Executive Summary
This is the second report of our Blockchain Mini-Series, in which we discuss the potential applications of blockchain technology in retail and supply-chain management. For a more detailed explanation of how blockchain technology works, you can refer to our report
Blockchain Technology: The World’s Game Changer?, and for our views on the impact of the rise of cryptocurrencies on the retail industry, you can read our first report of the
Blockchain Mini-Series: Cryptocurrencies.
Blockchain is a distributed and decentralized database that keeps digital records of historical transactions. We believe this new technology has the potential to revamp legacy supply-chain management systems and streamline transaction processes, while at the same time, improve supply-chain visibility.
The chart below summarizes some of the existing challenges of supply-chain management and how blockchain can help solve these issues.
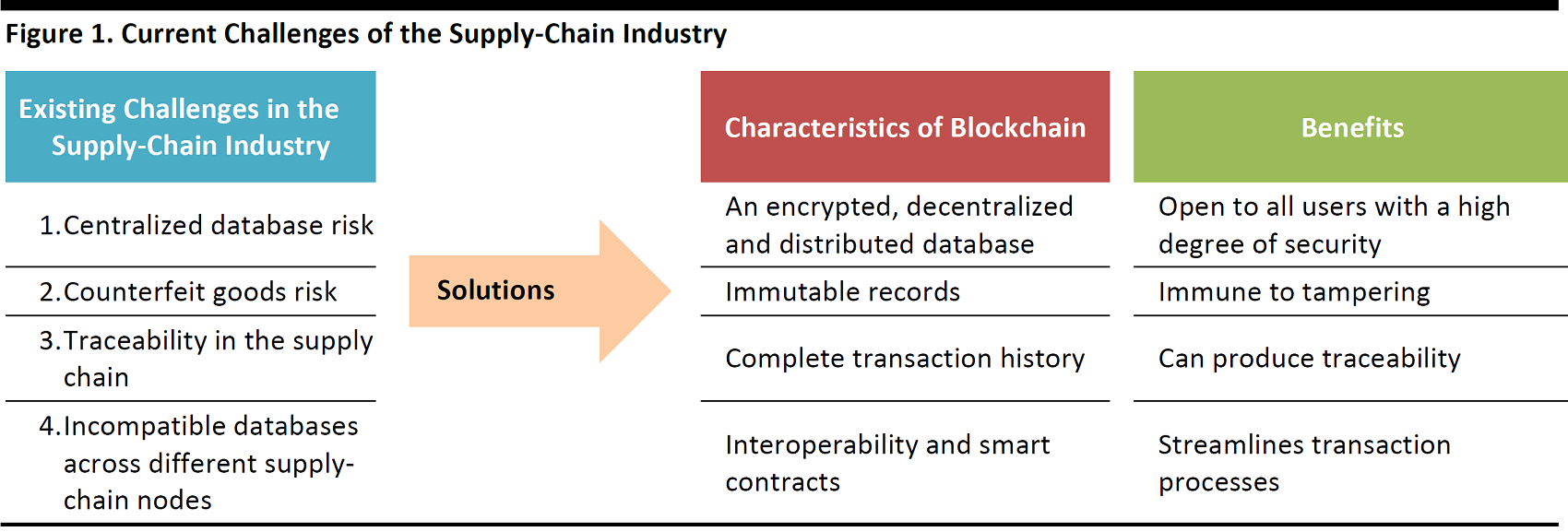
Source: FGRT
The first question a company needs to consider before implementing blockchain technology is: does its business need the technology? Since blockchain offers a new method of storing information which is accessible by multiple parties, the technology is naturally suitable for businesses that operate in a network environment, which requires both security and identity management. At the same time, existing database-management solutions could work just as well for businesses that do not require such sophisticated data processing.
That being said, we believe blockchain technology will be the key driving force behind improvements in how supply chains handle transaction data. However, we see this as having more of a mid-to-long-term impact on the industry rather than in the immediate future.
Introduction
Blockchain creates a secure ledger that stores every transaction record that occurs in a decentralized network. The technology eliminates the need for third-party verification and enables real-time information exchange.
Demand for transparency in production is increasing in the retail industry. Before reaching the end consumer, consumer goods have already travelled through a vast network of suppliers, producers, logistics providers, distributors and retailers, but in many cases, the processes in between are not visible to all participants.
Industry players still suffer from low visibility when it comes to supply-chain management, in addition to facing the challenges iin verifying the authenticity of products or raw materials. A lack of traceability, insecure transaction records and incompatible databases across different parties are the key pain points in the industry.
Blockchain offers an accurate and immutable database that allows users to trace and verify the origins of products, attributes and ownership. Hence, the technology can increase visibility in supply-chain management as well as strengthen the security of databases.
In this report, we take a closer look at the different blockchain applications. We identify the current challenges caused by legacy data systems and analyze how blockchain technology can solve these issues. We then discuss the challenges of adopting the technology, and finally, we introduce several notable startups to illustrate its different use cases.
Current Challenges of Legacy Data Systems
Challenge No.1: The Risks of Using a Centralized Database
Traditional tracking solutions are usually hosted in centralized databases with varying degrees of security. In some cases, these systems are vulnerable to cyberattacks, and in others, their records can be subject to tampering by agents acting in bad faith. Cybercrime is the largest concern, as we discuss in our
report on cybersecurity, in which we highlight the steady increase in the number of information-security incidents reported to US federal agencies.

Source: iStockphoto
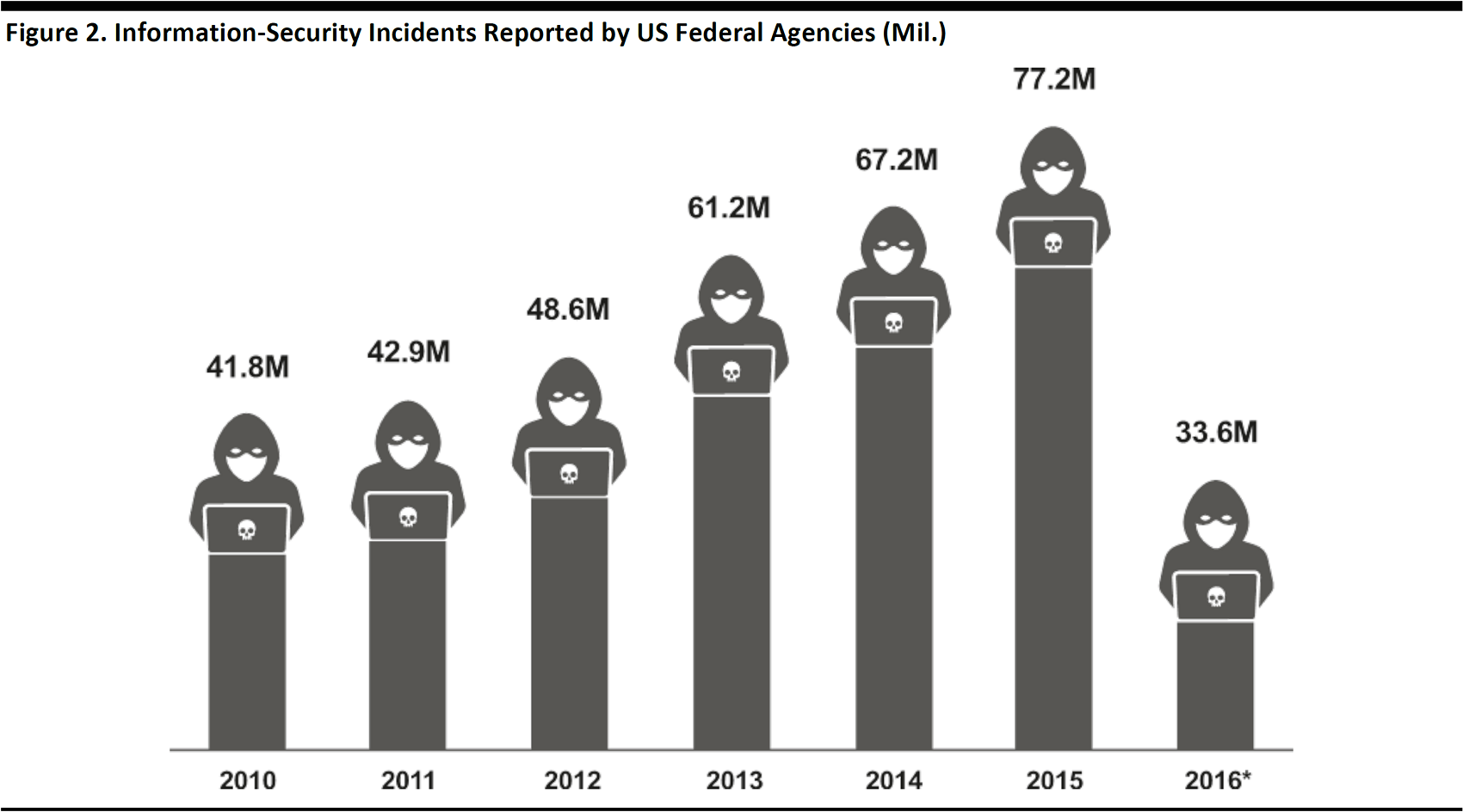
*Incident reporting requirements were revised in 2016 and agencies are no longer required to report non-cyber incidents or attempted scans
or probes of agency networks.
Source: US Government Accountability Office/US Office of Management and Budget
The Benefits of Using Blockchain Technology
A blockchain-based database is one that is fully decentralized and distributed. This means it is open to all participants, each of which is responsible for verifying the data as well as storing the transaction record. Since each user has a copy of the ledger, this minimizes the risk of a single point of failure.
The major advantage of blockchain cryptography is that the data encryption is practically impenetrable, i.e., impossible to break. Blockchain uses the SHA256 hash to encrypt data. A hash function is a computing operation which transforms input data of any size, to output data of a fixed size. The function will always produce a consistent output from a given input. It is statistically improbable to perform reverse engineering, not without the correct decryption key.
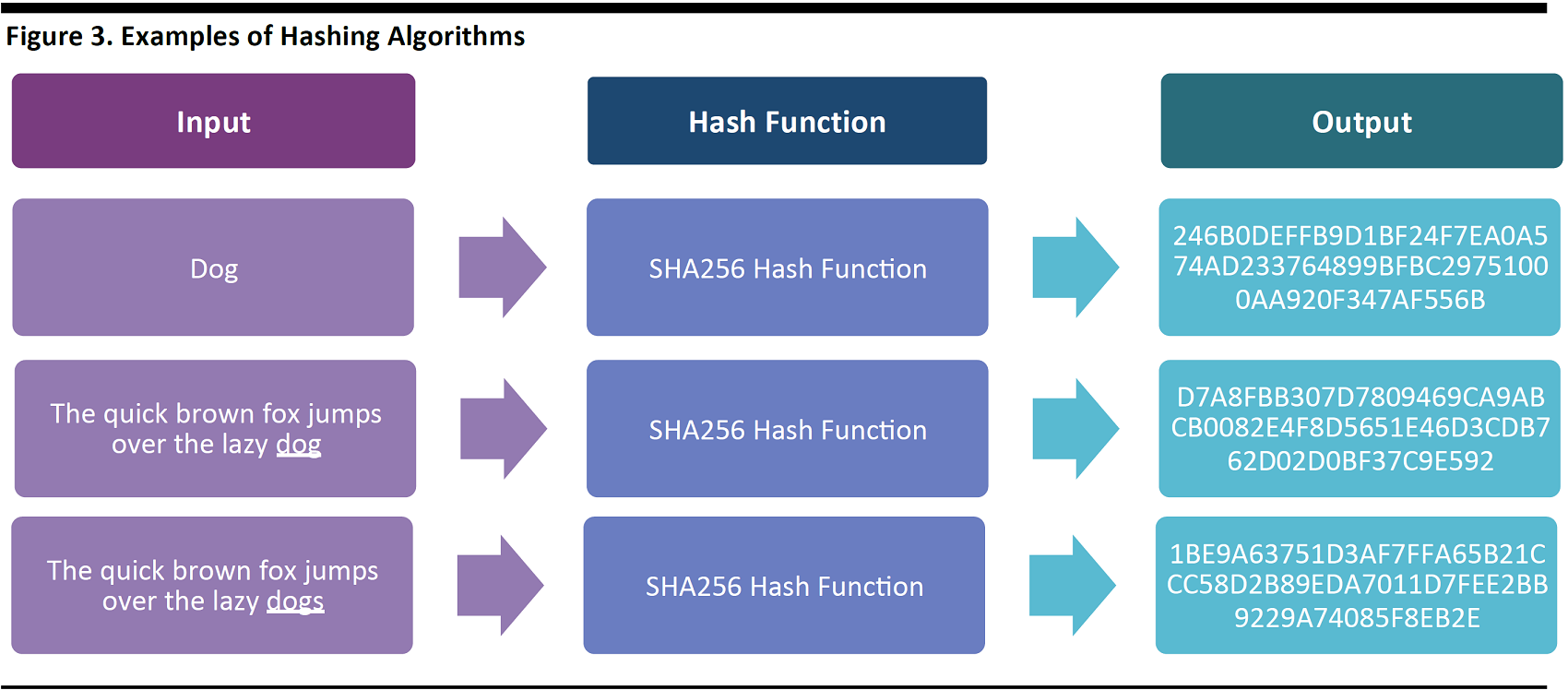
Source: FGRT
The hash function is an important element in cryptography, as it enables a secure method of data exchange, while ensuring the record is immune to tampering—both are key characteristics of blockchain.
Challenge No.2: Counterfeit Goods Risk
QR codes, UPC codes, serial numbers and bar codes are the most widely used identity systems. However, the level of security of these databases is considered weak, as they are not tamper-evident—which describes a device or process that makes unauthorized access to the protected object easily detected—and can be cloned or mimicked easily for counterfeit products and packages.

Source: iStockphoto
Luxury brands suffer from the loss of potential sales due to counterfeit products which are illegally traded in the market. According to a new report by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and the EU’s Intellectual Property Office issued in 2013, the total value of global trade in fake goods is estimated at nearly $500 billion in a year. Consumers usually find it difficult to verify the authenticity of a product if sold by a third party because the record of production is nontransparent and there are limited ways to guarantee authenticity.
The Benefits of Using Blockchain Technology
Decentralized ledgers can enable identity verification and authentication. By pairing hardware chips with blockchain technology, a digital history can be attributed to physical products, which allows users to trace and verify their origins, attributes and ownership. Blockchain technology can allow retailers and consumers to validate a product’s provenance and guarantee authenticity, helping identify counterfeit goods and reinforce the value of premium products.
End-consumers gain visibility into the entire production history, which tracks sub-assemblies, parts and raw materials used to make the finished product.
Using bitcoin to track wine bottles: The chart below illustrates an example on how bitcoin, a cryptocurrency based on blockchain technology, can help track wine bottles along the supply chain.
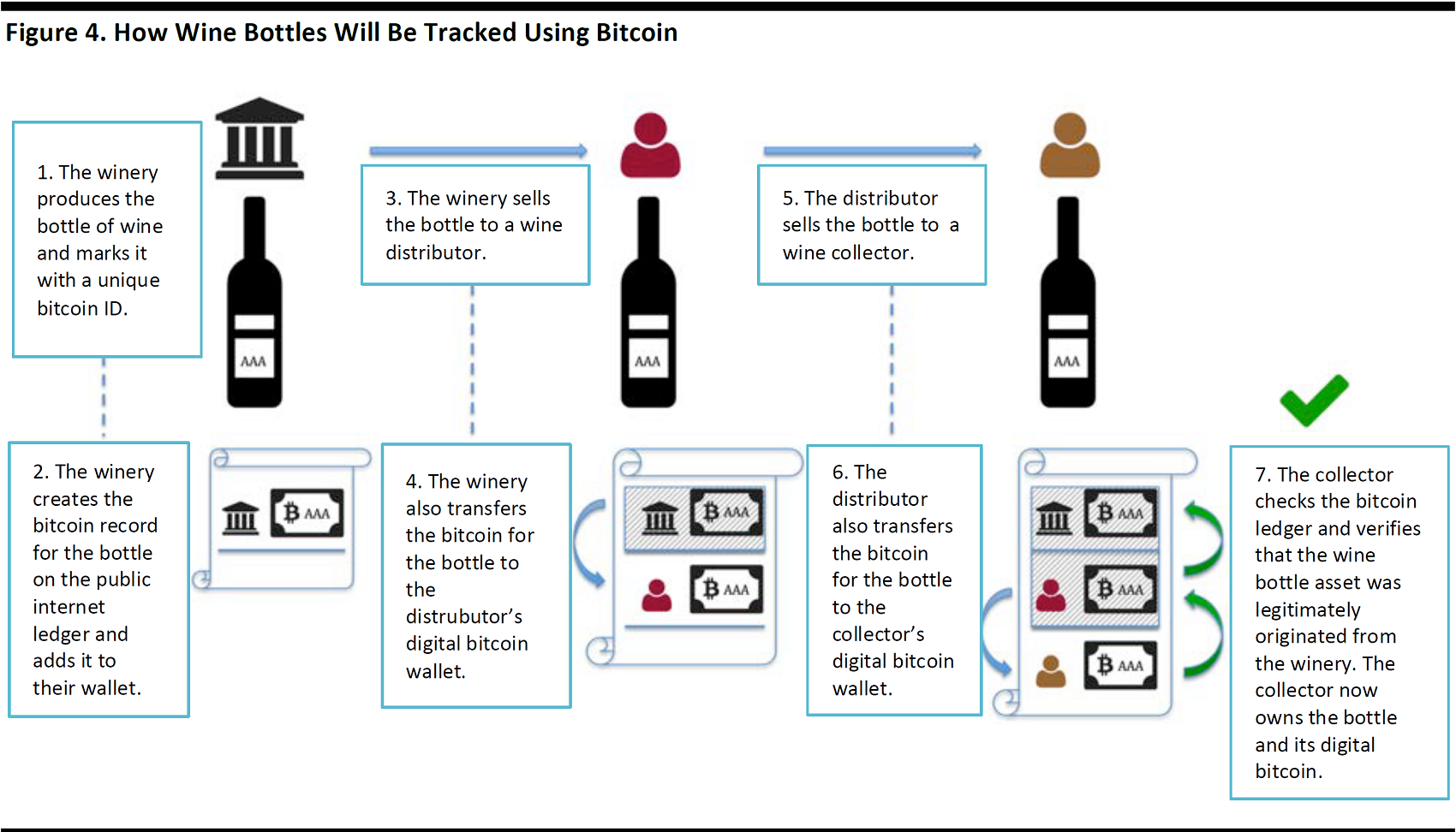
Source: Vinfolio
Using NFC chips to track prescription drugs: Another example is Chronicled, a blockchain and Internet-of-Things (IoT) technology company, which combines near-field communication (NFC) chips with seals and blockchain technology to track and secure prescription drugs. The seal contains secure information about the contents of a prescription bottle, registering the information on a blockchain, while also recording the registering party and location data. This tamper-proof technology solution adds a key layer of visibility, ensuring patients and physicians that the medication is authentic.
Using blockchain to tackle food fraud: Alibaba joined forces with AusPost, Blackmores and PwC to explore the use of blockchain technology to tackle food fraud. Because the ledger is immune to tampering, the blockchain technology creates better transparency between buyers and sellers as shipments are tracked in real-time, improves security and reduces the risk of fraud. The technology will also allow the company to pinpoint the exact source of a particular package that has been sold, so a product that is subject to a recall can be identified easily.
Source: Alibaba.com
Challenge No.3: The Lack of Traceability in the Supply Chain
Four years ago, a deadly fire incident at a factory in Bangladesh exposed that the factory had been supplying clothing to Walmart without having been authorized as a subcontractor. Rajan Kamalanathan, Walmart’s Vice President of Ethical Sourcing at that time, said the company’s current controls could only go so far in preventing and controlling subcontracting in its apparel supply chain.
Source: Walmart.com
Tracing raw materials is another pain point when it comes to supply-chain visibility. The ability to trace back the origin of the raw materials is a crucial feature for suppliers and retailers in order to guarantee the safety of consumers and the sustainability of the production process. It is particularly important in fields such as medicine and luxury goods, where products must meet very strict standards, or with precious metals and jewels.
The Benefits of Using Blockchain Technology
When blockchain technology is applied to supply-chain management, it addresses the traceability issues by enhancing the transparency and solving the problem of trust. Transaction records on a blockchain are immutable and can be traced back to their origins with certainty. In a supply-chain context, using blockchain technology offers traceability to track physical value in the supply chain. Enterprises that use blockchain technology to log the steps in the production and sourcing of products gain visibility across the entire supply-chain ecosystem, enabling agility and improving planning capabilities.
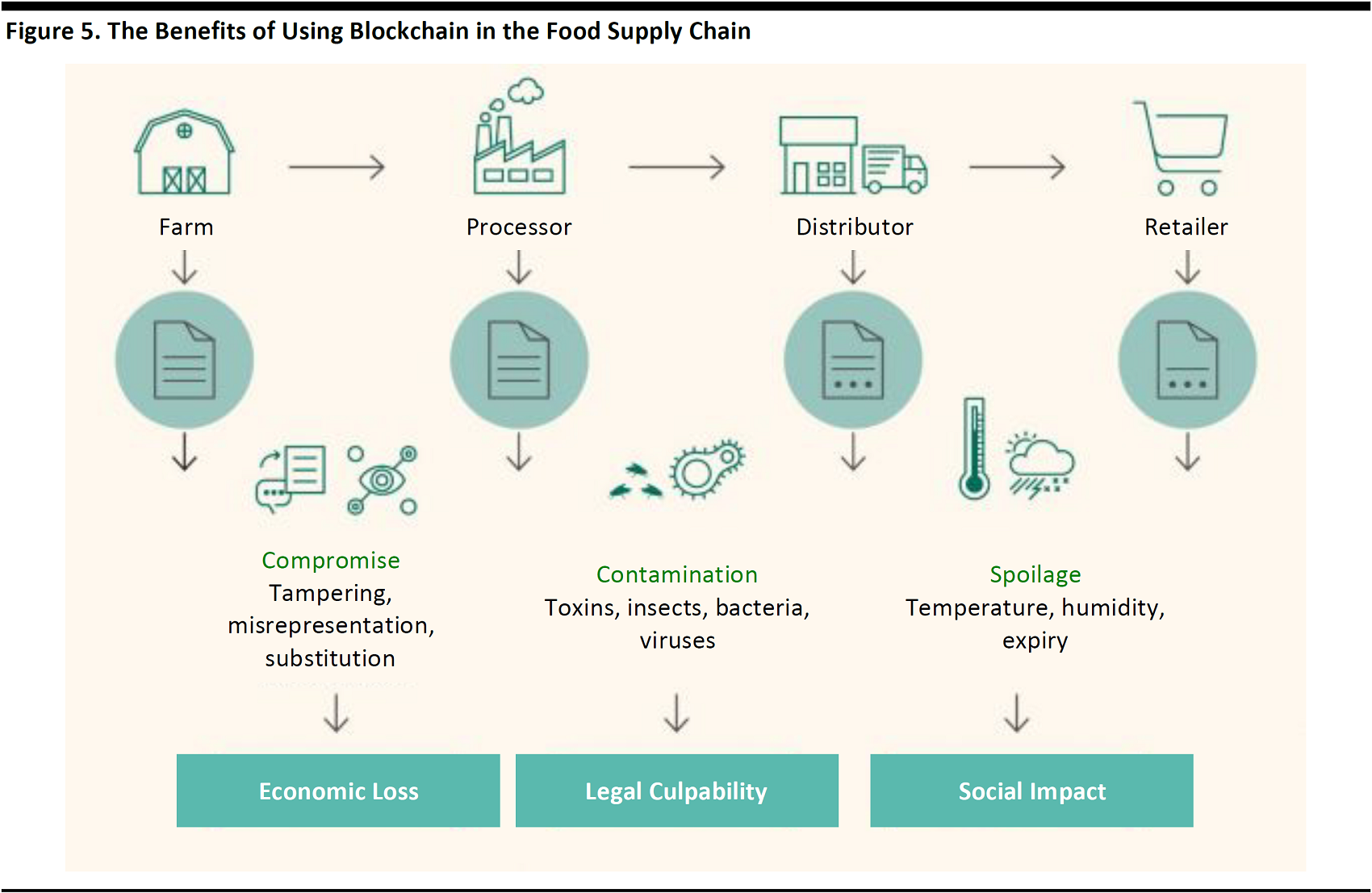
Source: IBM
Walmart using blockchain for logistics: Blockchain technology can also be used for logistics. For example, Walmart recently filed a patent for a drone-delivery tracking system that integrates blockchain technology. In this case, the blockchain would hold certain information such as the location, supply-chain transition, authentication of the courier and customer, and temperature of the container and product. In simple terms, Walmart aims to leverage blockchain technology to enhance the security of unmanned drone delivery, as well as the supporting authentication system.
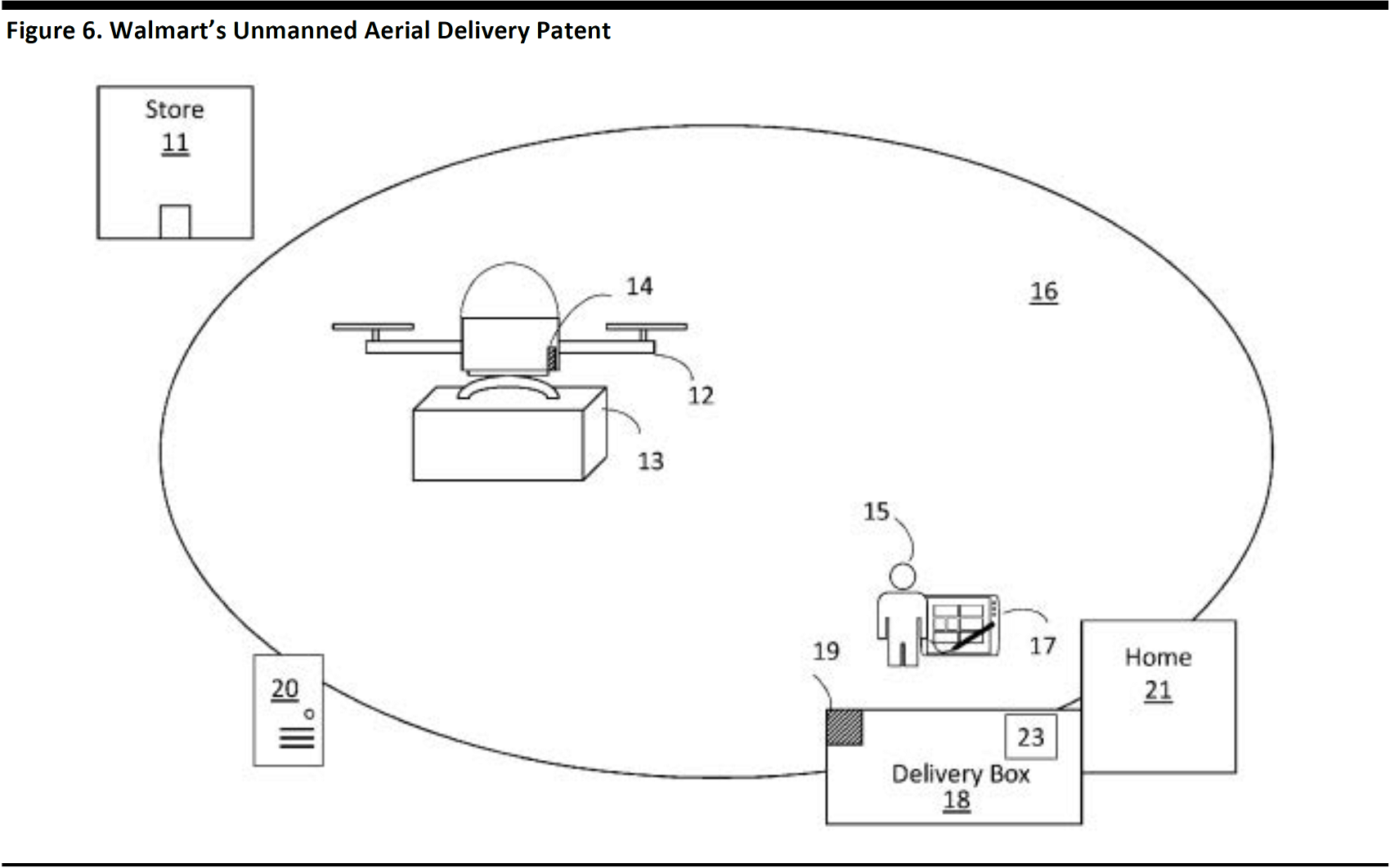
Source: United States Patent and Trademark Office
Challenge No.4: Incompatible Data Systems
Complex supply chains involve a large number of participants around the world, which requires a significant amount of paperwork and processing time at the various stages of shipping and receiving items. Because the data systems used by each party along the supply chain are not necessarily integrated or compatible, this can result in erroneous data and inefficiency.
The Benefits of Using Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology can streamline processes in supply-chain management, while adding greater intelligence along the way. By combining smart contracts—computer protocols built on top of blockchains, and ledgers—blockchain applications can automatically execute contracts between parties once certain criteria have been met.
Smart contracts built on top of blockchain technology can facilitate supply-chain operations and the transactions between shippers and receivers, as well as between third-party insurance and financing parties. Smart contracts eliminate the need for the middleman brokering the relationship between two transacting parties. For example, when a retailer confirms receipt of a shipment on the blockchain, a smart contract might automatically initiate payment to the appropriate supplier. Another example is a smart contract could automatically trigger the execution of an insurance policy if a sensor detects anomalies in a storage warehouse. Smart contracts could also be used to make procurement decisions based on a defined set of attributes, thus streamlining the procurement process.
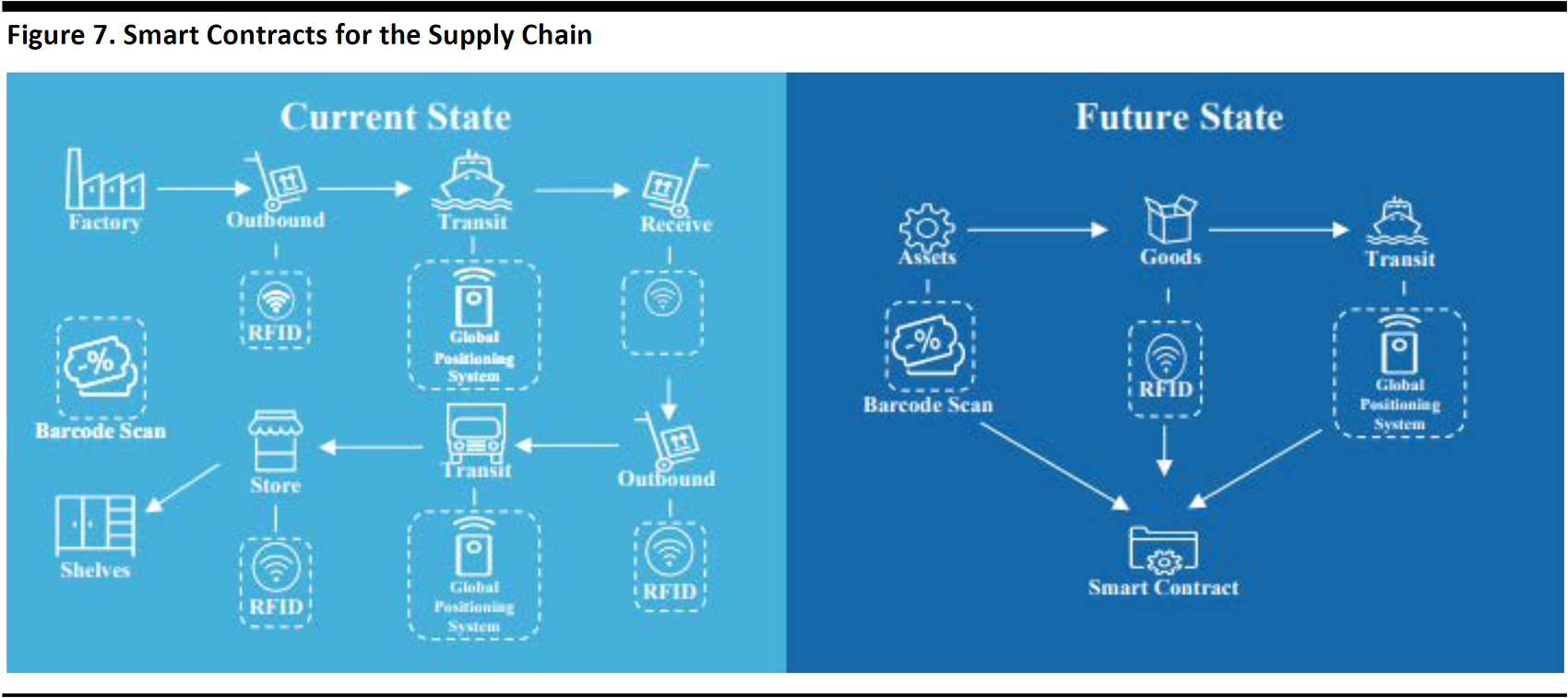
Source: Chamber of Digital Commerce
In March 2017, IBM announced a partnership with Maersk to establish a project based on blockchain technology for the freight industry. The two companies will work together to manage, digitalize and track shipping transactions. Accord to a study by IBM, the cost of processing documents and information for a container shipment is estimated at more than twice the cost of physical transportation. Deploying blockchain-based data management should significantly reduce delays and fraud, and hence achieve savings in freight management. The graph below demonstrates how shipping flowers can be digitized using blockchain technology.
Source: Maersk.com
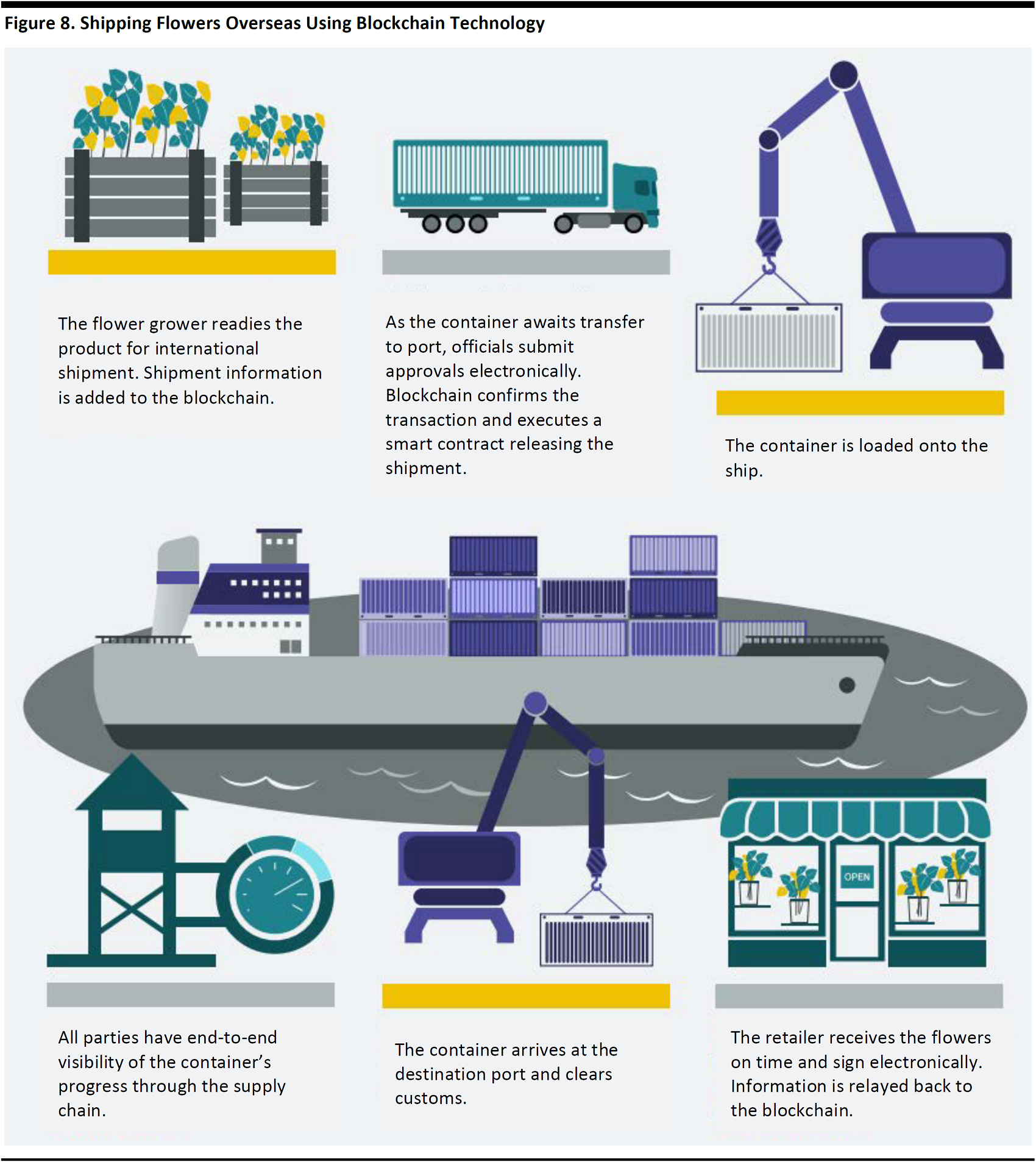
Source: IBM
How to Adopt Blockchain
The first question a company needs to consider before implementing blockchain technology is: does its business need the technology? Since blockchain offers a new method of storing information which is accessible by multiple parties, the technology is naturally suitable for businesses that operate in a network environment, which requires both security and identity management. At the same time, existing database-management solutions could work just as well for businesses that do not require such sophisticated data processing. The following flow chart by Bart Suichies, a blockchain tech program manager in SICPA, a privately-owned company providing secured identification, traceability and authentication solutions and services, illustrates a sample decision-making process for a company exploring to adopt blockchain solutions.
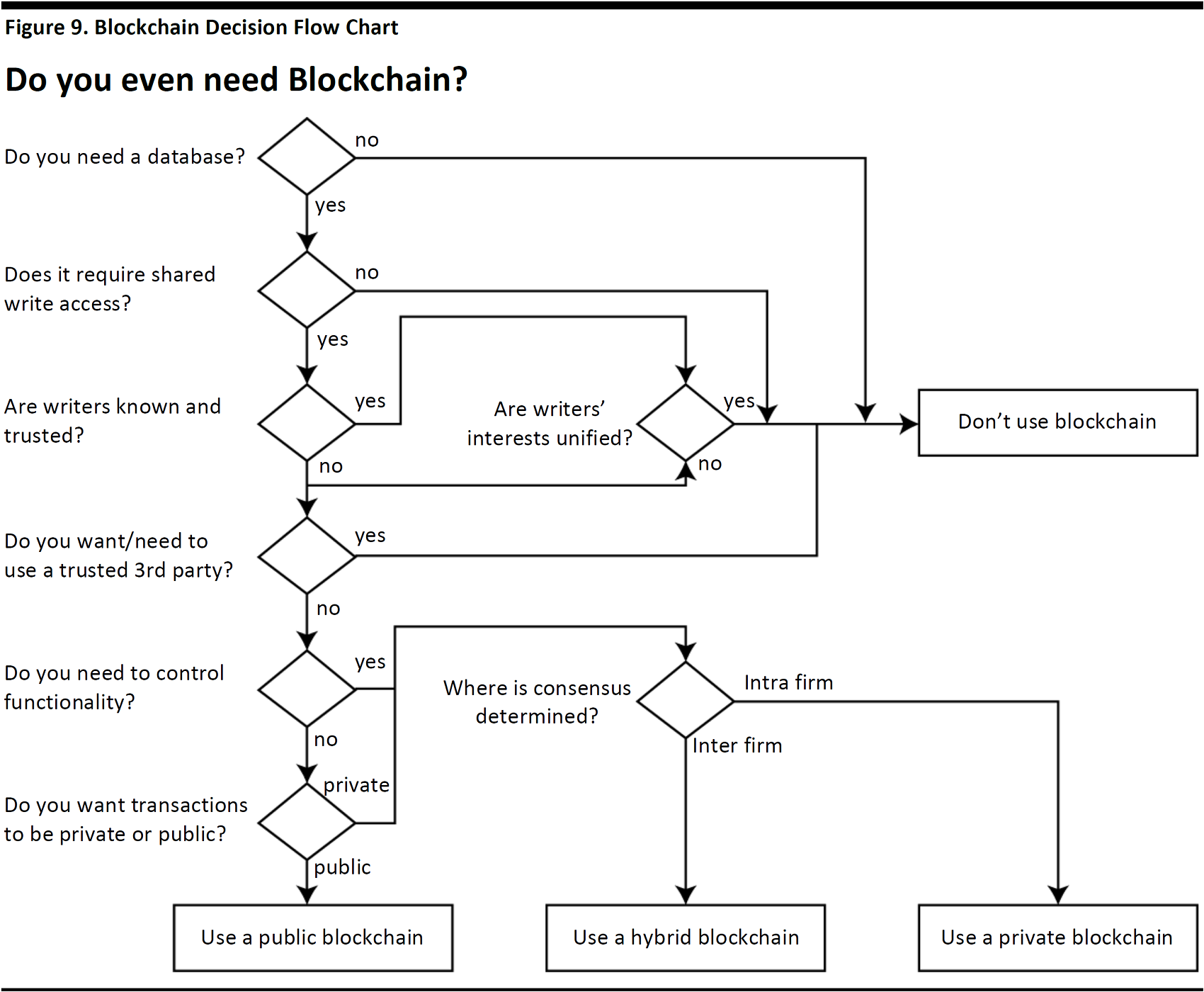
Source: Medium
Because of the complexities in the adoption of the technology, new consultancies which focus on blockchain implementation have emerged. For example, Chainsmiths, headquartered in Dublin, Ireland, provides consulting services such as blockchain education, research and development, advice and strategy.
For corporations who wish to participate in developing blockchains in order to better suit their needs, joining Enterprise Ethereum Alliance is a good starting point. The Enterprise Ethereum Alliance was established in March 2017 with a plan to standardize ethereum—an open-source, public, blockchain-based distributed computing platform—for business use cases. The alliance will collectively develop industry standards and facilitate collaboration with its member base. It is open to any members of the ethereum community who wish to participate.
Challenges in Adopting Blockchain Technology
Since blockchain technology is still in its infancy stage, companies will likely face significant adoption challenges, which is why we believe it will have a mid- to long-term impact on the industry rather than in the immediate future. Some of the challenges include:
Uncertainties in development: Blockchain technology is still in its early stage of development. There are inevitable uncertainties around the cost and design of the network infrastructure.
Interoperability between new and legacy systems: Legacy infrastructures will be the main obstacle that slows down the adoption of blockchain for many businesses, as blockchain solutions require significant changes to existing systems. This is coupled with the challenges of technical understanding—the implementation of decentralized databases likely falls outside of the traditional IT development skillset.
Scalability: There are lots of startups trying to create their own blockchains, which could create silos and walled gardens. As a result, the Enterprise Ethereum Alliance is trying to create a set of standard blockchain protocols to fit business needs. However, the initiative still has a long way to go to achieve its mandate.
Notable Startups

Chronicled is a blockchain and IoT technology company which focuses on securely linking physical properties with blockchain technology, such as authentication, e-commerce, provenance, supply chain and finance-related products. Chronicled adds identity microchips (Bluetooth Low Energy or NFC), which are tamper-evident and cryptographic sealed, to physical products and packaging. The cryptographic chip in the seal is then registered on the blockchain, creating an immutable digital record for each physical product or unit of packaging on the blockchain. The microchip can sign messages and transactions to create a time-stamped history of proximity, possession and provenance. Applications include: luxury product authentication, pharmaceuticals tracking, supply-chain provenance tracking, proximity-based commerce, physical product affiliate models, IoT interoperability, per-item insurance, military applications and fine art.
Source: Chronicled.com

Source: Chronicled
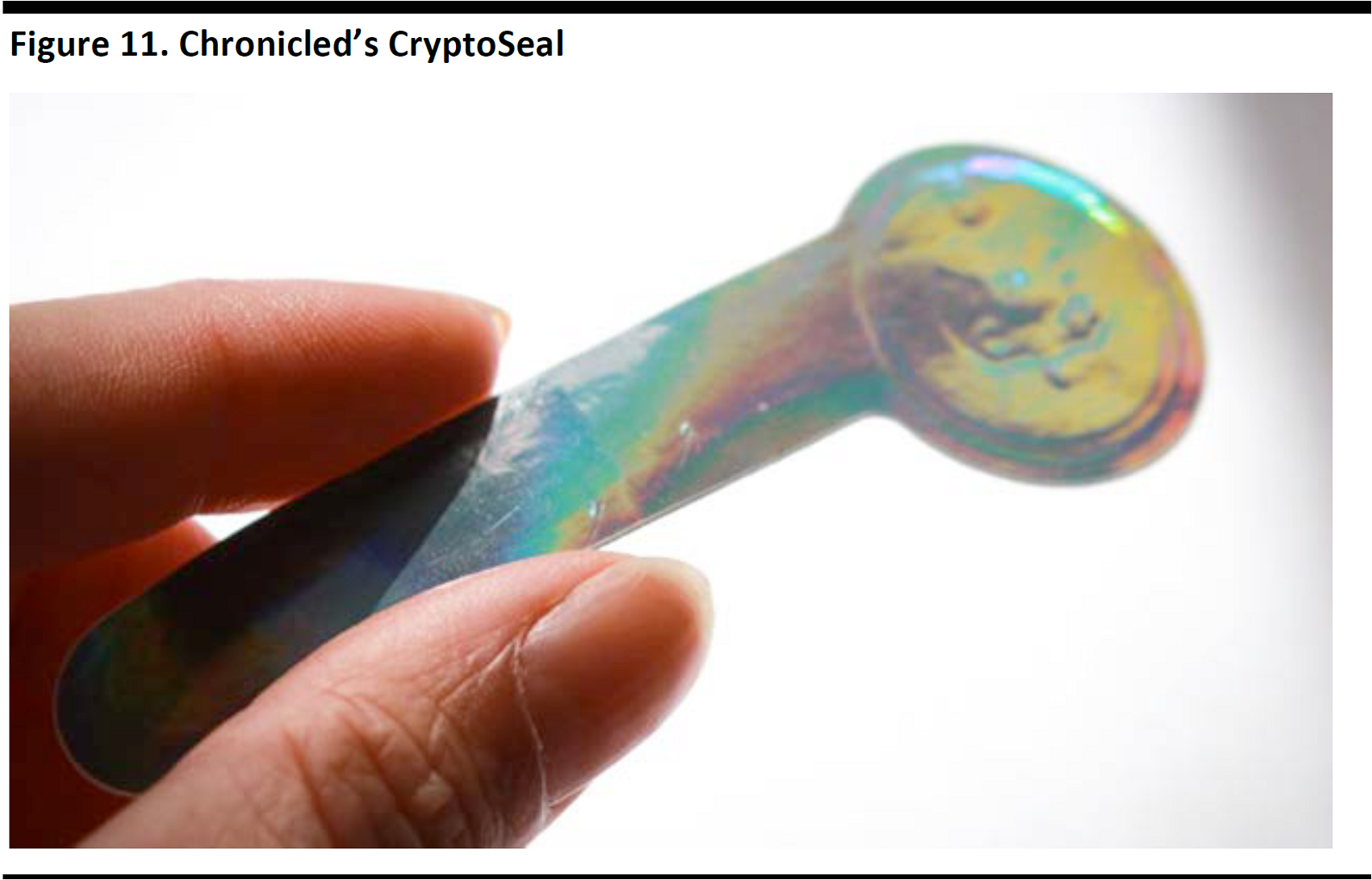

Source: Chronicled

Hijro is a marketplace for trade assets which optimizes working capital for businesses, and streamlines supply-chain operations by connecting suppliers and buyers in supply chains. Hijro leverages blockchain to avoid fraud and multi-financing, as well as to improve the visibility of transactions, documents and asset ownership for both parties. Suppliers can get paid earlier by selling their invoices on Hijro’s platform, while buyers can purchase trade assets at a lower rate.
Source: Hijro.com

ShoCard is built on a public blockchain that focuses on protecting consumer privacy. For example, ShoCard stores users’ credit scored which can be verified by banks and other associated institutions. Users can upload their travel documents, which are encrypted and hashed on the blockchain. Airline terminals, which are connected to ShoCard’s system, can verify the identity of a passenger.
Source: Shocard.com

Skuchain leverages the blockchain attributes of cryptography, immutability and decentralized trust to allow multiple parties within a supply-chain ecosystem to work with each other in a trustable and secure manner. Skuchain’s solution can provide real-time tracking of items and automated contract execution, which is decentralized among parties in the supply chain. However, control of the operation of the network remains within a set of entities designated by the organization. While this technology unlocks previously unattainable visibility into the supply chain, it allows for the selective obfuscation of sensitive information such as credit quality, purchase commitments and deep tier sources without sacrificing the level of insight the organization requires.

Source: Skuchain.com

WAVE connects all members of the supply chain—carriers, banks, forwarders, traders, etc.—to a decentralized network, and allow them to directly exchange documents and data. WAVE’s application can ensure that all parties can see, transfer and transmit shipping documents and other original trade documentation through a secure decentralized network. The platform eliminates many of the inefficiencies in international trade and could, therefore, speed up trade transactions and reduce costs for companies.
Source: Wavebl.com
Conclusion
Establishing a blockchain network can drive up efficiencies and enhance visibility across the entire supply chain, thanks to the benefits of a decentralized, distributed and secure database.
We believe the technology will be the key driving force behind improvements in how supply chains handle transaction data. Yet, most companies are in the exploratory phases of blockchain implementation. The mass adoption of this technology, in our view, is still far off, however, companies would be wise to start preparing for the shift today.


















 Hijro is a marketplace for trade assets which optimizes working capital for businesses, and streamlines supply-chain operations by connecting suppliers and buyers in supply chains. Hijro leverages blockchain to avoid fraud and multi-financing, as well as to improve the visibility of transactions, documents and asset ownership for both parties. Suppliers can get paid earlier by selling their invoices on Hijro’s platform, while buyers can purchase trade assets at a lower rate.
Hijro is a marketplace for trade assets which optimizes working capital for businesses, and streamlines supply-chain operations by connecting suppliers and buyers in supply chains. Hijro leverages blockchain to avoid fraud and multi-financing, as well as to improve the visibility of transactions, documents and asset ownership for both parties. Suppliers can get paid earlier by selling their invoices on Hijro’s platform, while buyers can purchase trade assets at a lower rate.

 ShoCard is built on a public blockchain that focuses on protecting consumer privacy. For example, ShoCard stores users’ credit scored which can be verified by banks and other associated institutions. Users can upload their travel documents, which are encrypted and hashed on the blockchain. Airline terminals, which are connected to ShoCard’s system, can verify the identity of a passenger.
ShoCard is built on a public blockchain that focuses on protecting consumer privacy. For example, ShoCard stores users’ credit scored which can be verified by banks and other associated institutions. Users can upload their travel documents, which are encrypted and hashed on the blockchain. Airline terminals, which are connected to ShoCard’s system, can verify the identity of a passenger.

 Skuchain leverages the blockchain attributes of cryptography, immutability and decentralized trust to allow multiple parties within a supply-chain ecosystem to work with each other in a trustable and secure manner. Skuchain’s solution can provide real-time tracking of items and automated contract execution, which is decentralized among parties in the supply chain. However, control of the operation of the network remains within a set of entities designated by the organization. While this technology unlocks previously unattainable visibility into the supply chain, it allows for the selective obfuscation of sensitive information such as credit quality, purchase commitments and deep tier sources without sacrificing the level of insight the organization requires.
Skuchain leverages the blockchain attributes of cryptography, immutability and decentralized trust to allow multiple parties within a supply-chain ecosystem to work with each other in a trustable and secure manner. Skuchain’s solution can provide real-time tracking of items and automated contract execution, which is decentralized among parties in the supply chain. However, control of the operation of the network remains within a set of entities designated by the organization. While this technology unlocks previously unattainable visibility into the supply chain, it allows for the selective obfuscation of sensitive information such as credit quality, purchase commitments and deep tier sources without sacrificing the level of insight the organization requires.

 WAVE connects all members of the supply chain—carriers, banks, forwarders, traders, etc.—to a decentralized network, and allow them to directly exchange documents and data. WAVE’s application can ensure that all parties can see, transfer and transmit shipping documents and other original trade documentation through a secure decentralized network. The platform eliminates many of the inefficiencies in international trade and could, therefore, speed up trade transactions and reduce costs for companies.
WAVE connects all members of the supply chain—carriers, banks, forwarders, traders, etc.—to a decentralized network, and allow them to directly exchange documents and data. WAVE’s application can ensure that all parties can see, transfer and transmit shipping documents and other original trade documentation through a secure decentralized network. The platform eliminates many of the inefficiencies in international trade and could, therefore, speed up trade transactions and reduce costs for companies.
