform.
Similar to Amazon’s model, JD.com has a direct sales platform whereby it holds inventory and sells directly to consumers. Its recent earnings results show a shift toward the higher-margin marketplace model. Furthermore, growing penetration into rural areas as well as continuous development of value-added services within its ecosystem will also provide strong momentum for growth. Below, we highlight what we consider to be the company’s four growth drivers:
- The shift to higher-margin segments in the direct sales product mix
- Marketplace expansion
- Increasing penetration into China’s lower-tier cities
- Growth of its ecosystem and value-added services
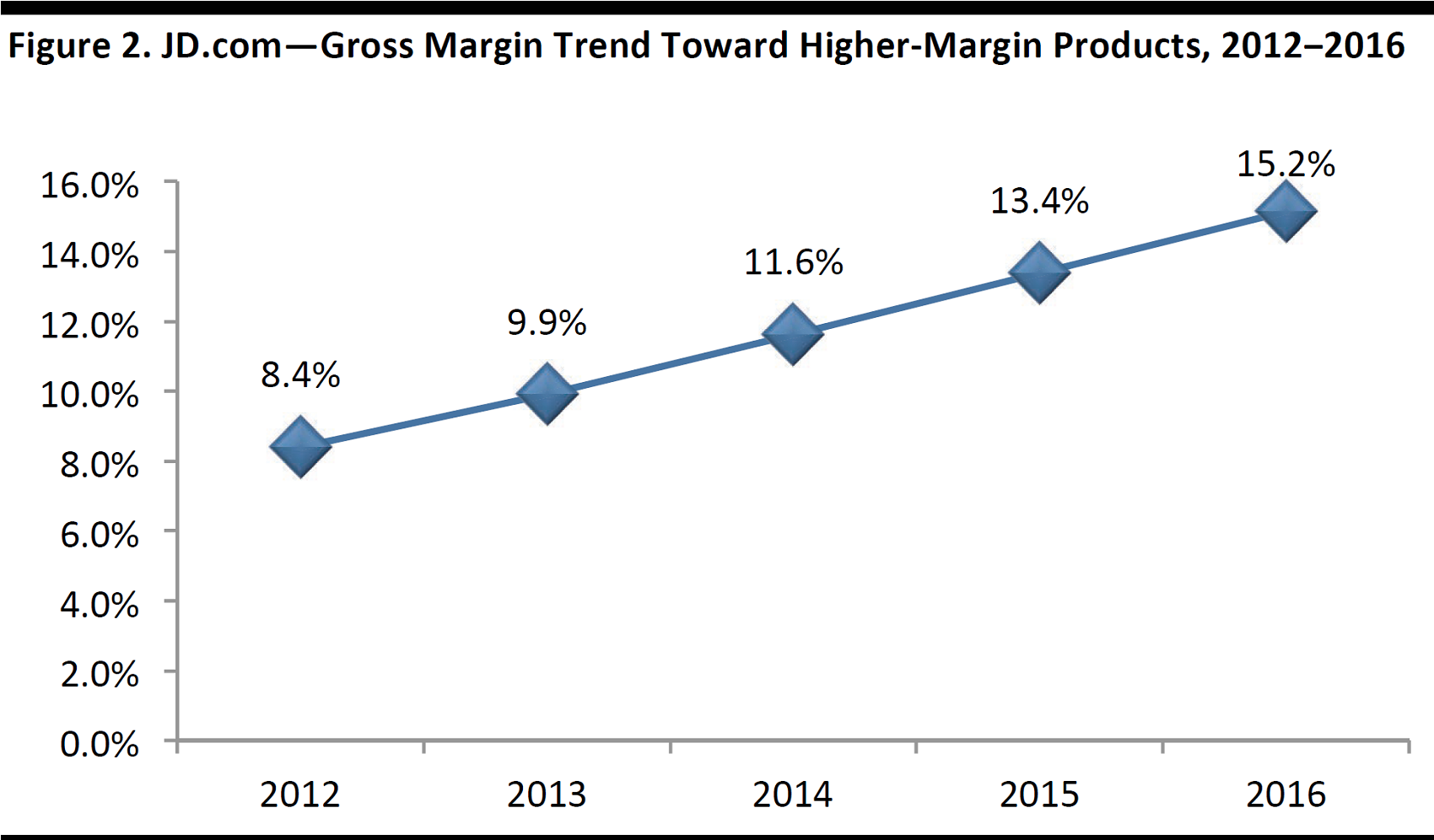
The Shift to Higher-Margin Segments in the Direct Sales Product Mix
When it first started out, JD.com (previously known as Jingdong Mall, then 360buy)focused on 3C products, which typically had lower margins. In 2008, it expanded its product offering to include general merchandise products, and then in 2010, it launched an online marketplace to further broaden its product offering and expand margins.
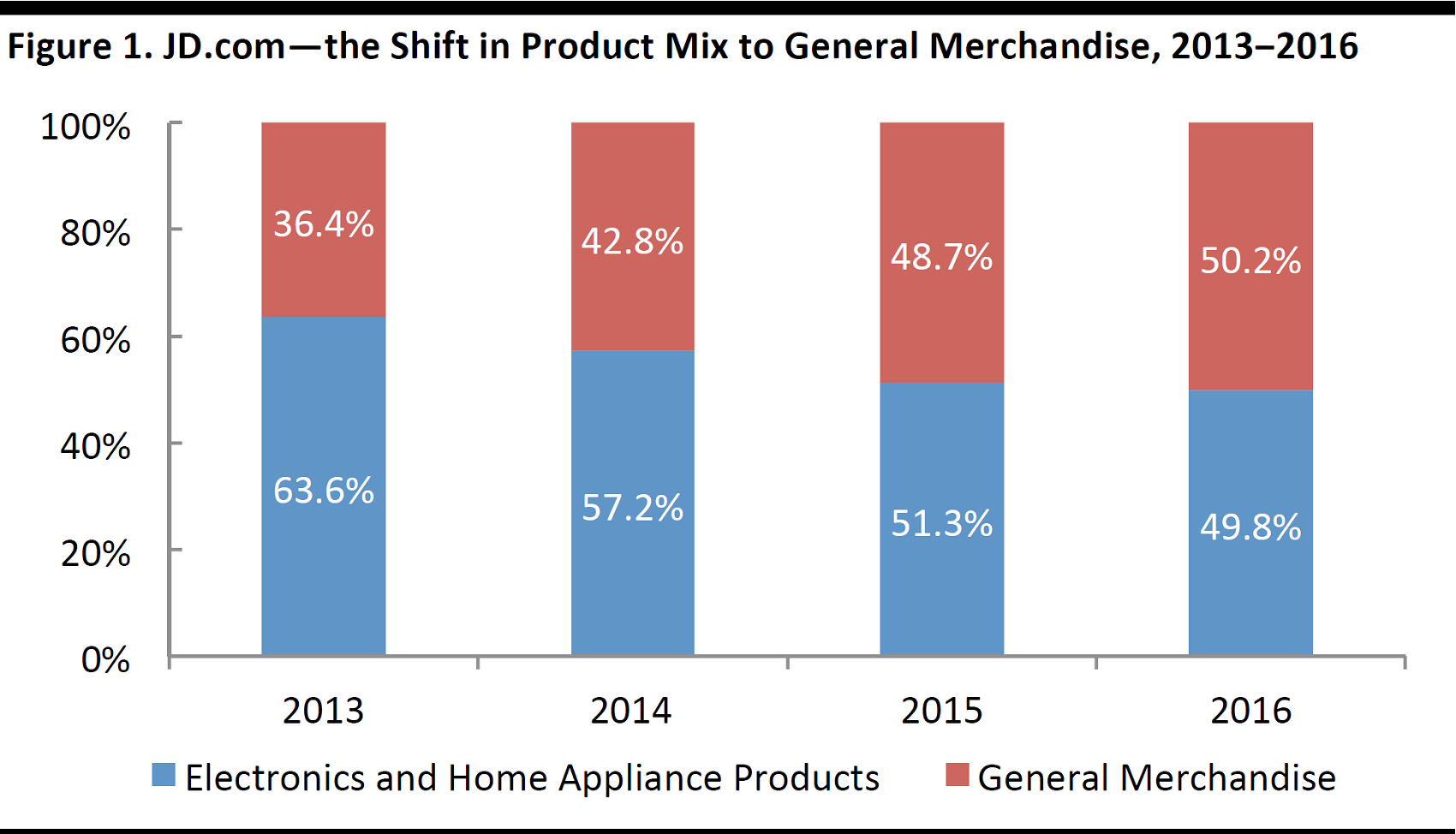
Shifting Product Mix
JD.com’s recent earnings results demonstrated a trend of margin expansion, driven by a shift to higher-margin products, such as private-label and virtual goods, as well as toward a marketplace model.
The contribution from general merchandise products as a portion of GMV increased to 50.2% in 2016 from 36.4% in 2013. This shift in product mix supports JD.com’s continuous efforts to expand margins.
Source: Company data
Source: Company data
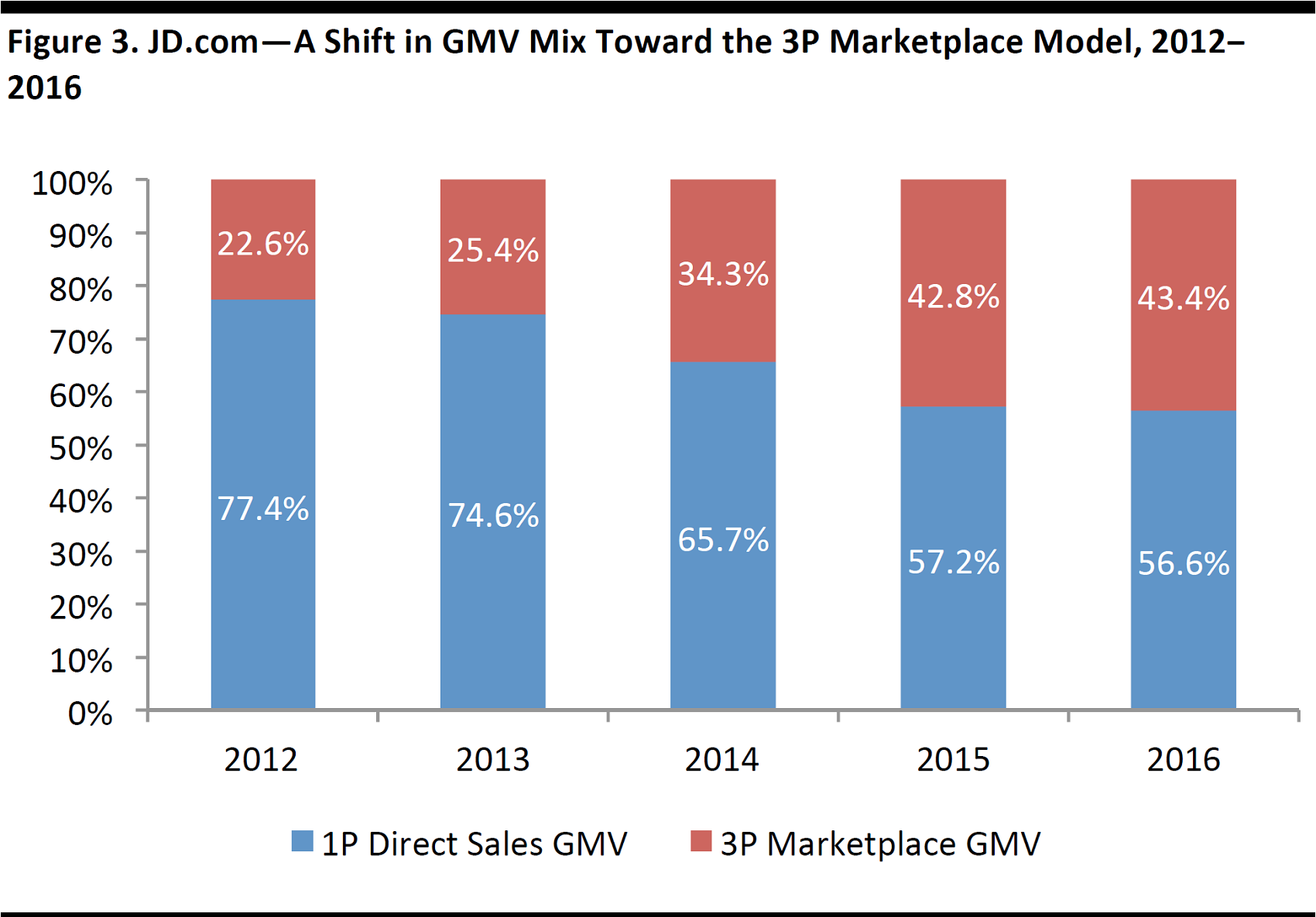
Expansion to an Online Marketplace Model
GMV Mix Shift
The shift in sales mix from a wholesale (1P) direct sales model to selling products as a third-party seller (3P) marketplace is helping JD.com to improve its margin performance. In order to increase scale and market share in the marketplace segment, JD.com will need to grow its active customer base, increase order sizes and expand its product offerings.
3P marketplace GMV accounted for 43.4% of total GMV in 2016, almost double the 22.6% in 2012. The shift toward 3P can help JD.com improve margins, as the marketplace model generally entails higher margins than the direct sales model, because of the minimal level of cost of revenues associated. The 3P marketplace take rate should improve going forward, once JD.com raises its commission and ad fees to the level which it can begin to monetize.
Source: Company data
O2O Initiatives
We believe JD.com’s offline retail partners can benefit from its online-to-offline (O2O) strategy by directing traffic from online to offline and drive incremental ordering and traffic growth on its site. JD.com’s existing cooperation with domestic retailers and convenience stores includes offering selected products online and delivering the physical merchandise through local retail stores at selected locations.
JD.com has unveiled the plan to have 300 physical 3C product experiential stores in tier-one and tier-two cities by the end of 2017. Some 92 stores under the brand names of JD Home and JD Specialty Store are already in operation, as of 9 August, with the majority located in Beijing, Shanghai, Shenzhen and Hangzhou. This physical store concept will greatly leverage on the data analytics of the retail environment that it is situated in, meaning consumer demand will be a key factor in the product offering of that location. Some 14,800 SKUs are currently available in these stores.
Efforts to Strengthen Mobile Commerce
JD.com’s strategic cooperation with tech giant Tencent also allows JD.com to capture mobile commerce market share and access Tencent’s enormous mobile user base. JD.com is able to directly reach the 938 million (as of the first quarter of 2017) monthly active users (MAU) of WeChat, China’s largest instant-messaging platform.
Efforts to Expand its Luxury Brands Offering
In June 2017, JD.com invested $397 million in Farfetch, an online marketplace for luxury brands, to become one of the largest shareholders of the London-based company.
Source: Farfetch.com
Farfetch has partnered with over 200 luxury brands and more than 500 multi-brand retailers, providing a tremendous boost to JD.com’s high-end offering. We believe the move will help drive traffic to JD.com, as Chinese consumers increasingly demand more sophisticated products. The reputation of Farfetch also helps guarantee the quality and authenticity of products in the eyes of consumers, but, more importantly, strengthens JD.com’s credentials among overseas brands that have, until now, been reluctant to enter the Chinese e-commerce market, due to reputational risk.
In July 2017, French fashion house Saint Laurent became one of the largest luxury brands to launch online sales in China, through a joint platform between Farfetch and JD.com. By offering authentic luxury products, JD.com can distinguish itself from its domestic rival Alibaba, which is struggling to maintain product authenticity.
Increasing Penetration into Lower-Tier Cities
JD.com’s fulfillment capabilities in lower-tier cities in China should enable it to capture long-tail consumer demand. We expect JD.com to acquire additional customers as it penetrates into lower-tier cities, increases its product selection, builds out its logistics infrastructure across the nation and further ramps up its drone delivery service.
Fulfillment Infrastructure Tailored to Lower-Tier City Penetration
JD.com has over 1,700 brick-and-mortar service centers located in lower-tier cities, towns and villages, as of October 2016. These centers provide after-sales service—including delivery, installation, and maintenance—for home appliances purchased on JD.com. The aim is to drive down the high cost of selling in rural areas compared with urban areas, because of a lack of infrastructure.
Meanwhile, its delivery and pickup stations, covering 92% of counties, are well suited to meet consumer demand in China’s lower-tier cities. The development and implementation of JD.com’s drone delivery service also greatly enhances the company’s ability to service remote areas.
Convenience Stores—Key to Rural Expansion
In April 2017, Founder and CEO Richard Liu announced his intention to open 1 million convenience stores across the country within five years. This is another initiative as part of JD.com’s signature O2O strategy, which aims to expand the e-commerce player’s presence offline. Roughly 50% of these convenience stores will be located in rural villages, with lower-tier cities as the core focus of its convenience store business.
JD.com is adopting a franchise model for its convenience stores. It will provide training, marketing, product procurement and logistics services to franchisees. Although the 1-million store target seems quite ambitious, we believe convenience stores are a very suitable offline format to pursue in China’s less developed regions. Venturing into locally-based convenience stores could help boost JD.com’s brand awareness and logistics network, as these stores can also serve as delivery and pickup stations.
WeChat Helps Broaden JD.com’s Reach to Consumers in Lower-Tier Cities
With 938 million MAU, as of 1Q17, WeChat, the country’s largest instant-messaging platform, has a wide reach in both urban and rural China, serving as the entry point for rural consumers to access JD.com’s platform. Chinese consumers are extremely savvy when it comes to mobile commerce, therefore, this strategic partnership with WeChat gives JD.com an advantage as it expands into lower-tier cities.
Growth of its Ecosystem and Value-Added Services
JD.com’s long-term strategy is to build scale and user traffic through its core B2C business, and to leverage its large user base to cross-sell value-added services such as finance and logistics. JD.com aims to overtake Alibaba as the largest e-commerce company in China by 2021, according to a speech Liu made in February 2017.
To achieve these ambitions, JD.com has been aggressively building up an ecosystem with various value-added services, including: Internet finance, logistics, cloud computing, and online marketing services.
JD Finance
JD Finance is the Internet finance arm ofJD.com, which will complete its spin-off in the second quarter of 2017. Its verticals span across eight different areas: supply-chain finance, consumer finance, wealth management, online payment crowdfunding, insurance, securities services and village finance. These services aim to create a complete ecosystem on which both consumers and suppliers can conveniently leverage.
Since its inception, JD Finance has served over 100 million users and 200,000 enterprises, with a total transaction value of ¥1 trillion in 2016. It was valued at ¥46.7 billion ($7 billion) after its latest round of financing in early 2016. Although much smaller than Alibaba affiliate Ant Financial, which was valued at ¥388.5 billion ($60 billion), it is worth noting that Alibaba launched Alipay in 2004, whereas JD Finance was only launched in 2012. JD.com has come a long way in only five short years, and the impact of its finance business on the entire ecosystem has been quite significant.
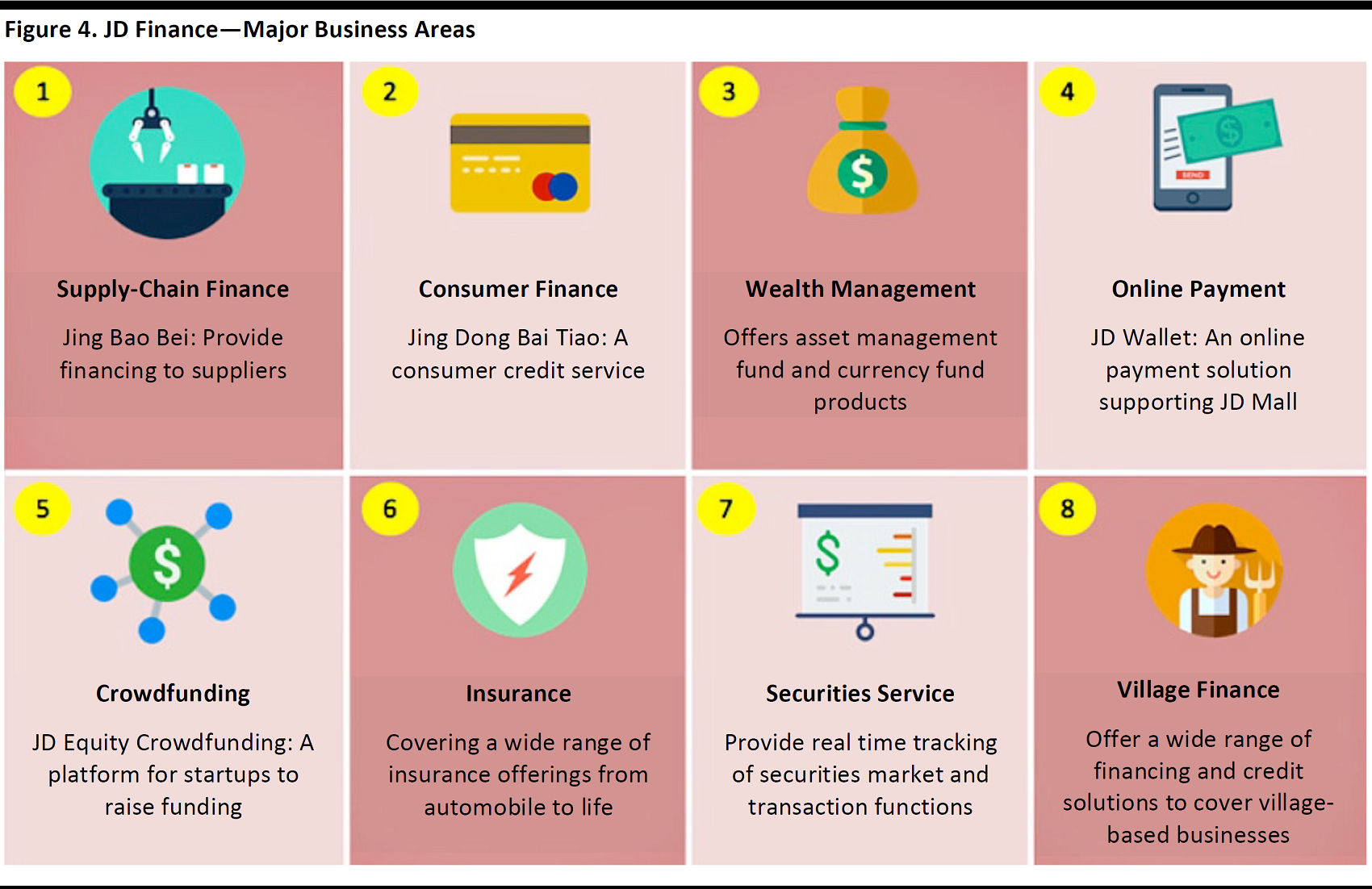
Source: Company data, FGRT
Supply-chain and consumer finance: Jing Bao Bei was the first supply-chain finance solution product launched by JD Finance, with the aim of providing flexible funding to suppliers under its B2C direct sales model. It has since grown to become one of the key infrastructures supporting the supplier community in JD.com’s core e-commerce business. Together with its consumer credit product Jing Dong Bai Tiao, total transaction volume reached¥200 billion in 2016.
Source: Z.jd.com
Online payment and crowdfunding: After its late entry into the online payment market, which is dominated by Tencent and Alibaba, JD.com launched JD Wallet in 2015, and has continued to expand. Since the launch of JD Crowdfunding three years ago, the platform has already raised over ¥4.4 billion for 10,000 startup projects, with a crowdfunding success rate of over 90%. The crowdfunding platform is critical to product innovation at JD.com, as well as technology development.
Insurance and securities services: JD Finance continues to aggressively match Ant Financial’s offerings, launching online insurance and brokerage businesses in 2016, while eying a banking license in the immediate future.
JD Cloud Computing
Launched in the second quarter of 2016, JD Cloud is still in its infancy stage. Recognizing the importance of cloud computing, JD.com is leveraging on its technological capabilities and experience gained over the years to offer the service to external parties.
The cloud computing services JD.com provides include computing, data storage, network management, cloud solutions, retail cloud, logistics cloud, e-commerce cloud, sales cloud, and operation cloud. Different offerings target different stakeholders within its ecosystem. It currently has data centers located in northern, southern and eastern China as well as Hong Kong.
JD.com’s cloud computing technology was recently put to the test when it managed the entire operation of JD.com Mall’s 2017 6.18 Festival, for which transaction value reached ¥120 billion.
Risks
The key downside risks to our positive view of JD.com include:
- Aggravated concerns about counterfeits as it expands the online marketplace model
- Scalability of its in-house fulfillment service
- Pressure on margin expansion
Aggravated Concerns About Counterfeits as it Expands its Online Marketplace
As JD.com continues to shift toward an online marketplace model, the risk of counterfeit products being sold through its marketplace platform increases. This is mainly due to having less control over product quality in the online marketplace model compared to the direct sales model. Counterfeit Coach handbags were found on JD Worldwide in September 2016, sparking a backlash from consumers. Although JD.com tries to minimize or limit the possibility of counterfeits through guarantees on product authenticity, we believe any failure in maintaining the high product quality and authenticity of its products could result in both loss of consumers and brands.
Scalability of its In-House Fulfillment Service
JD.com’s in-house fulfillment service has been one of the company’s key differentiators. However, we believe there is a risk to its scalability in the wake of rapid GMV growth and the potential opening up of logistics services to clients with the spin-off of JD Logistics. If JD Logistic is unable to keep up with the pace of business growth, this key differentiator may turn into a hindrance for JD.com. Moreover, the labor-intensive nature of the logistics service, and last-mile delivery, in particular, is also a risk that JD.com needs to address. The key will be to maintain efficiency while expanding and investing in delivery capabilities.
Pressure on Margin Expansion
JD.com’s aggressive expansion into lower-tier cities and heavy investment in its fulfillment network will likely put significant pressure on margins. To promote brand recognition and achieve e-commerce penetration, sizable marketing expenses will likely need to be incurred. Although net margins turned positive for the first time in the first quarter of 2017, management has already cautioned on its 1Q17 earnings call that margin expansion is unlikely in the near term as it is planning heavy investment and marketing expenses in the coming quarters.
Key Strengths
Two of JD.com’s distinguishing features that set it apart from the competition are its best-in-class, in-house nationwide fulfillment capabilities and its guarantee of product authenticity. In terms of business model, JD.com differs markedly from Alibaba but is more similar to Amazon. Both e-commerce companies have best-in-class logistics and fulfillment networks that offer value-added services to their customers. Meanwhile, JD.com is strategically positioned as the No.2 player in the fast-growing B2C market in China, second only to Alibaba’s Tmall. Under its strategic partnership with Tencent, JD.com has gained excess to its partner’s enormous user base and, therefore, is well positioned to benefit from the strong momentum in mobile commerce.
JD.com is Strategically Positioned in China’ Fast-Growing B2C Market
JD.com is currently the No.2 player in China’s B2C market, second only to Alibaba’s Tmall. Over the years, JD.com has managed to gradually catch up with Alibaba, while widening the gap with the trailing competitors. According to data from iResearch, JD.com had a 26.0% market share in China’s B2C market in the first quarter of 2017, up from 18.6% in 2014, compared to Tmall’s share of 56.6% and 61.4%, respectively.
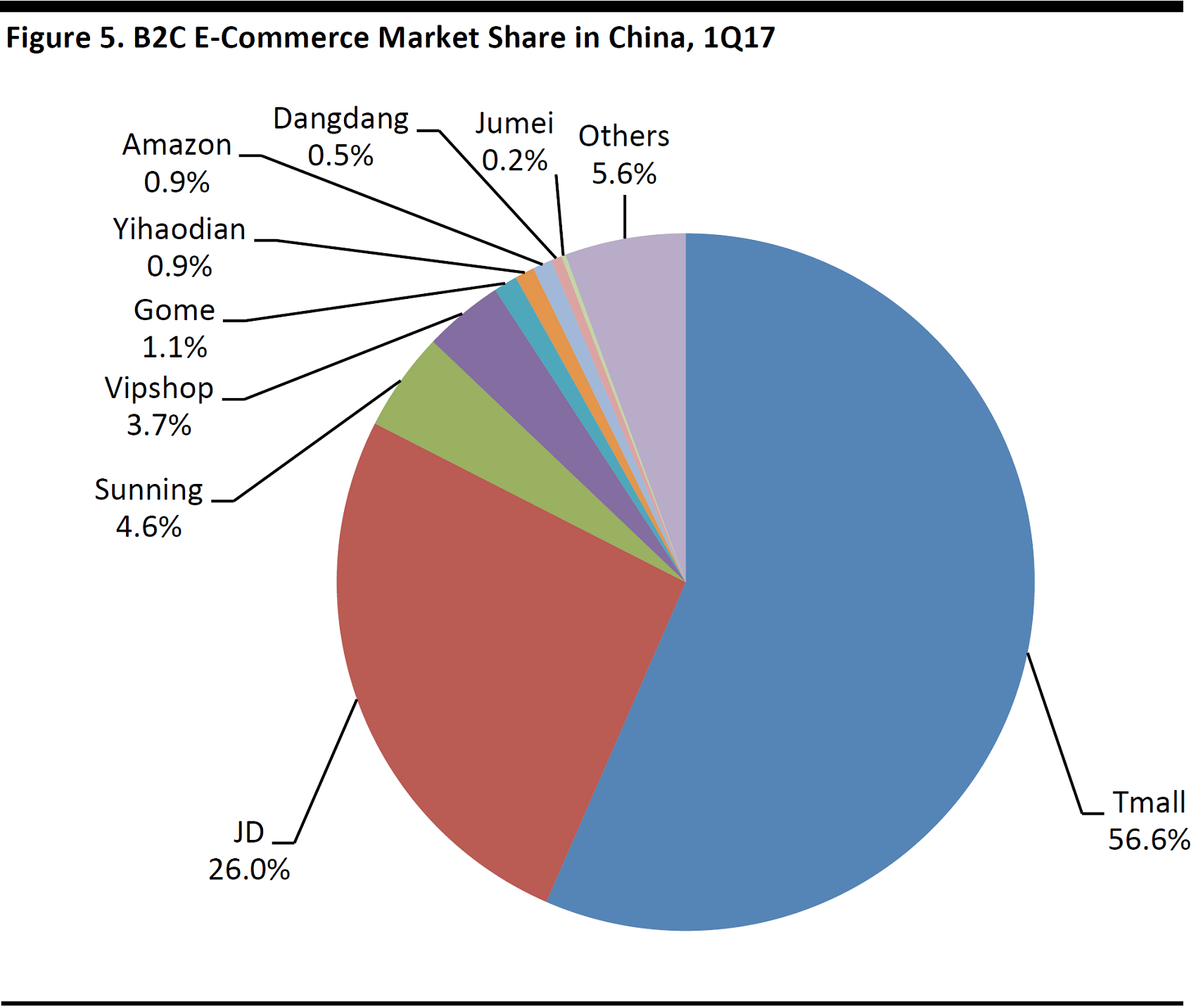
Source: iResearch
Within China’s B2C e-commerce market, JD.com is the leading player in the direct sales category. A direct sales model (1P) means the e-commerce platform is fully involved in the entire transaction value chain, from product procurement, warehousing and delivery to after-sales service. This model has two notable advantages:
- Control of product quality and authenticity
- Control of the fulfillment process
The direct sales model inherently suits JD.com; its largest product categories are consumer appliances and electronics, both standardized products with a relatively low number of stock keeping units (SKUs). These types of products work best with a direct sales model. However, under this model, JD.com has to shoulder inventory risk, while platforms such as Tmall do not. Although we are seeing a gradual shift to the B2C marketplace model, the direct sales channel will continue to be one of the key drivers of JD.com’s growth.
Strategic Partnerships Are Key to Sustaining Growth
JD.com has formed strategic partnerships with China’s social media leader Tencent, international retailers such as Walmart and search engine giant Baidu. These partnerships allow JD.com to leverage on the core competencies of the experienced industry players, and will be instrumental to further develop the company as a whole.

Source: Corporate.jd.com
Strategic Partnership with Tencent
JD.com and Tencent entered into a strategic cooperation agreement in March 2014 to leverage their respective strengths in e-commerce and social messaging in order to strengthen their competitive position against Alibaba. Pursuant to the agreement, JD.com acquired certain e-commerce businesses from Tencent and gained access to Tencent’s enormous user base. In return, Tencent took a 15% stake in JD.com.
Tencent’s Weixin/WeChat and QQ are the two most popular social messaging apps in China. Weixin/WeChat has 938 MAUs, while QQ has 861 million MAUs, as of March 2017.
Growing mobile traffic through WeChat: By leveraging Tencent’s social messaging presence and large mobile user base, JD.com has been able to grow its mobile user traffic. Fulfilled orders placed through mobile increased sequentially in the quarters following the signing of the partnership: up 534% in 3Q14, up 372% in 4Q14 and up 329% in 1Q15, on a year-over-year basis. Meanwhile, mobile orders fulfilled accounted for 81% of all fulfilled orders, as of March 2017, compared to only 24% in June 2014.
Acquiring new customers: WeChat has also become JD.com’s most important channel for new customer acquisition, with one-third of new customers making purchases through WeChat and Mobile QQ, according to JD.com Vice President Hou Yanping. Orders placed through mobile device during Singles’ Day, which was mainly driven by WeChat, has increased from 40% of total orders in 2014 to 85% of total orders in 2016.
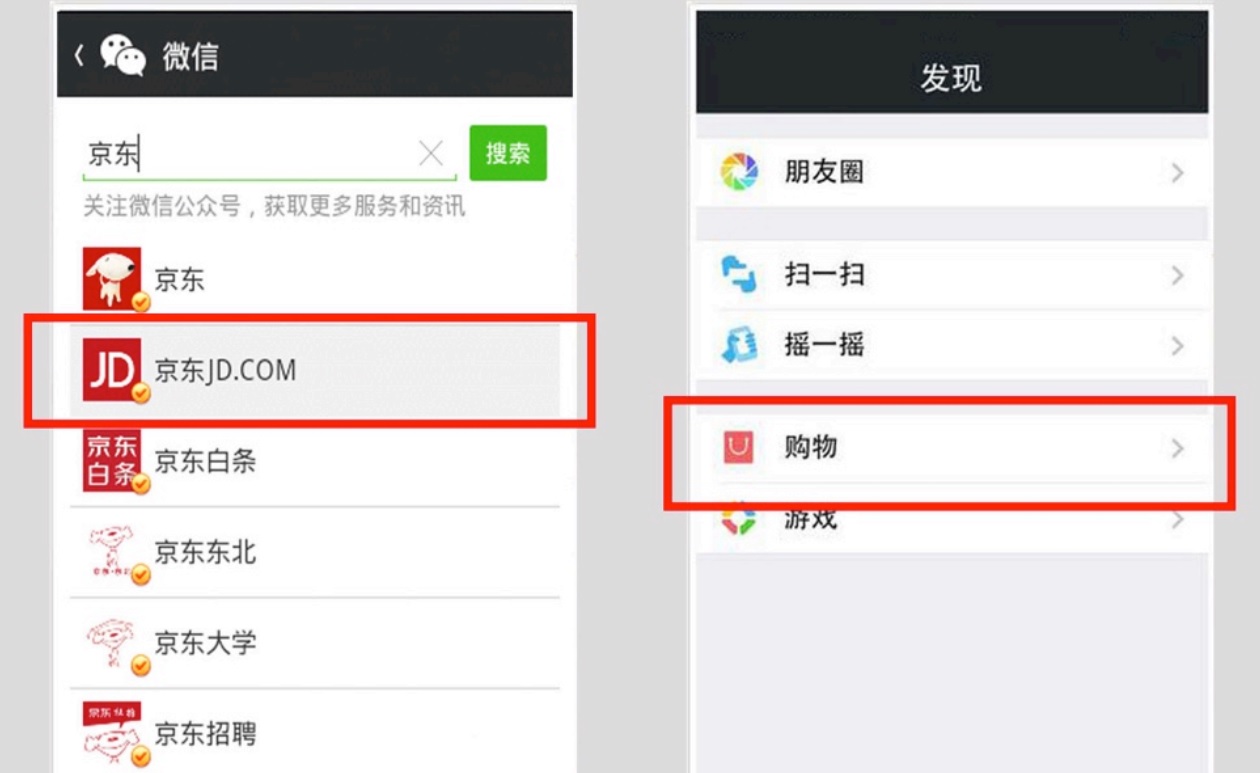
Tencent’s social message applications, Mobile QQ, and WeChat, help cultivate user habits and improve conversion rates for JD.com. Their partnership provided Weixin/WeChat and Mobile QQ with direct access to its Level 1 entry points, which allow users to directly access the app interfaces upon clicking on the home screen. One feature built into the WeChat app is a Level 1 entry point that gives users direct access to browse merchandise offered by JD.com, while remaining in the chat app.
Source: FGRT
WeChat users can directly access JD.com through both the embedded shopping and newsfeed function.
Source: Analysys
JD.com acquired some of Tencent’s e-commerce assets: Immediately Pursuant to the agreement, JD.com acquired certain e-commerce businesses from Tencent, including Paipai.com (C2C) and QQ Wanggou (B2C). Paipai.com has since been shut down in early 2016, while QQ Wanggou was integrated into JD.com’s own B2C platform.
Strategic Partnership with Walmart
The strategic partnership between JD.com and Walmart has allowed JD.com to broaden its product offering on its online marketplace and expand its offline reach.T he partnership was recently expanded in July 2017 to include the integration of their respective supply chains in support of the first-ever 8.8 shopping festival in China co-organized by the two companies.
Supply-chain integration to improve inventory management: Announced in July 2017, Walmart and JD.com will roll out a jointly developed supply-chain system to integrate inventory management. When an order is placed on JD.com, the integrated supply-chain system will analyze the inventory data of both companies and determine the most efficient delivery option, from the closest Walmart or the closest JD.com warehouse. This new initiative is expected to optimize delivery routes for JD.com and increase inventory turnover at Walmart.
Establishing pickup stations at Walmart stores: Meanwhile, JD.com is establishing pickup stations at Walmart stores to enhance the reach and efficiency of its logistics network. As of July 2017, 134 Walmart stores across 18 cities in China have joined the JD Daojia network to offer fast one-hour delivery of orders.
Strengthening grocery e-commerce operations: Under the strategic alliance formed in June 2016, JD.com acquired Yihaodian’s marketplace assets and will leverage Walmart’s global supply chain. Walmart swapped the Yihaodian platform to JD.com for a 5.9% stake (which was subsequently increased to 12.1% in February 2017).

Source: Wal-martchina.com
Onboarding Walmart and Asda products helps expand JD.com’s product offering:In October 2016, Walmart and JD.com announced a series of joint initiatives, which included launching Sam’s Club stores on JD.com and introducing a two-hour delivery service from selected Walmart locations. The latest round of cooperation initiatives has opened a channel for quality British products from Asda, a subsidiary owned by Walmart, to expand its exposure in the Chinese market through JD.com’s platform.
Strategic Partnership with Baidu
In August 2017, JD.com announced the new strategic partnership with Baidu, the leading search engine company in China. The partnership will emphasize the sharing of data and analytics improvement, with the aim of turning searches into sales more efficiently.
Search engine data allow JD.com to make more efficient use of marketing expenses: Search engine data is considered a very quality source of information for painting a comprehensive picture of consumer preferences, mainly because Internet searches are initiated by the consumer. Baidu will open up its search engine data to JD.com, thus helping the e-commerce platform to better market and sell its products. It is expected JD.com’s marketing initiatives will be more accurate and efficient under this partnership, and eventually help lower marketing expenses.
JD.com gains access to Baidu’s active users: JD.com gained a Level 1 entry point into the Baidu App’s interface, meaning that users can access JD.com’s e-commerce platform and shop without leaving Baidu. Such an arrangement greatly speeds up the process from search to purchase for the consumer. At the end of 2016, Baidu has 665 million MAU, which will provide significant momentum for JD.com to drive the growth of its user base.
JD.com’s In-House Fulfillment Infrastructure
JD differentiates itself by providing a best-in-class in-house fulfillment service with its own infrastructure. To put this into context, fulfillment services in China, including warehousing, logistics and last-mile delivery, are less developed relative to that of other countries. Logistics costs as a percentage of GDP are 14.9% in China, 5 percentage points higher than the global average, according to China Federation of Logistics & Purchasing. It is double that of developed economies such as Japan, the US, and Germany. Cold chain logistics in China, in particular, are lagging, which directly contributes to annual wastage of ¥300 billion of agricultural products, according to the Chinese Ministry of Commerce.
Logistics as a Key Differentiator
JD.com’s best-in-class fulfillment infrastructure, which serves a large catchment area and can provide same-day delivery, is what differentiates it from its peers. JD Logistics’ business model is akin to that of Amazon, which also has a strong in-house fulfillment capability.
Because of the fulfillment infrastructure challenges in China, JD.com’s focus on quality, in-house fulfillment capabilities have the following benefits:
- Last-mile delivery capabilities position JD.com well to penetrate rural China: One of the key characteristics of the rural market in China is the lack of logistics infrastructure access, which gives JD.com’s e-commerce platform an important competitive edge. Expansion of the JD Logistics network would be fully in-line with JD.com’s rural e-commerce strategy, creating synergies and improving efficiency in the process.
- Quality control over the fulfillment process: Since all fulfillment is done in-house, JD.com has much better control over the quality of the process than its e-commerce peers, which rely on third-party logistics providers. High-quality logistics and delivery are instrumental in creating a positive consumer experience.
- Enhance operational efficiency: This is particularly important for the e-commerce industry, which is, in general, a low-margin business, as maintaining competitive pricing is crucial. JD.com’s in-house fulfillment infrastructure should increase user stickiness and attract sustainable traffic to its platform, enabling the company to benefit from operational efficiency. We believe JD.com’s efforts to scale up its logistics network across the country with more warehouses and distribution centers could eventually drive down delivery costs. JD Logistics has also begun generating revenues by serving third-party merchants.

Source: Corporate.jd.com
Overview of JD Logistics
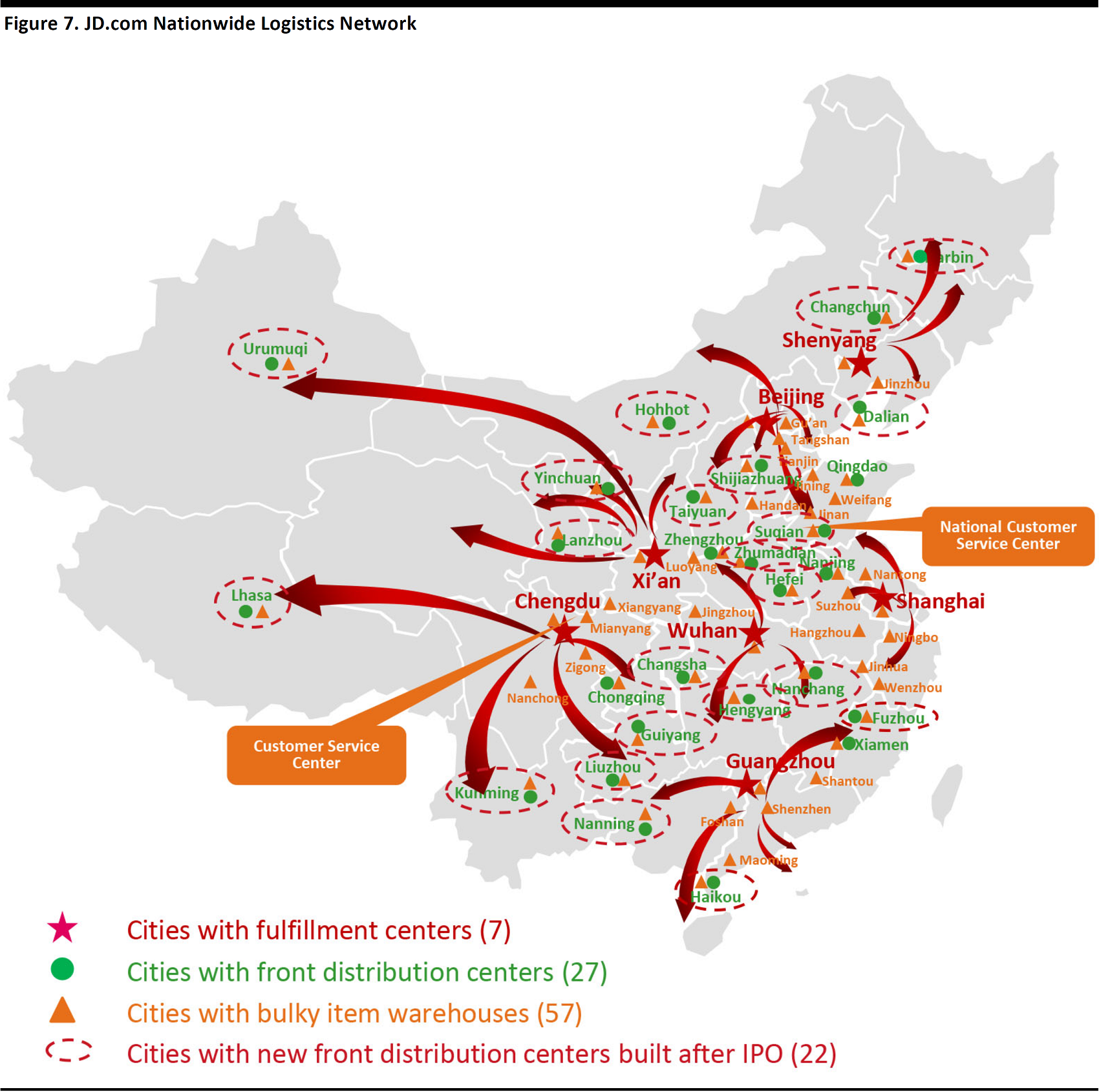
JD Logistics was spun off as a separate business group under JD.com in April 2017. It has one of the largest fulfillment infrastructures of any e-commerce company in the world:
- Seven fulfillment centers in seven major cities
- 256 warehouses
- 6,906 delivery and pickup stations
- 6 million square meters of gross floor area
- Over 65,000 full-time delivery staff
According to JD.com, as of December 2016, its logistics network covers 2,655 counties across China, which translates to national coverage of 92%. Together with its 1,700 JD Bang Service Centers (run under a franchising model) located primarily in rural areas, JD.com not only has all the major cities in China covered, but is also well positioned to deliver orders in the growing and increasingly important rural market.
Source: JD.com4Q16 presentation
Some 85% of JD.com’s direct sales packages are delivered within the same day or the next day, as reported in 2Q16. Meanwhile, JD.com ranks first in terms of delivery services (with a satisfaction level of 19.7%) and delivery personnel (a satisfaction level of 21.2%), according to a customer survey conducted by the China Electronic Commerce Research Center in 2016. Competitor Vipshop, which also provides in-house logistics, ranks behind JD.com in terms of delivery personnel ranking, with a satisfaction level of 19.6%.
Open Logistics Platform
JD.com has made its fulfillment services and warehousing facilities available to all merchants, regardless of whether they sell on its platform or not, instead of limiting its fulfillment services to its own products. While this move may not drive profitability in the near term, as merchants need time to transition to JD Logistics’ platform and build up scale, we believe it will help JD.com increase platform stickiness and customer satisfaction. It also opens up a new revenue stream for the company, and is therefore positive for its long-term strategy.
It is reported that for merchants using JD Logistics, average inventory days has been reduced by eight days, while time needed for delivery was also on average down two days, according to official figures from JD.com. The level of customer satisfaction for the merchants was up an average of 113%.

Source: Corporate.jd.com
Fulfillment and Technology Innovation
JD.com is putting significant effort into improving its fulfillment infrastructure and core technologies through R&D and partnerships.
- Drone delivery system: JD.com has been a strong advocate for enlisting drones to deliver parcels, especially in remote areas. It recently signed an agreement with the Sichuan provincial government to provide a 24-hour drone delivery service. Under the agreement, JD.com will build 185 drone bases in the province. JD.com’s CEO Richard Liu, believes that logistics expenses could be reduced by as much as 70% with the wide adoption of drone delivery.
- Cold chain delivery: JD.com has partnered with Japanese logistics company Yamato Transport to develop its cold chain delivery capability. Yamato will provide cold chain consultation and international-standard technologies, allowing JD.com to pursue expansion in China’s currently comparatively primitive fresh-food delivery market. The partnership also allows JD.com to leverage on Yamato’s global fresh-food delivery network and introduce more unique products to local consumers.
Business Segments
JD.com has two distinctive B2C business segments: direct sales and an online marketplace. The direct sales business has been the company’s main revenue driver and, in our view, will remain so for the near future. The higher-margin online marketplace model represents a growth opportunity that JD.comis actively pursuing.
Direct Sales Business
JD.com began its direct sales B2C business with a focus on 3C—computers, communications and consumer—products. It has since expanded the product offering to include apparel, home appliance, fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG), fresh food and other general merchandise items.
Source: Company data/FGRT
Source: Company data/S&P Capital IQ/FGRT
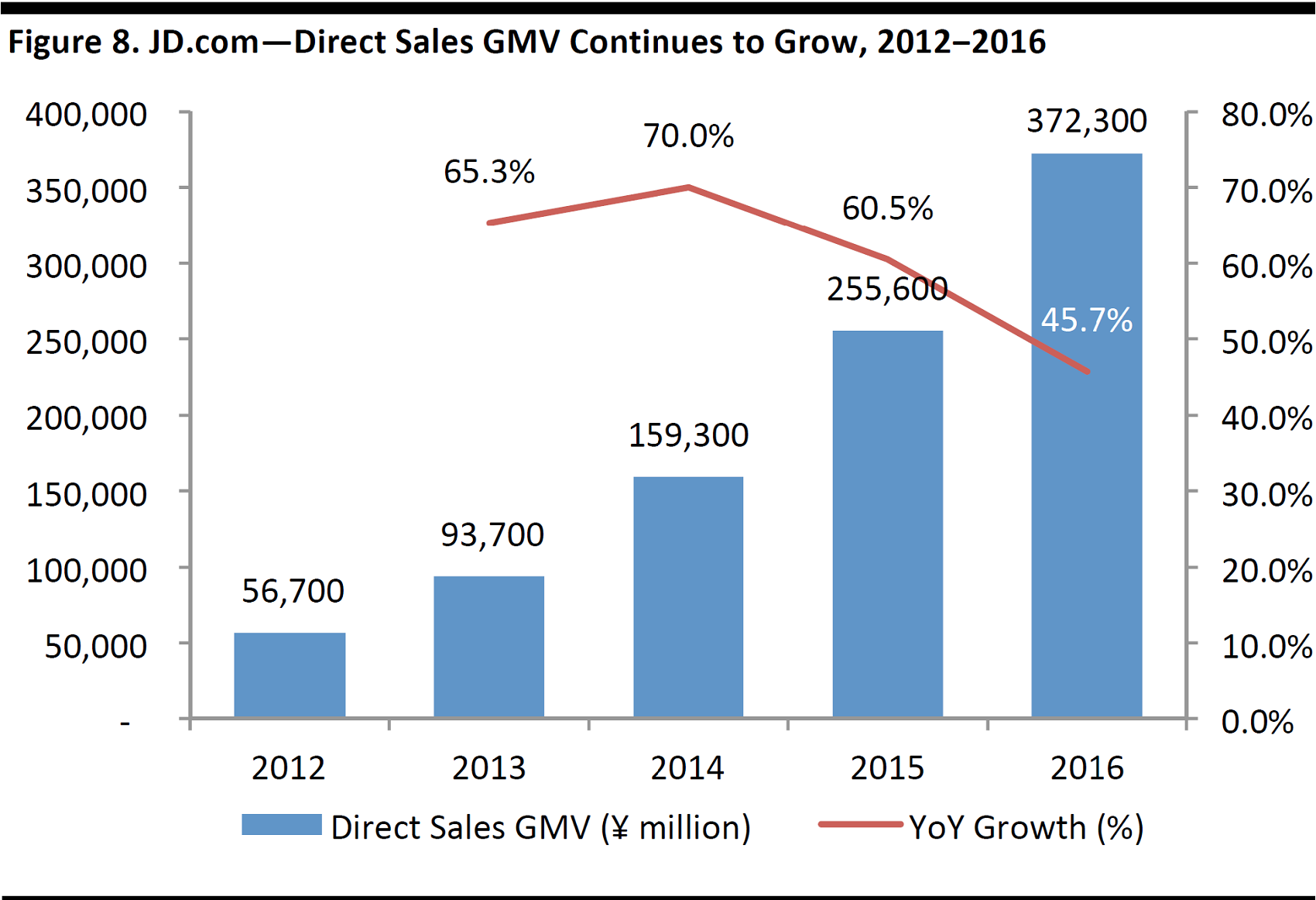
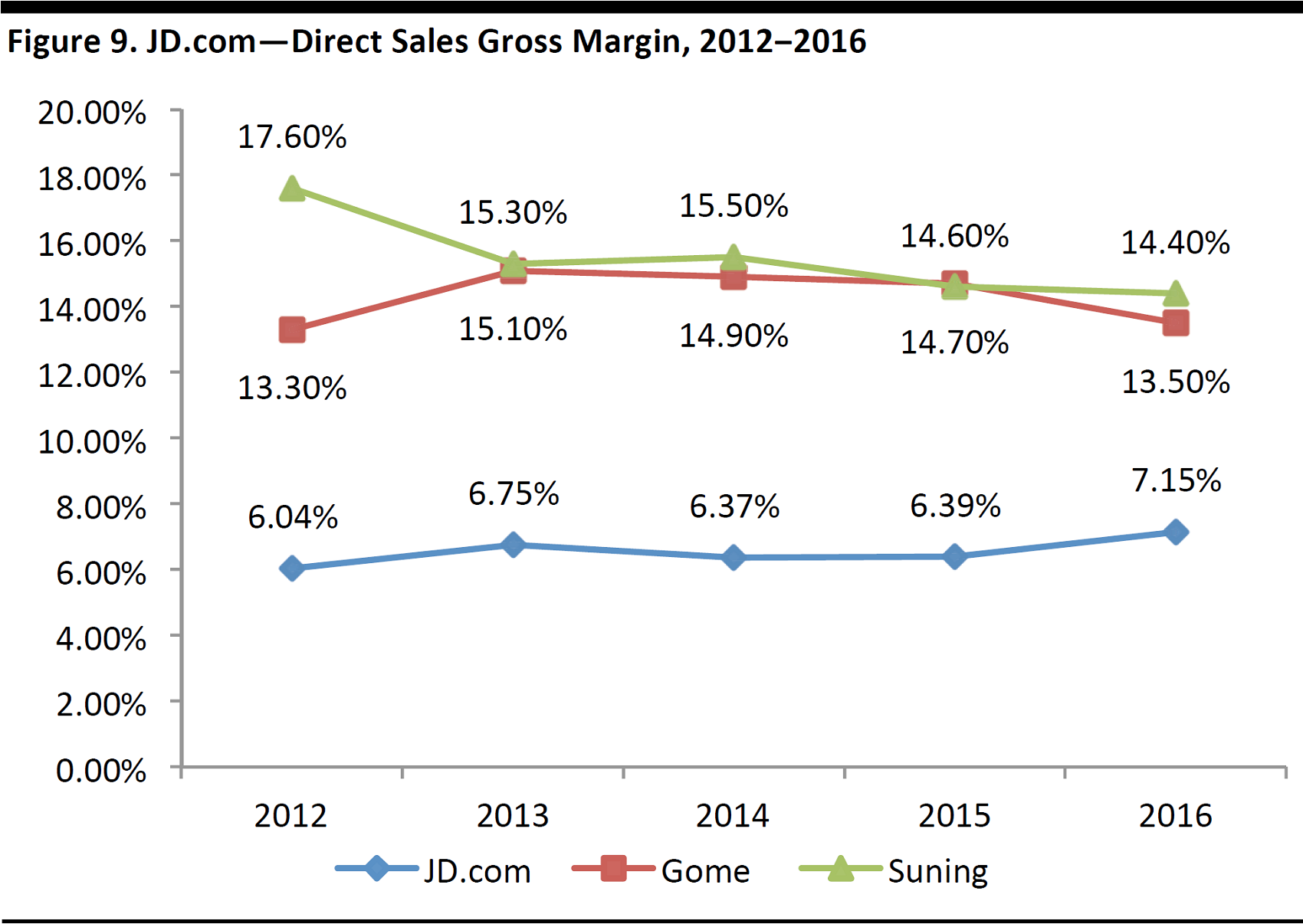
The direct sales business is JD.com’s main revenue generator, accounting for 91.4% of revenues in 2016. GMV of direct sales was ¥372 billion in 2016, representing a four-year CAGR of 60.1% from 2012 to 2016. Gross margin has also continued to expand, reaching 8.3% in 1Q17, and is likely to continue on this upward trajectory going forward. As discussed in the previous section, we believe a shift in product mix to higher-margin products such as home appliances and cosmetics will help improve JD.com’s gross margins in the direct sales segment.
Online Marketplace
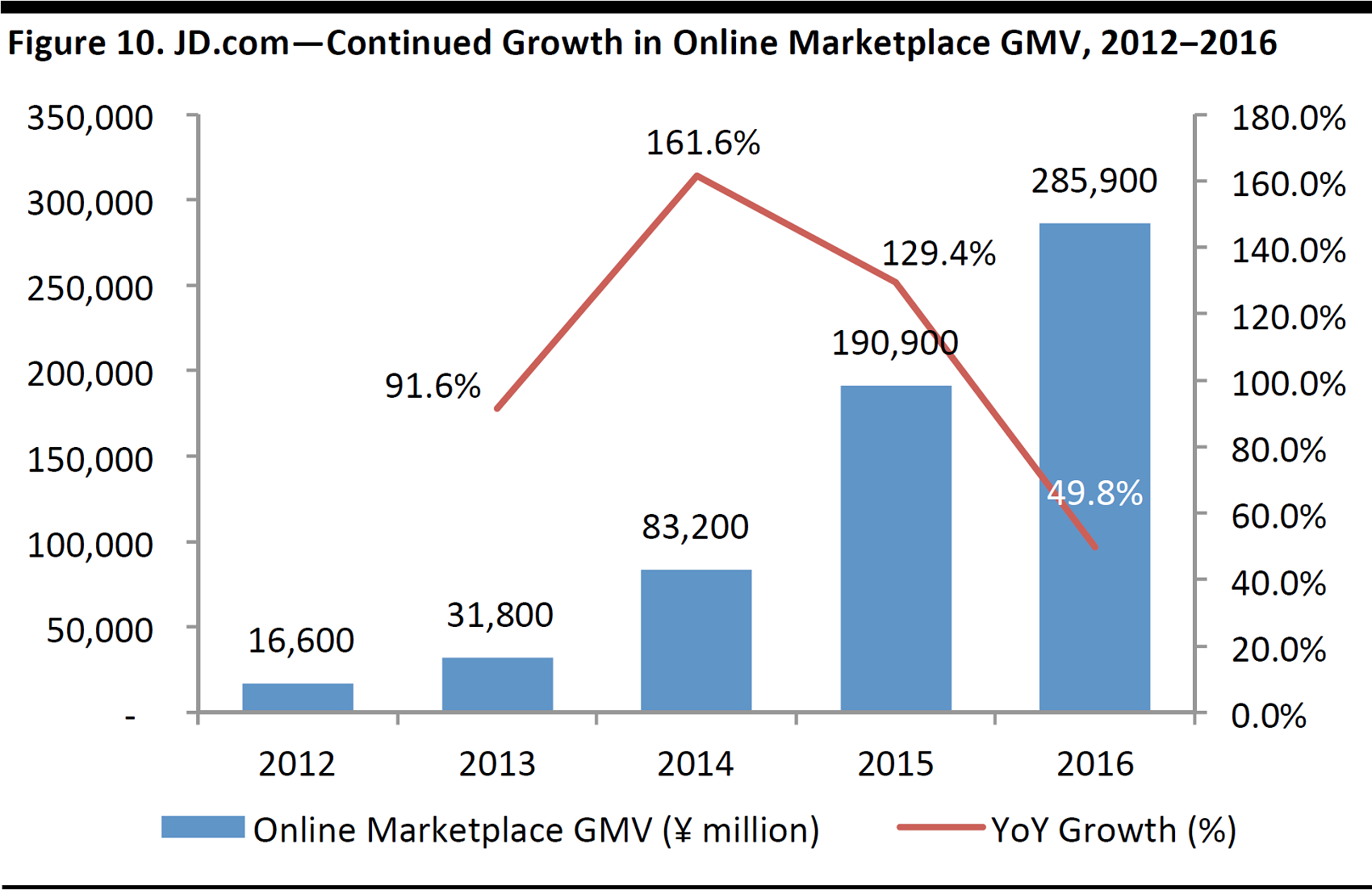
JD.com launched its online marketplace in 2010. In 2016, online marketplace contributed to 43.4% of total GMV, almost doubling from 22.6% in 2012. JD.com’s online marketplace also adopts a B2C focus, similar to its direct sales business. JD.com attempted to gain a foothold in the consumer-to-consumer marketplace with Paipai.com, a C2C platform it acquired from Tencent in 2014, but failed to deal with the problem of counterfeits and illegal sales. The website was closed in 2016 and JD.com has since focused on the B2C model.
Source: Company data/S&P Capital IQ/FGRT
JD.com’s online marketplace has grown rapidly in the past few years, driven by the gradual shift from a direct sales model to a marketplace model. However, online marketplace still generates only a relatively modest portion of the company’s revenues, accounting for only 8.6% of revenues in 2016. We believe there is significant room for growth once the platform attains greater scale, which should lead to higher commission and advertising income.
As a relative newcomer to the online marketplace, JD.com’s GMV is only a fraction (18%) of that of Alibaba’s Tmall, which was ¥1,565 billion for the financial year ending in March 2017, so it will not be easy for JD.com to catch up in this category. However, we expect strong growth momentum for its online marketplace, mainly attributable to:
- Increased traffic driven by the direct sales business
- Retailers’ need for marketplace diversification
Financial Performance
GMV: JD.com’s GMV increased to ¥658.2 billion in 2016, up from ¥73.3 billion in 2012, representing a CAGR of 73.1%.
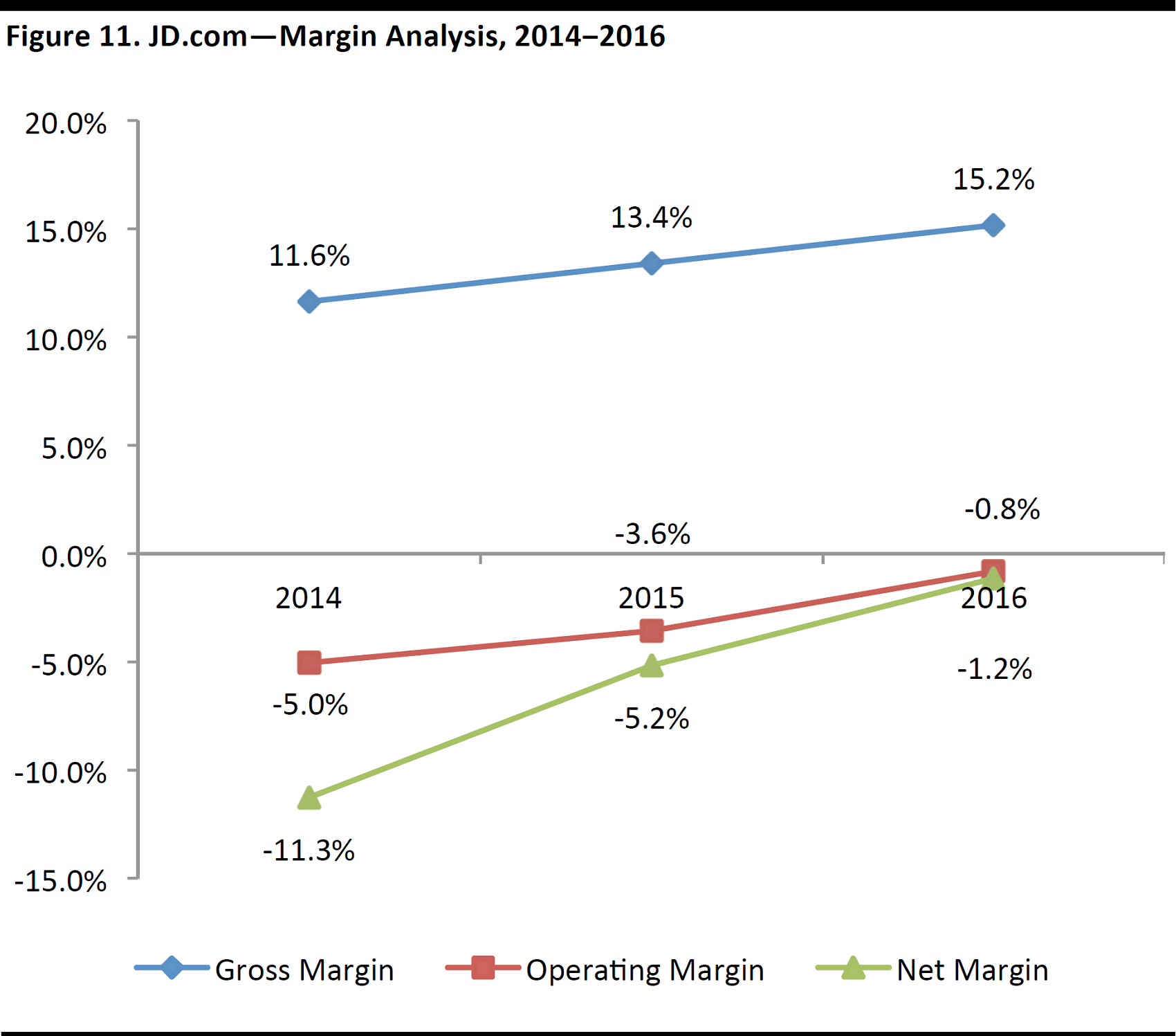
Operating margin: JD.com’s operating margin has been in negative territory, but has been improving, due to greater operational efficiency. In its latest earnings results, the company reported that GAAP operating margin turned positive for the first time, at 1.1% in 1Q17.
Net income: JD.com has been reporting a net loss since its inception, which is not uncommon in the technology industry, however, in 1Q17, it reported GAAP net income for the first time, of¥472.3 million. We should not expect this positive trend to continue, however. Management cautioned on the earnings call that as the company continues to invest heavily in fulfillment, technology, and marketing, net income will likely return to negative territory for the near term. We believe that profitability is currently not the company’ top priority, as JD.com is still trying to scale up its business.
Source: Company report
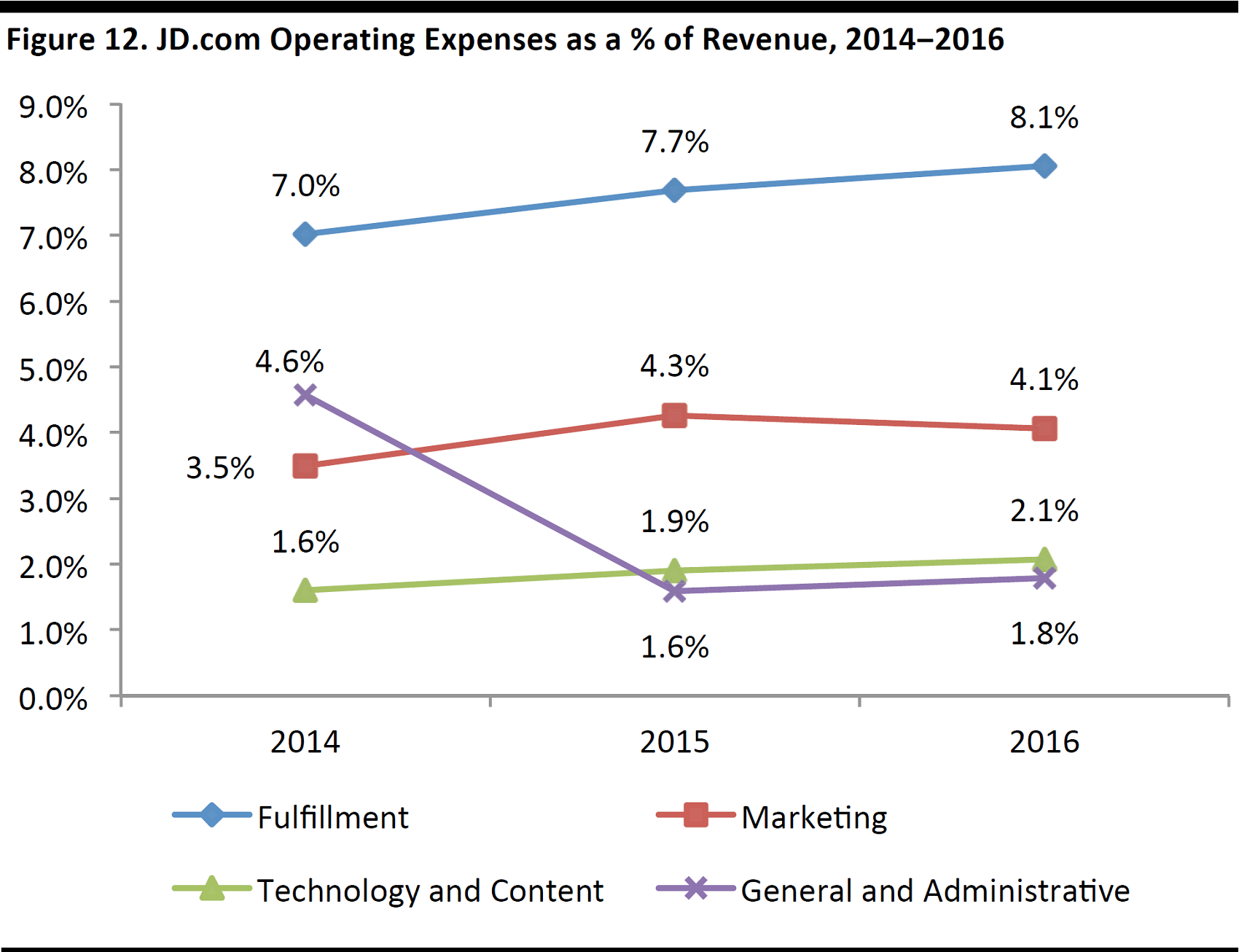
Operating expenses: As JD.com possesses a best-in-class, last-mile delivery and logistics infrastructure, fulfillment expenses account for the largest portion of operating expenses. The company is also very determined to build strong brand awareness through various marketing activities and promotions.
Source: Company data
Capital expenditure: The company plans to continue to invest heavily in the areas of: 1) market penetration; 2) Internet finance, logistics and other value-added services; and 3) mobile commerce and O2O. As such, capex will continue to be a significant use of funds going forward.
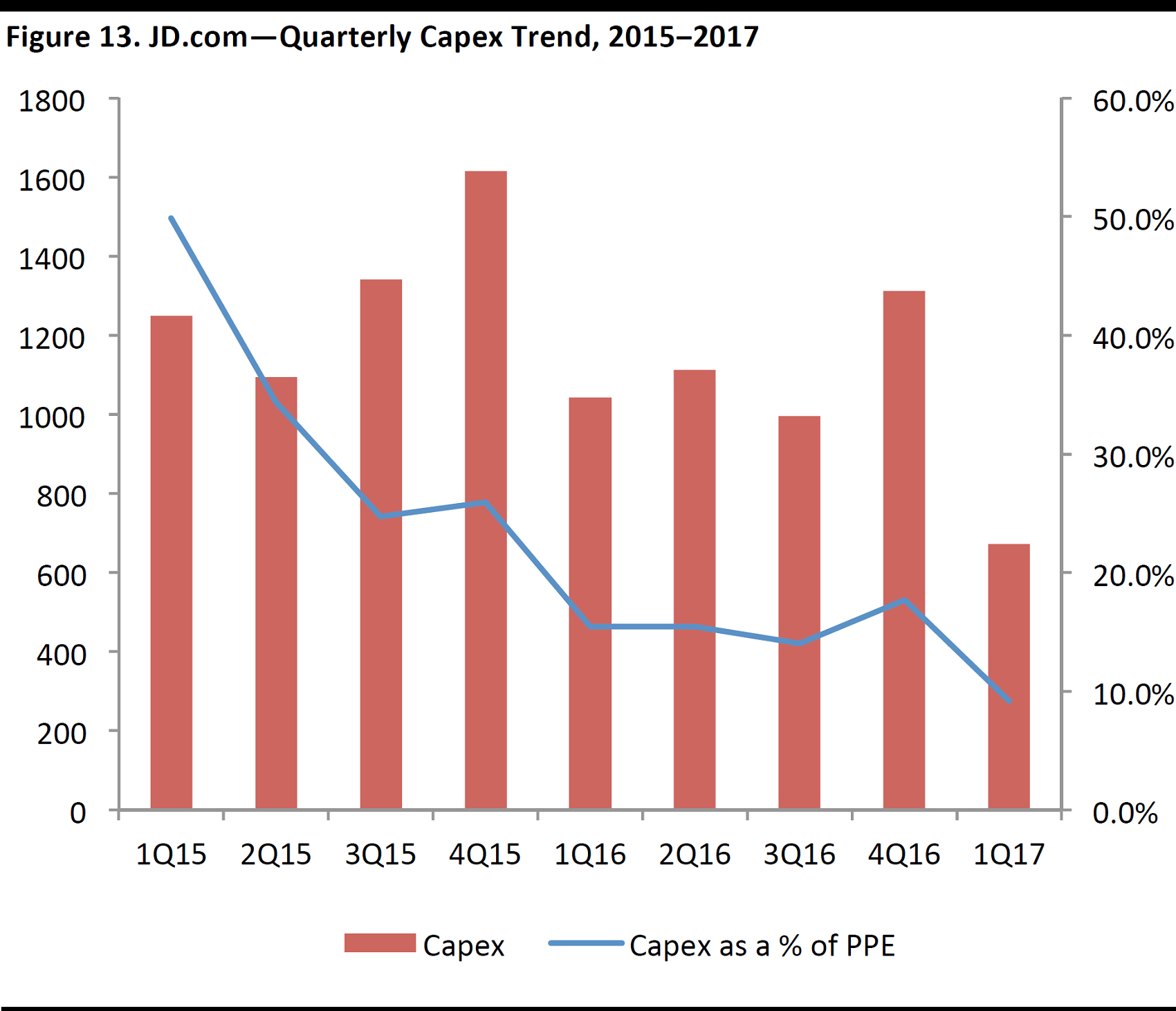
Note: PPE = plant, property and equipment.
Source: S&P Capital IQ
Key Industry Trends
The success of JD.com hinges greatly on the evolving Chinese retail industry. Key trends in China’s e-commerce market and how it is changing the retail landscape include:
- Secular growth of e-commerce transaction volumes in China
- China’s growing B2C market
- The rise of cross-border e-commerce (CBEC)
- China’s transition to mobile commerce
- The increasing sophistication of Chinese online shoppers
Secular Growth of E-Commerce Transaction Volumes in China
As China’s No.2 e-commerce player in terms of revenues, we expect JD.com to benefit from robust growth of the sector and see further room for market-share gains to support continued earnings growth.
The Prevalence of Online Shopping in China
China’s online shopping penetration (measured by e-commerce sales as a percentage of total retail sales)is expected to increase to 19.2% in 2018from 5.6% in 2012,on the back of increasing Internet penetration and improving online transaction infrastructure, according to iResearch.
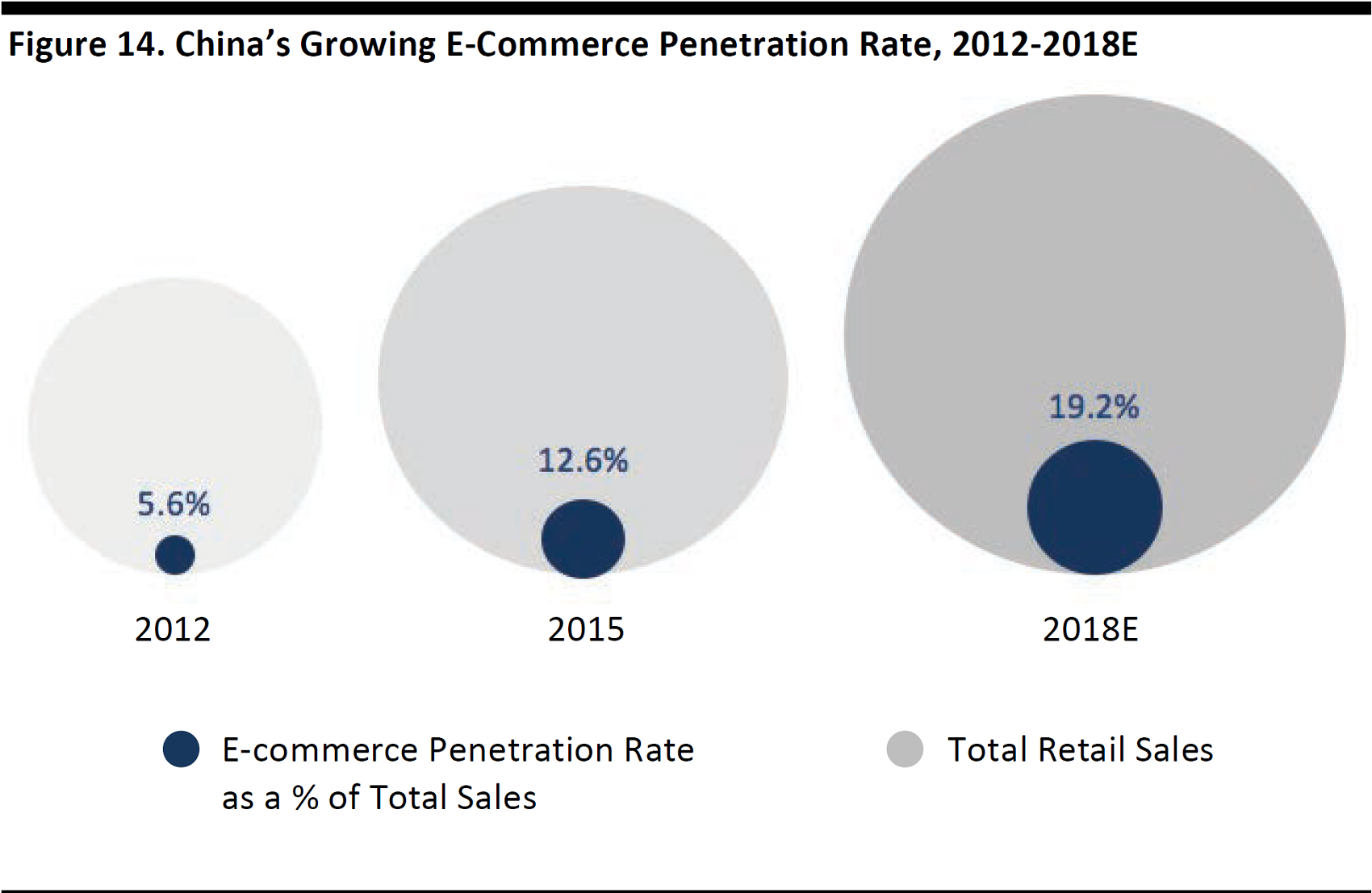
Source: iResearch/FGRT
Online Shopping Is Expected to Outperform Offline
The growth of China’s e-commerce market has outperformed the growth of the physical economy. As such, we expect online retail to continue to gain share over offline retail. O2O has become a major theme in the retail industry, and e-commerce players are aggressively investing in both online and offline resources to build a seamless shopping experience for consumers. As part of itsO2O initiatives, JD.com is opening convenience stores across China (mainly rural China) as well as investing in traditional retailers such as Yong Hui Supermarket.
Consolidation of China’s Retail Industry
The evolving retail industry has created opportunities for e-commerce players. The overall retail market in China is quite fragmented, with the top 20 retailers accounting for just17% of the total market share in 2015, compared to 43.4% in the US.
Secular Growth of China’s E-Commerce Industry
According to research from iResearch, GMV China’s e-commerce industry is forecast to increase at a 17.7% CAGR over 2015–2019 to surpass the $1 trillion mark in 2019. The domestic e-commerce market reached $770 billion in 2016, accounting for15.5% of the country’s total retail market, according to data from the National Bureau of Statistics of China.
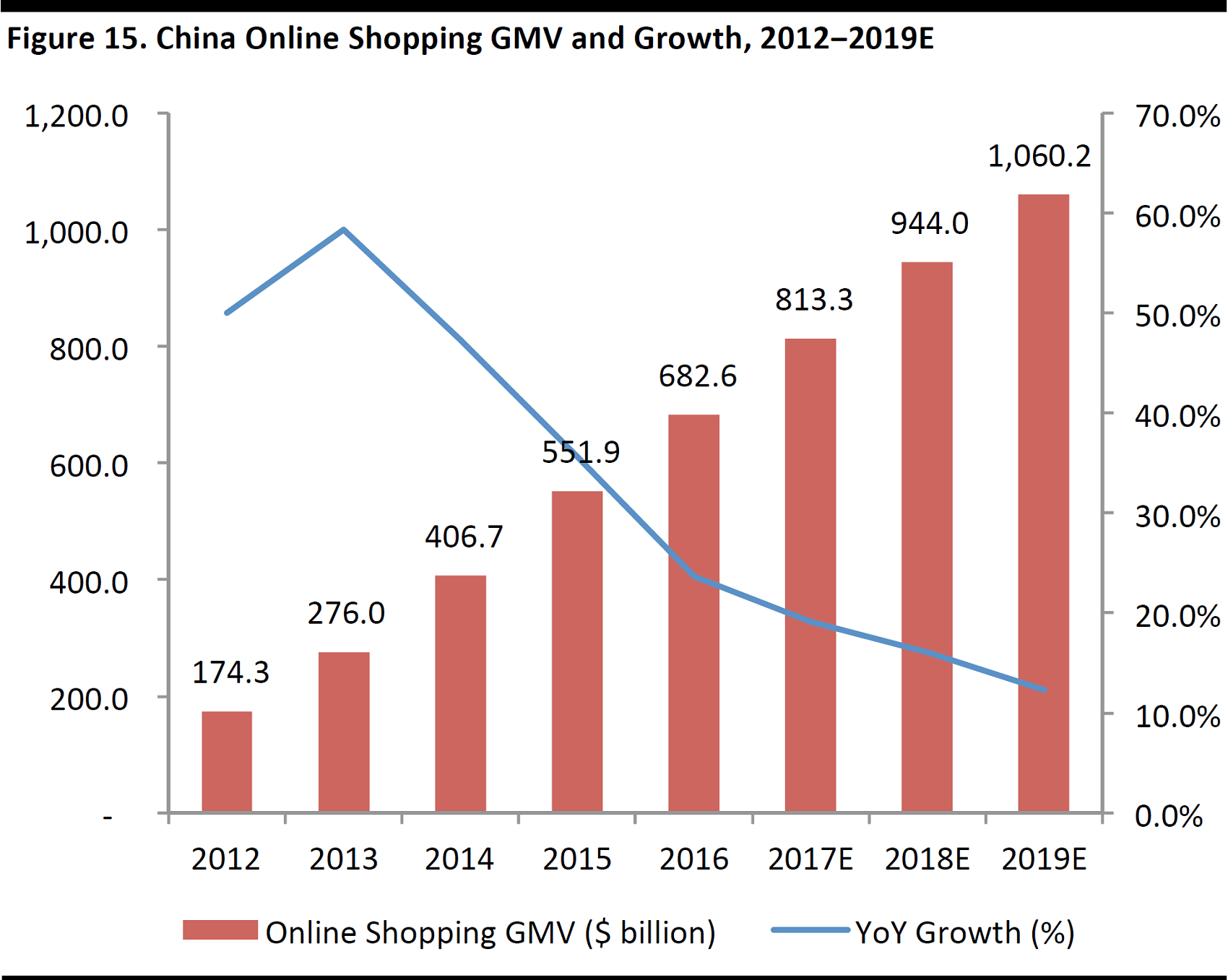
Source: iResearch/FGRT
China’s Growing B2C Market
JD.com is strategically positioned to benefit from the increasing shift in Chinese consumers’ preference for online shopping. Its core business is B2C direct sales, the segment in which JD.com holds the No. 1 spot. Online direct sales totaled ¥238 billion in 2016, accounting for 91% of net sales generated.
B2C Outperforming C2C
We expect China’s B2C e-commerce market to continue its robust growth.GMV of the B2C market is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 22% over 2015–2019, according to iResearch, outpacing that of the C2C market at 12%. The online shopping market will continue to shift toward B2C, which is forecast to reach 60.4% in 2019, from 52.1% in 2015, also according to iResearch.
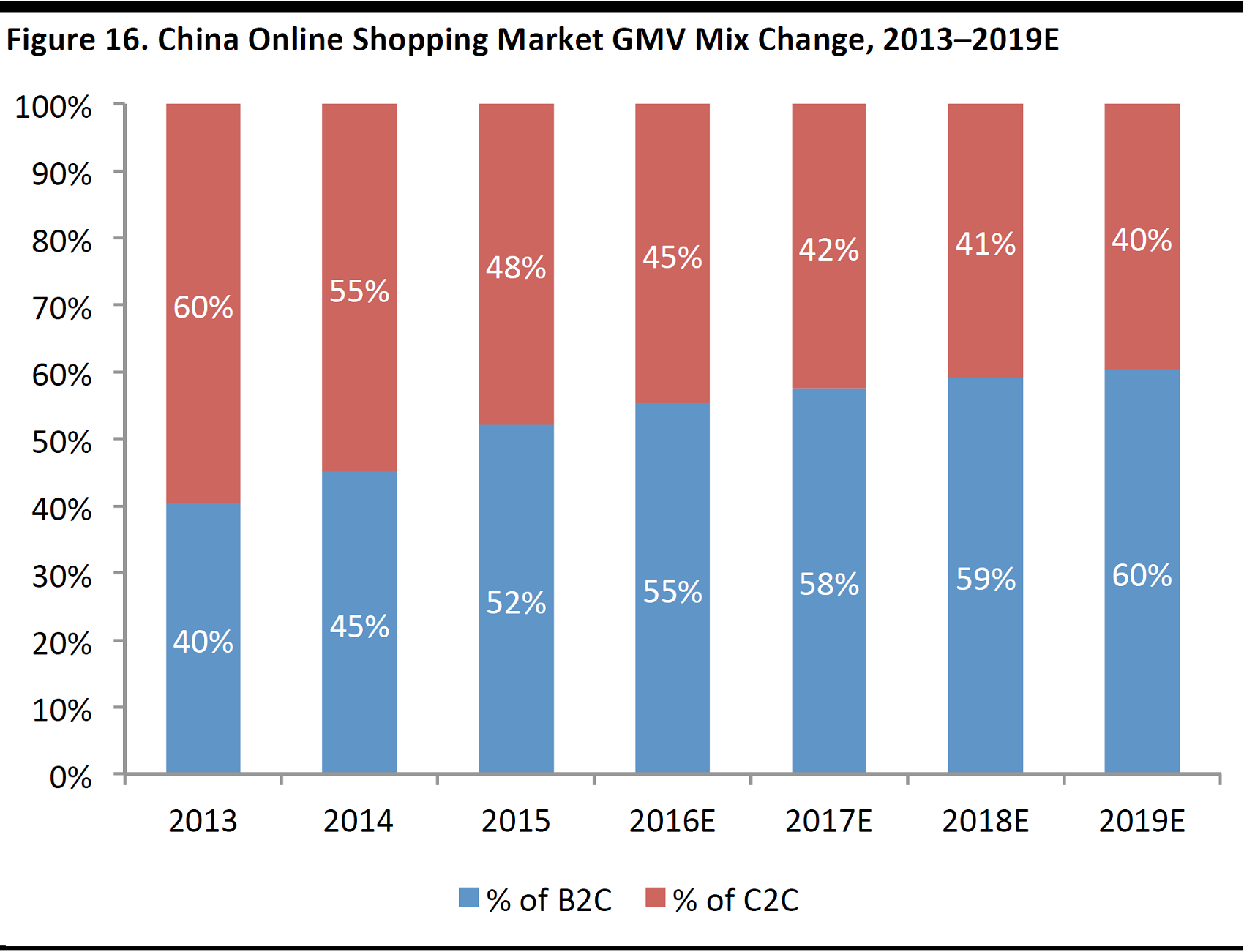
Source: iResearch
Counterfeit Products Are More of an Issue for C2C than B2C
C2C platforms have always been plagued by the problem of counterfeits, due to the lack of control over product quality sold by participating merchants. The increasing sophistication of the Chinese consumer, coupled with pressure from the international community, necessitates that B2C e-commerce platforms have greater control over product quality, thus mitigating the sale of counterfeits. JD.com had to shut down its C2C platform Paipai.com after it failed to curb counterfeit issues, and instead it has focused all of its resources on direct sales and building a quality B2C marketplace.
The Rise of Cross-Border E-Commerce
JD.com is exposed to cross-border e-commerce (CBEC) through JD.com Worldwide, a leading CBEC platform which offers a broad product selection, competitive pricing and greater convenience to Chinese consumers who want to purchase overseas products online. Furthermore, because JD Worldwide has zero tolerance for fakes, consumers feel more protected from counterfeit products.
CBEC Imports on the Rise
CBEC has grown rapidly and will likely drive the next leg of e-commerce growth in China. China’s CBEC imports, reached $31.9 billion in 2015, and are forecast to reach $76.4 billion in2018, according to iResearch.
Drivers of CBEC Growth
The rise in CBEC has mainly been driven by the rising standards of living in China, which has led to greater demand for quality foreign products and international brands.
In addition, the Chinese authorities have put in place supportive measures to reduce illegal gray-market imports and simplified the procedures for cross-border online purchases, such as introducing a new import duty regime that established specific trade zones and expedited customs clearance. For example, only registered international infant milk formula can be imported through CBEC channels after January 1, 2018, thus reducing gray-market products from entering China.
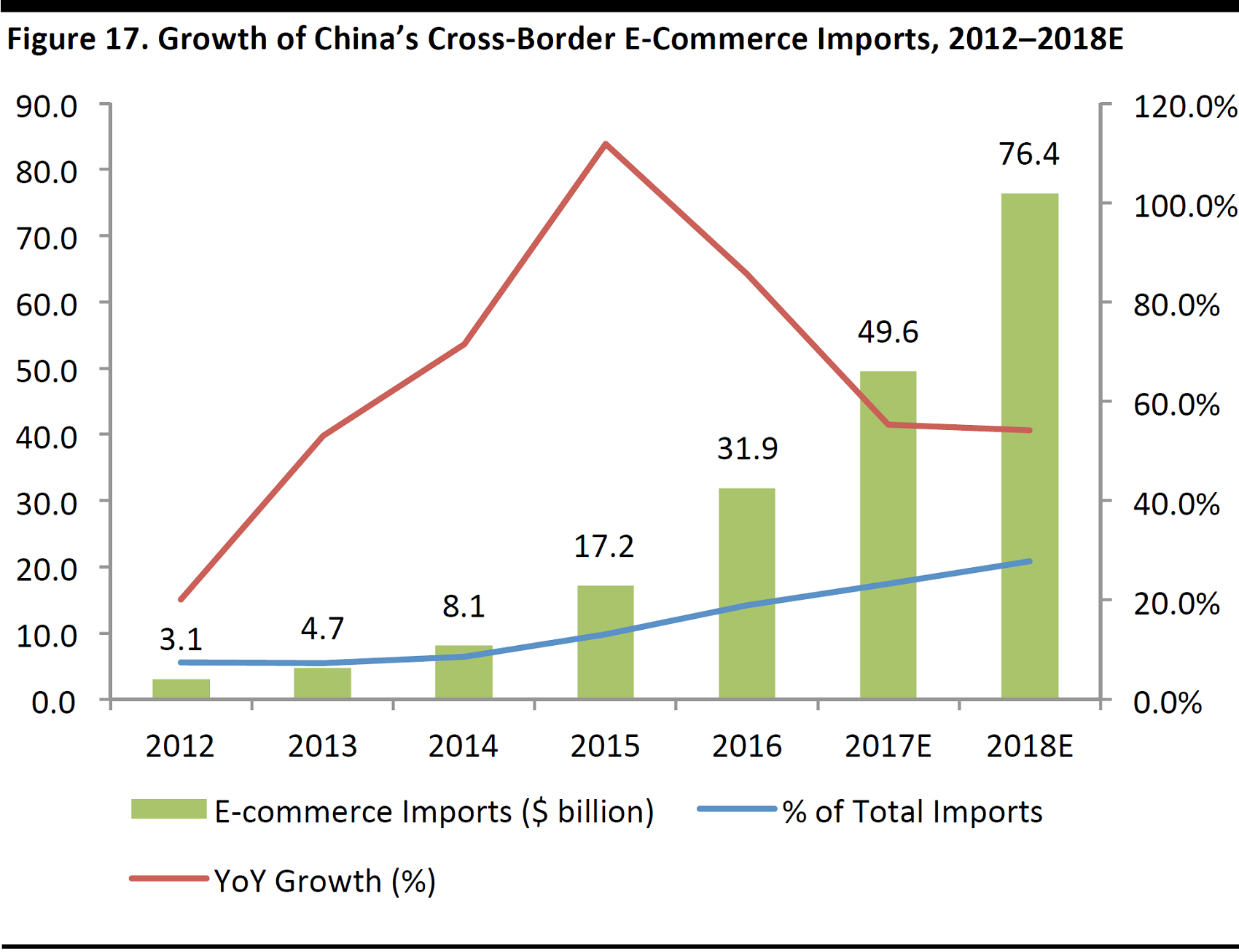
Source: iResearch/FGRT
China’s Transition to Mobile Commerce
JD.com’s strategic partnership with Tencent opened up access to WeChat’s enormous based of mobile users. JD.com is experiencing strong mobile commerce growth momentum—fulfilled orders placed via mobile accounted for 81% of total fulfilled orders in 1Q17, almost double the42% in 1Q15.
Strong Growth of Mobile Commerce in China
Mobile shopping accounted for over60% of total online shopping transactions in 2016, up from 33.8% in 2014, according to iResearch, and it is estimated that the number of mobile commerce users will increase to 5.1 billion in 2018from 2.4 billion in 2014. The sales generated from mobile commerce are estimated to grow at a CAGR of 24.2% between 2017 and 2019, giving e-commerce players a solid playing field.
Advantages of mobile: An e-commerce platform can use mobile to increase user stickiness with targeted advertising and in-app purchases, which can lead to higher retention rates. Mobile also offers e-commerce platforms data that paints a more comprehensive picture of individual consumer’s spending behavior compared to desktop users, which is key to further unlocking potential sales opportunities.
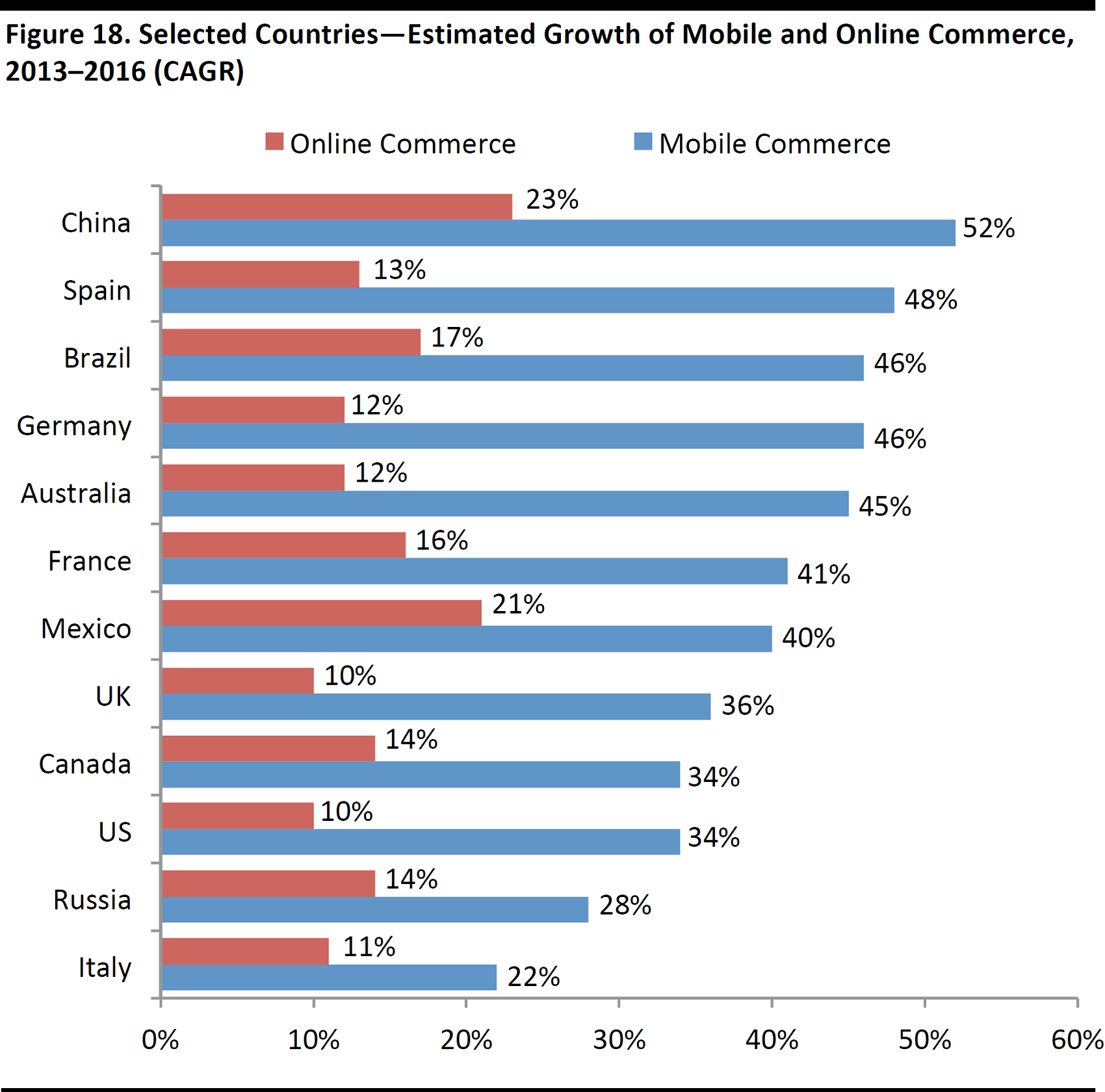
Source: PayPal/FGRT
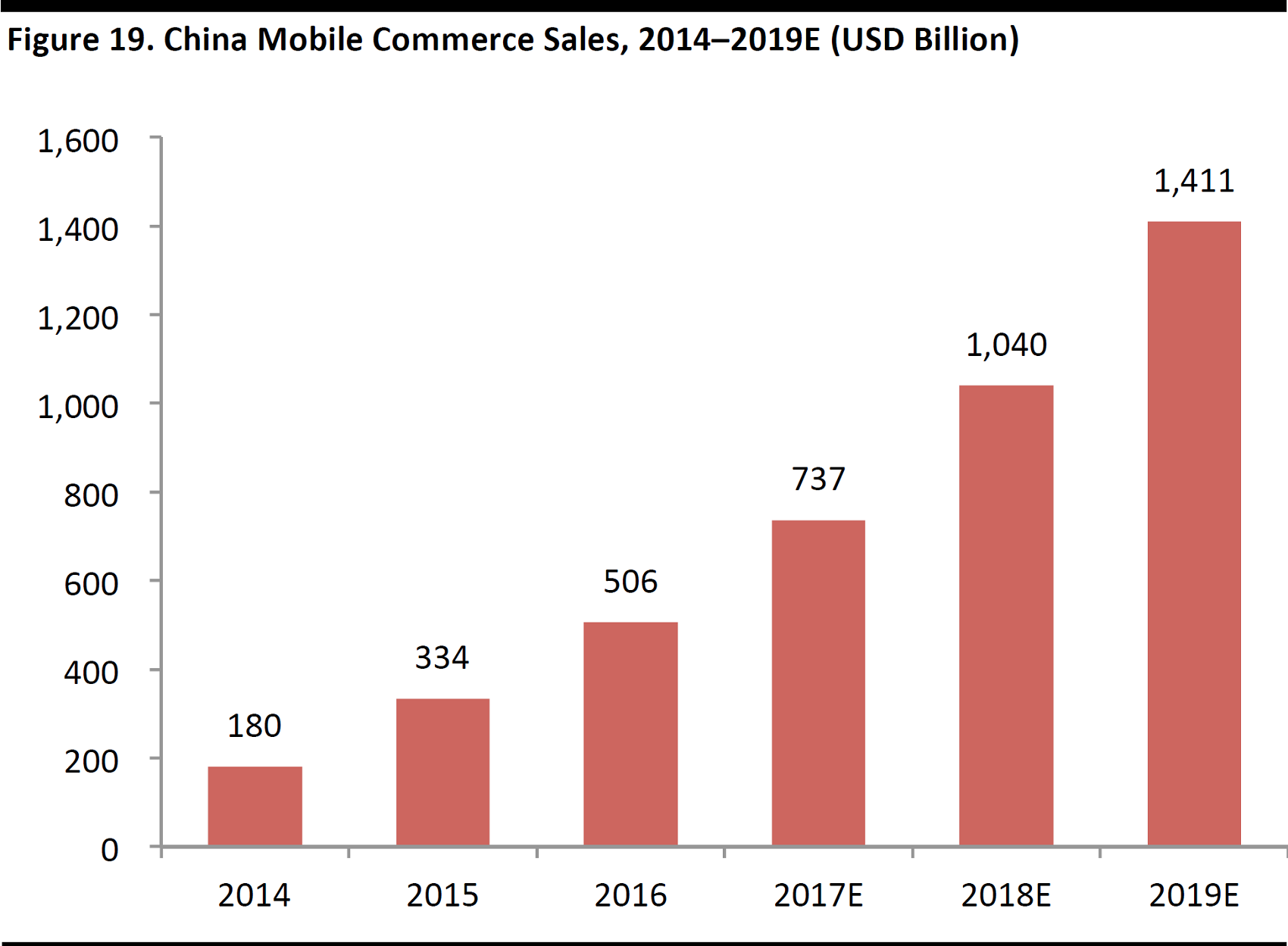
Source: Statista/FGRT
Chinese Online Shoppers Are Becoming Increasingly Sophisticated
Through its direct sales platform, JD.com can better guarantee product quality and can also offer convenient delivery options through its best-in-class, in-house, nationwide fulfillment infrastructure. In mid-2017, it launched a new luxury delivery service—White Glove Service—for selected luxury goods sold on its platform.
Emerging Trends
There has been a shift in Chinese online consumers’ preference to more of a focus on product and service quality, user experience and convenience. In the past, price was typically the differentiating factor driving purchase decisions, as Chinese consumers are price-sensitive.

Source: zol.com.cn
The Rise in Disposable Incomes Leads to Higher Sophistication
Annual disposable income per capita in China reached ¥23,821 ($3,469) in 2016, up 6.3% year over year. On the back of improving standards of living, especially for urban Chinese, consumers are becoming more sophisticated and are now more focused on quality. They are also becoming more familiar with international brands, thus driving demand for overseas products.
Appendix
JD.com Key Milestones





























