Executive Summary
This is the first report of our Blockchain Mini-Series in which we discuss the latest trends in cryptocurrencies, the emerging applications of blockchain technology and the retail implications of blockchains. We believe that the blockchain technology which underlies cryptocurrencies has the potential to become the global standard for digital transactions in the coming decade and, as such, requires ongoing attention. For a more detailed explanation on how blockchain technology works in theory, please refer to our report
Blockchain Technology: The World’s Game Changer.
The definition of a cryptocurrency, according to Investopedia, is that it is a digital currency which uses encryption techniques to regulate the generation of units of currency and verify the transfer of funds, operating independently of a central bank.
Bitcoin is the first and most famous cryptocurrency, but there are now more than 1,000 different cryptocurrencies available in the market (latest count), with a total combined market capitalization of over $115 billion as of June 2017.
As cryptocurrencies become increasingly more commonplace, they have the potential to penetrate many aspects of commerce and our daily lives, from shopping online to raising funds for a cause or new creative project. In this sense, the adoption of cryptocurrencies should be of significant interest not only to financial institutions but to consumer-facing businesses at large, including retailers in particular. Knowing about and understanding cryptocurrencies is the first step on the journey of exploring this exciting concept brought about by the development of cryptography and advancements in network computing.
In the first part of this report, we take a closer look at the cryptocurrency landscape, the currencies’ value proposition, as well as the associated risks with owning, transacting and investing in them.
In the second part of this report, we analyze four popular cryptocurrencies—Bitcoin, Ether, Ripple XRP and Litecoin—looking at their key features, adoption and future outlook.

Introduction
Cryptocurrencies are built on top of blockchains. A blockchain is a new type of transaction database that enables multiple users to access and share data on a real-time basis without a central intermediary governing the interactions. A blockchain is often referred to as a decentralized distributed ledger.
The Pioneer—Bitcoin
Since its introduction in 2009, Bitcoin has continued to generate increasingly more attention year after year. This culminated in June 2017, when the price of Bitcoin reached an all-time high of $3,000. Following in its initial success, a plethora of new cryptocurrencies has emerged, and, at last count, there are now over1,000 digital currencies, according to coinmarketcap.
Three Major Types of Cryptocurrency
The three major types of cryptocurrency are categorized by their function:
- Digital gold: A digital currency that specializes in transactions and storing value, serving the same purpose as fiat money would, e.g., Bitcoin. (Note: Fiat money is currency that a government has declared to be legal tender, but is not backed by a physical commodity.)
- Platform coins: A specific currency that is used on a blockchain-based platform which facilitates the transactions within the platform, e.g., Ripple that allows Banks to transact on its platform, and Ethereum that allows users to program their own contract.
- Anonymous coins: Digital currencies focused on providing the anonymity of the transaction parties, e.g., Dash.
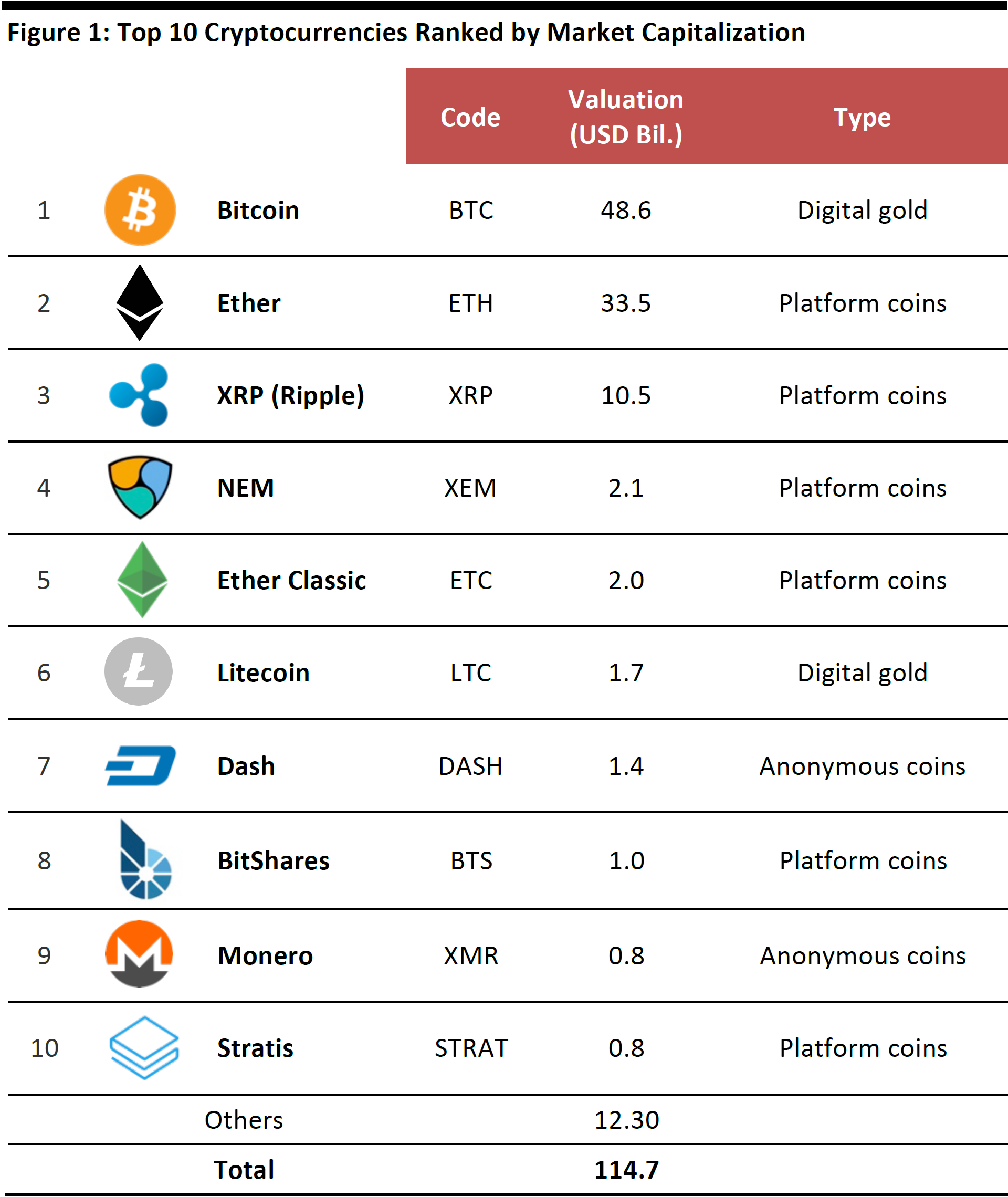
Note: As of June 26, 2017.
Source: coinmarketcap/Fung Global Retail & Technology
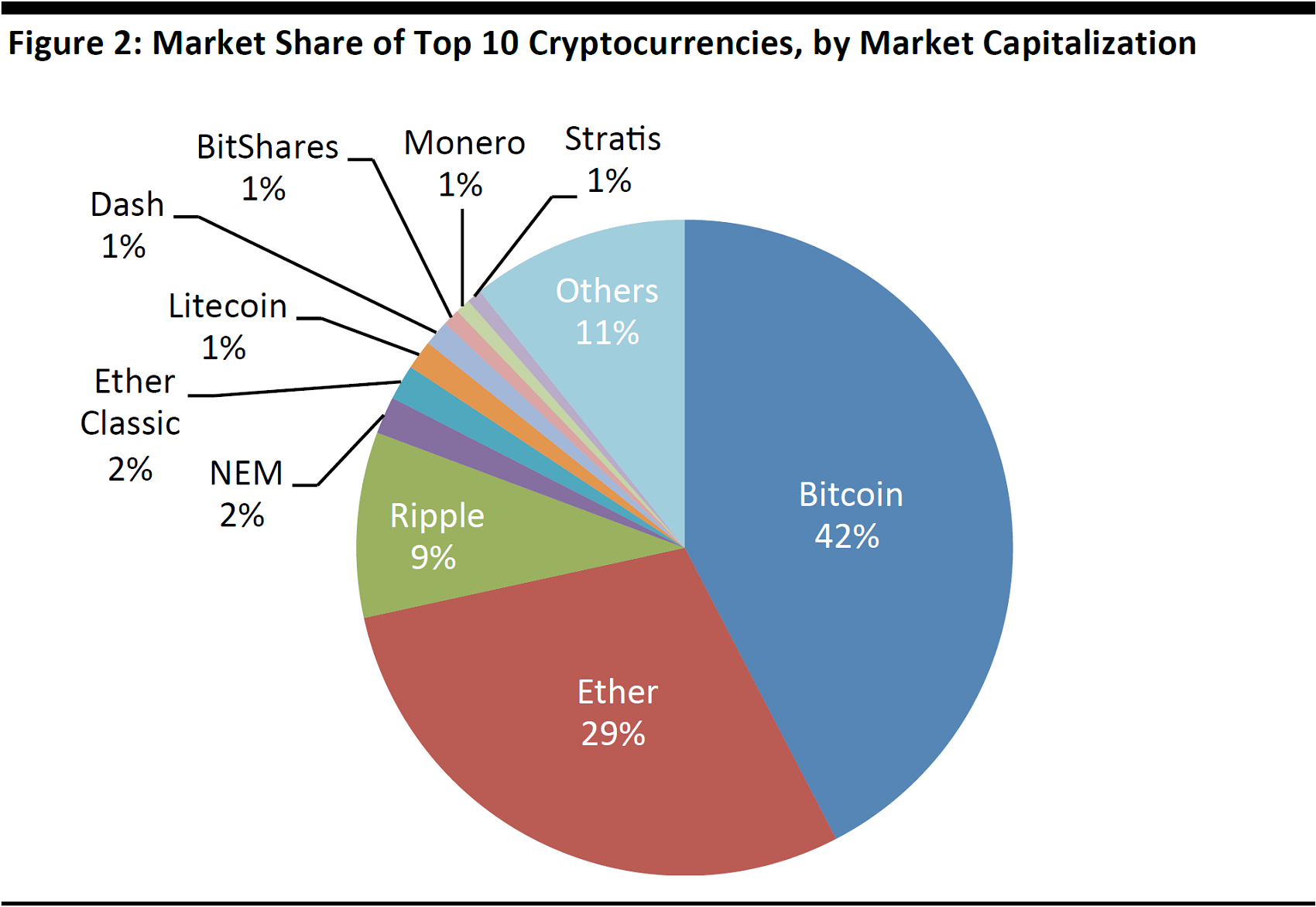
Note: As of June 26, 2017.
Source: coinmarketcap/Fung Global Retail & Technology
The Value Proposition of Cryptocurrencies
The four key value propositions of cryptocurrencies can be described as follows:
Predictable money supply: The supply of most cryptocurrencies is controlled by design. For example, the practical limit of Bitcoin’s total supply is 21 million BTC, with 78% of the supply already in the market and the remainder expected to be mined by 2140. By definition, Bitcoin is a deflationary currency, meaning the purchasing power of its holders will increase as long as demand is stable and growing faster than the supply of the currency. The same holds true for other digital currencies such as Dash, Ether and Litecoin.
Alternative payment method: There is an increasing number of corporations worldwide that accept Bitcoin as a payment: Subway, Expedia, Shopify, Peach Airline, etc. Customers use Bitcoin just like fiat money to trade for services and products from businesses.
Lower transaction costs: Cryptocurrencies, being decentralized networks, can cut out the additional costs that accrue during transactions, since they do not bear the infrastructure costs of traditional centralized systems.
Transactions are decentralized and secured: Cryptocurrencies allow a network of computers to maintain collective book-keeping over the Internet. In this distributed network, all transactions are logged, including information on the time, the participants and the transaction amounts. Each computer holds a full copy of the ledger, which is continuously verified by the majority of users on the system. If anyone tries to corrupt a transaction, the network of computers will not arrive at consensus and hence prevent the attack.
Risks Associated with Owning and Investing in Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies do not come without risks. Below, we highlight the key risks of owning and investing in cryptocurrencies.
Governance: Although cryptocurrencies are built on top of decentralized networks, some of the digital coins have centralized governance related to certain aspects. For example, the core developers of Bitcoin are, by design, the people who determine and implement the technical features of the platform. The potential risk that Bitcoin will be split in August 2017 (“a fork”) is the result of two different solutions proposed by two developers: Bitcoin Core and Bitcoin Unlimited. Both sides want to increase the capacity of the network, but they want to do it using different methods.
Source: bitcoin.org/en/bitcoin-core
Source: www.bitcoinunlimited.info
Authorities divided over cryptocurrencies: Cryptocurrencies are self-regulating due to their decentralized nature, which means users are responsible for validating each transaction. However, authorities around the world are taking different positions concerning the regulation of cryptocurrencies. For example, in February 2017, the price of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies plunged after the announcement from China that two of its major exchanges had suspended Bitcoin and Litecoin withdrawals for one month. The PRC government decided to suspend the currency, as it was focusing on preventing illegal activities such as money laundering. Japan introduced legislation to protect consumers, putting restrictions on the entities providing digital currency exchange services. The amended act forced Bitcoin exchanges to comply with anti-money-laundering regulations, while also recognizing Bitcoin as a legal payment method. Uncertainty relating to upcoming changes in regulations globally has significant potential to drive the value of cryptocurrencies up or down.
A 51% attack: A 51% attack refers to someone controlling a majority (more than 50%) of the network’s computing power, with the resulting ability to reverse transaction history and prevent new transactions from achieving consensus. Krypton, a currency based on Ethereum, was the first cryptocurrency to suffer from such an attack, back in August 2016. The attackers managed to steal around 21,465 KRby double spending on the network. Controlling 51% of the computing power of a larger scale network, such as Bitcoin, is nearly impossible, however. Thus, as the network of a cryptocurrency continues to grow, the probability of a 51% attack becomes ever lower.
Ownership of coins: Due to the anonymity characteristic embedded in the design of most cryptocurrencies, whoever holds the coin’s private key (or encryption code) is its owner. In April 2017, hackers stole the private keys of $5 million worth of user funds from South Korean bitcoin exchange Yapizon. As there is nothing in the coin’s coding that can prove the ownership of the coin, the original owners have little chance of getting their coins back.
Deep Dive into Cryptocurrencies
In the second part of the report, we look at four popular cryptocurrencies—Bitcoin, Ether, Ripple XRP and Litecoin—and their key features, adoption and future outlook.
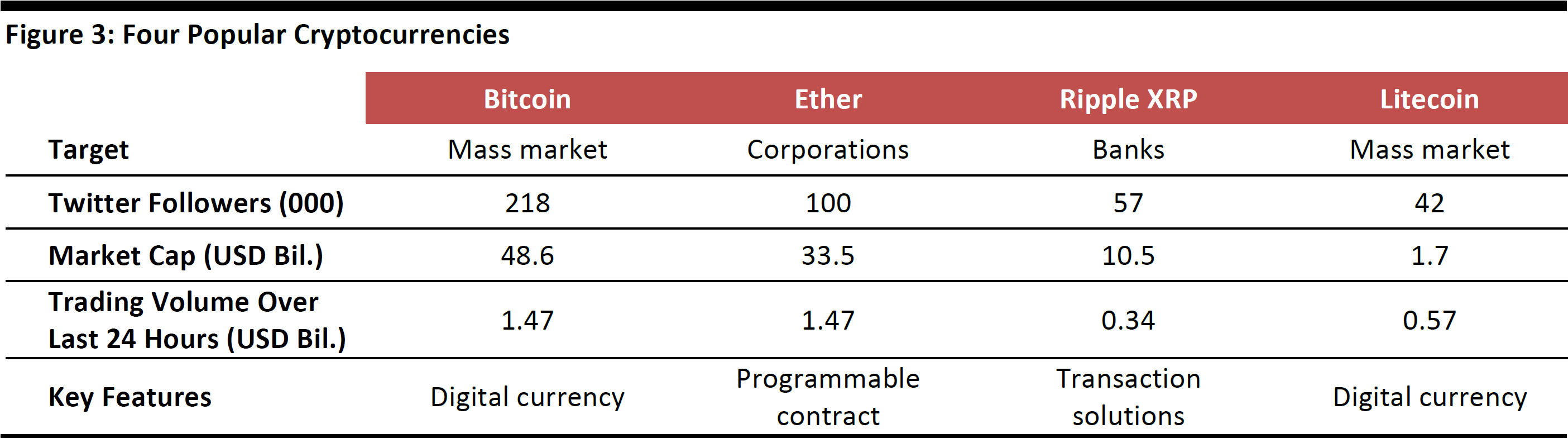
Note: As of June 26, 2017.
Source: Twitter/Bitcoinity/Coinmarketcap
Bitcoin

Bitcoin has been the leading cryptocurrency since it was first introduced in 2009. There is an increasing number of merchants worldwide who accept Bitcoin as payment, both offline and online.
Major Events/Milestones
January 2017—Chinese capital outflows: After the renminbi depreciated in late 2015, data from Bitcoinity, a Bitcoin data provider, shows that until January 2017, renminbi transactions accounted for over 98% of global Bitcoin trading volume. The inverse correlation between the price surge of Bitcoin and the weakening renminbi drove speculation that the digital currency was contributing to Chinese capital outflows. On January 6, 2017, The People’s Bank of China met with the three largest Chinese Bitcoin exchanges, huobi.com, btcchina.com, and okcoin.cn, to remind them to follow relevant regulations about risk controls and irregular practices. This caused the Bitcoin price to fall as much as 25% in a single day.
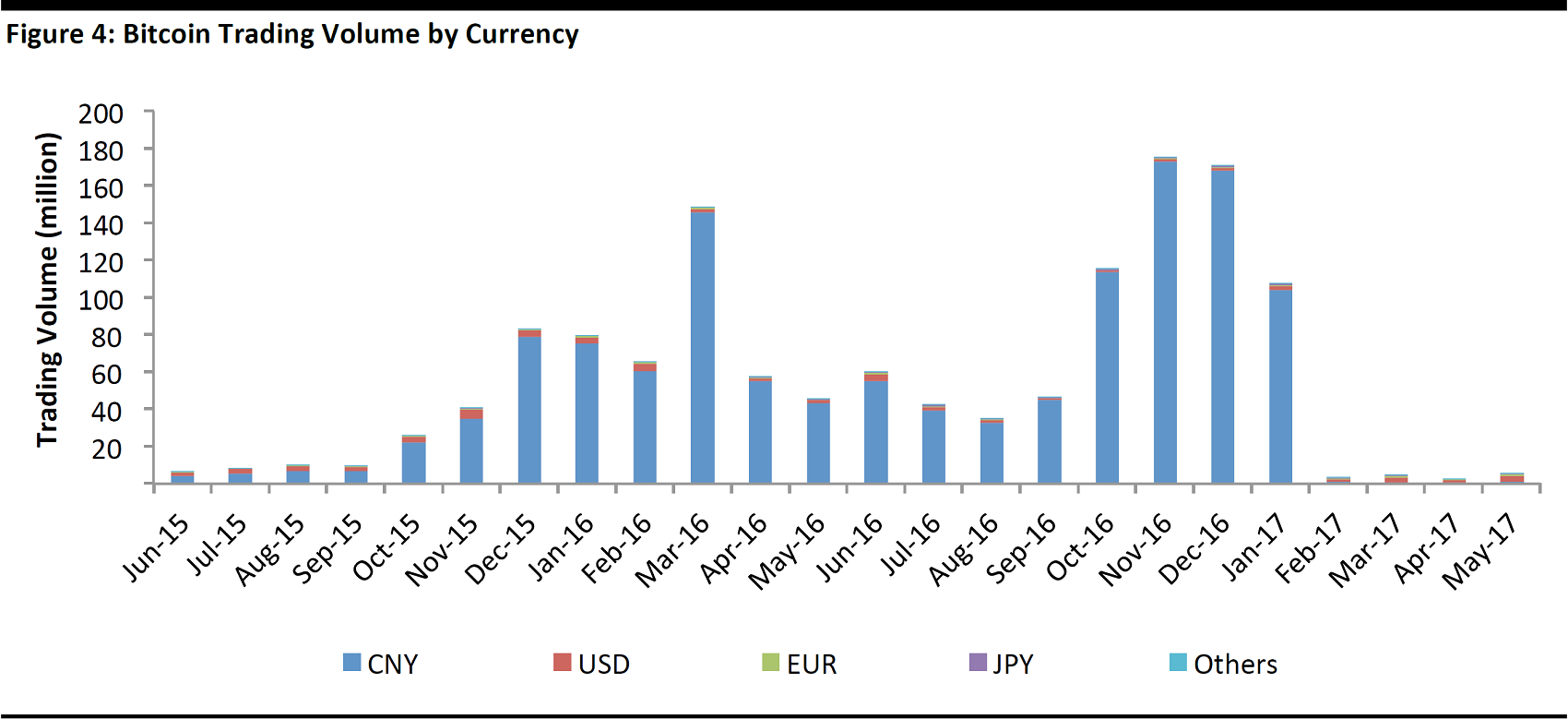
Source: Bitcoinity/Fung Global Retail & Technology
March 2017—US regulators reject a Bitcoin ETF: In March 2017, the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) rejected the first Bitcoin ETF, which was introduced by Investors Cameron and Tyler Winklevoss. Bitcoin’s price plunged following the news, declining as much as 18%.
April 2017—surging demand in Asia: On April 1, 2017, Japan’s Financial Services Agency recognized cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin as a legal method of payment. Soon after, Peach Aviation, a Japanese airline, started accepting Bitcoin as payment for airline tickets. Japanese yen transactions accounted for 7% of Bitcoin’s total trading volume in the last 30 days, according to data from Bitcoinity.
A popular currency on the dark web and for ransomware payments: Silk Road, an infamous marketplace for illegal goods and services, has been resurrected again as “Silk Road 3.0.” The website supports Bitcoin as the main transaction method. Dark web trade is one of the main use cases for Bitcoin, and as long as marketplaces for illegal goods and services supporting Bitcoin exist, there will be a sustainable source of demand for the digital currency.
The Future of Bitcoin
Increasing delays in transaction execution: Bitcoin blocks store transaction information and their size has a hard-coded limit of one megabyte. As the volume of transactions has increased, the one-megabyte limit has proven to be too small, causing delays in transaction processing as well as increasing transaction fees. While there have been multiple proposals to solve this scaling issue, a consensus among the Bitcoin ecosystem has yet to form as to the best approach to upgrade the currency. The solution will prove to be a pivotal moment for Bitcoin.
August 2017—potential Bitcoin fork: In order to solve Bitcoin’s scaling issue, two Bitcoin developers, Bitcoin Core and Bitcoin Unlimited, have proposed two different solutions. After some debate, the result is Bitcoin will be undergoing a user activated soft fork (UASF)on August 1, 2017. A UASF can be regarded as a software upgrade to Bitcoin, similar to a regular upgrade of Window OS. There are three possible outcomes, one of which involves splitting Bitcoin into two different coins, one with an activated Segregated Witness (new block structure) and one without (the current version). This could result in some Bitcoin owners losing their Bitcoin after August 1.
Source: cointelegraph
Our Take
We believe the high volatility of Bitcoin’s price will continue because of the uncertainty stemming from the potential hard fork expected to take place in August. However, Bitcoin has a large ecosystem of users, developers and mining operators, and we believe the currency will continue to be the leading cryptocurrency in terms of market capitalization.
Ether (Ethereum)

Ethereum was founded by the Ethereum Foundation, a Swiss nonprofit organization headed by VitalikButerin in August 2014. Ethereum is a platform that runs smart contracts, which enable developers to code and program transactions. A smart contract is a self-operating computer program that automatically executes a preset action when specific conditions are met. For example, WeiFund, a crowdfunding platform running on Ethereum, uses smart contracts to refund committed funds if a campaign goal is not met.
Ethereum has its own native tokens called Ether (ETH), which can be exchanged for Bitcoin or other fiat money. The Ether acts as the “fuel” which powers the transactions within the Ethereum platform.
Major Events/Milestones
February 2017—launch of the Enterprise Ethereum Alliance: This alliance was officially launched in late February 2017. The group’s aim is to develop a clear roadmap to meet enterprises’ needs on Ethereum. There are currently more than 100 corporations in the alliance, including Samsung, JP Morgan, Intel and Microsoft, and the idea is to create a positive feedback loop that leads to improvements of Ethereum. The diversity of the members could facilitate greater collaboration between the Ethereum platform and a number of different industries.
June 2017—Ether vs. Ether Classic: Similar to Bitcoin’s potential hard fork in August, Ether underwent a hard fork, which split the currency into Ether Classic and Etheron June 20. In Ether’s case, the fork was a way to fix a hacker attack. Ether Classic has a market capitalization of$2 billion as of June 26, 2017, which makes it the fifth-most-valuable cryptocurrency. Even though Ether and Ether Classic technically came from the same source code, they are not compatible with each other, and that is generally the aftermath of the hard fork. At the moment, the majority of the Ethereum community has moved onto the new chain.

Source: Enterprise Ethereum Alliance
The Future of Ethereum
Ethereum developers are planning a switch from a Proof-of-Work consensus model to a Proof-of-Stake consensus model in the future.
The proof-of-work model used by Bitcoin works by rewarding miners for processing complex algorithms. A new Bitcoin block is created every time a miner finds a solution. The difficulty of the algorithm adjusts so that new blocks can be created once every 10 minutes. The drawback of this model is that it consumes large amounts of energy and computer processing power.
The proof-of-stake model is conceptually different, as new blocks are randomly or deterministically generated and attributed to the stakeholders participating on the network, who prove that they have ownership, or a stake, in the system. This is a more efficient and cheaper way to produce new blocks on a blockchain.
Our Take
As a currency, Ether has some unique advantages over Bitcoin. The major one is that it is tied to the growth of Ethereum. If Ethereum proves to be a viable enterprise platform, then the value of Ether will increase dramatically.
Ripple

Ripple is a real-time transaction solution based on blockchain technology that enables banks to send payments across networks. It is different from Bitcoin and Ethereum in that it is a private blockchain that serves a number of banks worldwide. Ripple primarily aims to improve and speed up the processes related to financial transactions. Ripple’s digital currency is called the Ripple XRP.

Source: Ripple
Our Take
Surprisingly, Ripple XRP’s valuation reached a market cap of around $11 billion, as of 26 June, with only $0.3 billion daily trading volume on average. The liquidity is relatively low, despite it being the third-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization. XRP’s supply is limited to 100 billion XRP, with only a portion of it currently in circulation. Ripple, the startup behind XRP, owns over 60% of Ripple coins (Ripples or XRP) in circulation, which made the company extremely valuable overnight. However, this has also raised questions about the governance of the blockchain. On May 16, 2017, Ripple announced that it would place 55 billion XRP into a cryptographically-secured escrow account for a period of at least four-and-a-half years and release a billion XRP into the market every month.
Litecoin

The market has widely recognized Litecoin as a clone of Bitcoin, due to the similarity of the two digital currencies, but while Bitcoin is the “gold” Litecoin is the “silver.” Litecoin was founded in 2011 and positioned itself as a proven medium of commerce complementary to Bitcoin. However, Litecoin has a different mining algorithm which ensures faster transaction speeds compared with Bitcoin. The price of Litecoin was only 2% of Bitcoin’s, as of June 20, 2017, as the acceptance level and the size of its user base is still far away from those of Bitcoin.
Source: litecoin.org
Our Take
While we think Litecoin may never surpass Bitcoin in popularity or market capitalization, we do believe the digital currency is well positioned as an alternative to Bitcoin.
Conclusion
Although the prices of the various cryptocurrencies are still highly volatile, the foundational principals behind their existence and applications are solid. While we think we are a long way out before the mass market accepts any particular cryptocurrency as an alternative to fiat money, the idea of decentralized distributed ledgers is revolutionary, and the trend of digital currency adoption certainly deserves attention, as it carries the significant disruptive potential to commerce at large.







 Bitcoin has been the leading cryptocurrency since it was first introduced in 2009. There is an increasing number of merchants worldwide who accept Bitcoin as payment, both offline and online.
Bitcoin has been the leading cryptocurrency since it was first introduced in 2009. There is an increasing number of merchants worldwide who accept Bitcoin as payment, both offline and online.


 Ethereum was founded by the Ethereum Foundation, a Swiss nonprofit organization headed by VitalikButerin in August 2014. Ethereum is a platform that runs smart contracts, which enable developers to code and program transactions. A smart contract is a self-operating computer program that automatically executes a preset action when specific conditions are met. For example, WeiFund, a crowdfunding platform running on Ethereum, uses smart contracts to refund committed funds if a campaign goal is not met.
Ethereum has its own native tokens called Ether (ETH), which can be exchanged for Bitcoin or other fiat money. The Ether acts as the “fuel” which powers the transactions within the Ethereum platform.
Ethereum was founded by the Ethereum Foundation, a Swiss nonprofit organization headed by VitalikButerin in August 2014. Ethereum is a platform that runs smart contracts, which enable developers to code and program transactions. A smart contract is a self-operating computer program that automatically executes a preset action when specific conditions are met. For example, WeiFund, a crowdfunding platform running on Ethereum, uses smart contracts to refund committed funds if a campaign goal is not met.
Ethereum has its own native tokens called Ether (ETH), which can be exchanged for Bitcoin or other fiat money. The Ether acts as the “fuel” which powers the transactions within the Ethereum platform.

 Ripple is a real-time transaction solution based on blockchain technology that enables banks to send payments across networks. It is different from Bitcoin and Ethereum in that it is a private blockchain that serves a number of banks worldwide. Ripple primarily aims to improve and speed up the processes related to financial transactions. Ripple’s digital currency is called the Ripple XRP.
Ripple is a real-time transaction solution based on blockchain technology that enables banks to send payments across networks. It is different from Bitcoin and Ethereum in that it is a private blockchain that serves a number of banks worldwide. Ripple primarily aims to improve and speed up the processes related to financial transactions. Ripple’s digital currency is called the Ripple XRP.

 The market has widely recognized Litecoin as a clone of Bitcoin, due to the similarity of the two digital currencies, but while Bitcoin is the “gold” Litecoin is the “silver.” Litecoin was founded in 2011 and positioned itself as a proven medium of commerce complementary to Bitcoin. However, Litecoin has a different mining algorithm which ensures faster transaction speeds compared with Bitcoin. The price of Litecoin was only 2% of Bitcoin’s, as of June 20, 2017, as the acceptance level and the size of its user base is still far away from those of Bitcoin.
The market has widely recognized Litecoin as a clone of Bitcoin, due to the similarity of the two digital currencies, but while Bitcoin is the “gold” Litecoin is the “silver.” Litecoin was founded in 2011 and positioned itself as a proven medium of commerce complementary to Bitcoin. However, Litecoin has a different mining algorithm which ensures faster transaction speeds compared with Bitcoin. The price of Litecoin was only 2% of Bitcoin’s, as of June 20, 2017, as the acceptance level and the size of its user base is still far away from those of Bitcoin.
