
albert Chan
We outline the possible economic impact of the coronavirus outbreak in China. We will follow up with further estimates in subsequent reports.
Retailers with China Operations
Many restaurants and retail establishments have closed, particularly in Hubei Province:
- IKEA announced it would close about half its 30 stores in China until further notice.
- LVMH has reportedly closed some stores in Hubei Province.
- McDonald’s has closed all its restaurants in Hubei Province, 300 of its 3,00 restaurants in China.
- Shanghai Disney Resort closed on January 24 and Disneyland Hong Kong closed on January 25.
- Starbucks announced more than half its stores in China are currently closed and that the company continues to monitor and modify operating hours for all stores in China.
- Uniqlo has temporarily shut about 50 stores in China.
- WeWork is temporarily closing 55 offices in China and encouraging employees to work from home or private locations.
- Yum China temporarily closed some of its KFC and Pizza Hut restaurants in Wuhan Province.
Other companies including Facebook, PriceWaterhouseCoopers and Shiseido are restricting business travel to Wuhan and/or China, or requesting that employees work from home for a two-week period.
In addition, cinemas owned by Bona, CGV, Dadi, Emperor, Lumiere Pavilions and Wanda closed before the Lunar New Year holiday.
Empty Shelves
The Coresight Research team in China saw empty shelves in markets in Shanghai, for all products but in particular for nonperishables such as instant noodles.
[caption id="attachment_102946" align="aligncenter" width="700"] Vegetable market (left) and instant-noodle shelves (right) in Shanghai Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Vegetable market (left) and instant-noodle shelves (right) in Shanghai Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
And despite the addition of more self-checkout counters, the average wait time in a medium-sized Freshippo supermarket in Shanghai was over an hour.
[caption id="attachment_102947" align="aligncenter" width="700"]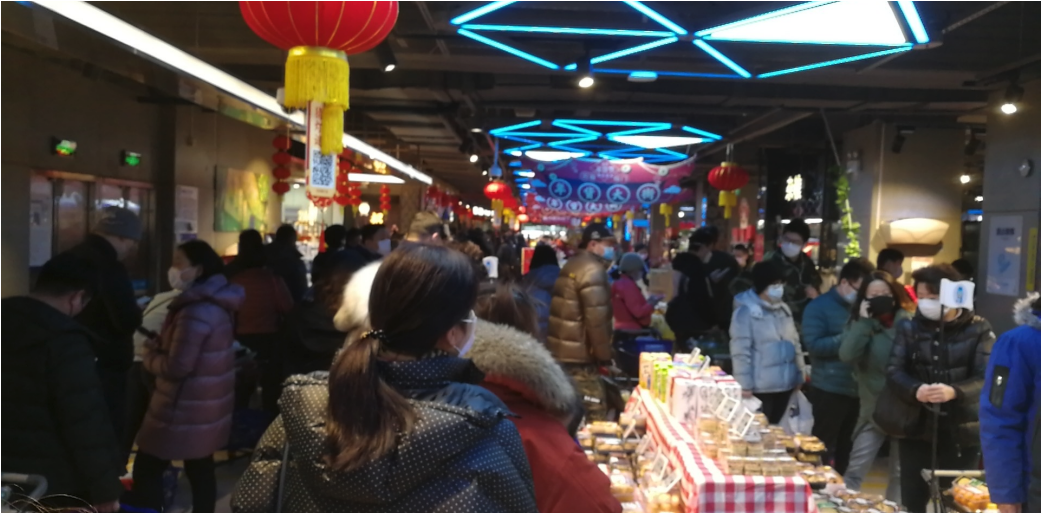 Freshippo market in Shanghai Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Freshippo market in Shanghai Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Airlines Cut Flights
Several airlines are cutting or reducing flights to China, including:
- American Airlines, which is canceling flights from Los Angeles to Shanghai and to Beijing from February 9 to March 27, but will continue to operate flights to China from Dallas-Fort Worth and from Los Angeles to Hong Kong.
- Delta Air Lines issued a travel waiver that allows passengers traveling to, from or through Beijing and Shanghai during January 24–31 to change their itineraries without penalty.
- United Airlines suspended some flights between the US and Beijing, Hong Kong and Shanghai from February 1 to 8 due to a significant decline in demand.
- Other carriers stopping or reducing China air service include Air Canada, Air France-KLM, Air India, British Airways, Cathay Pacific, Iberia, Finnair, Jetstar Asia, Lufthansa and Seoul Air.
The cut in China service will adversely affect tourism-related and retail sales in destination cities, as well as in-airport retail sales.
Updated Coronavirus and SARS Timeline
The figure below illustrates the general timeline from when early forms of the virus were discovered to now. As of this report’s writing, it has been about one month since the first pneumonia cases were discovered.
[caption id="attachment_102965" align="aligncenter" width="700"]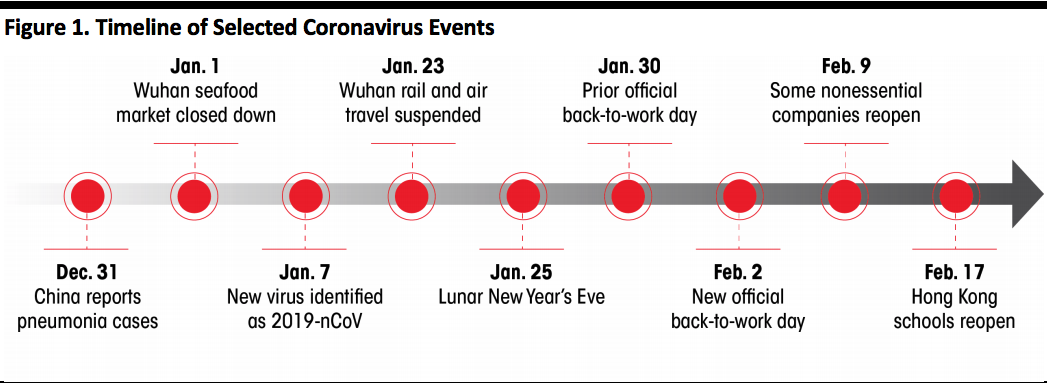 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
For comparison purposes, a timeline of the SARS outbreak is displayed below. The timeline represents a span of 231 days from the first reported pneumonia cases until the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the virus contained.
On a positive note, the coronavirus causing the outbreak has a fatality rate of about 2% (based on Chinese government figures), far below the 10.8% mortality rate reported for the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) during the 2018 flu season due to influenza and pneumonia and also below the 10-20% rate reported for SARS (which varied by country).
[caption id="attachment_102966" align="aligncenter" width="700"]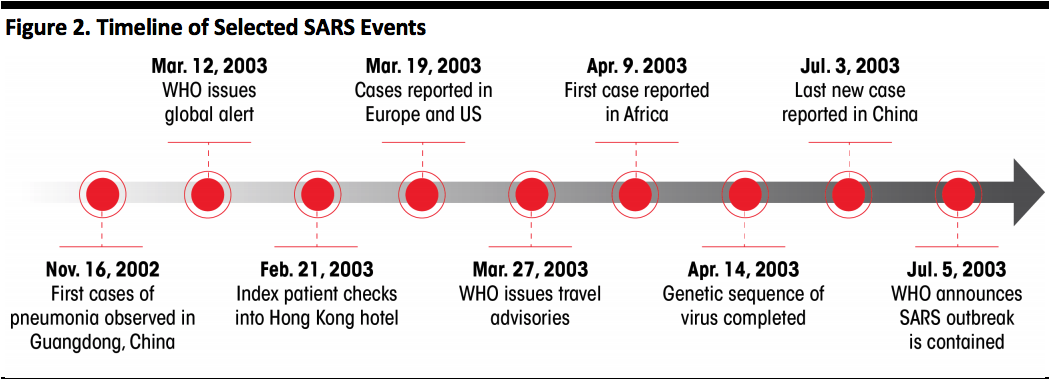 Source: CDC/Coresight Research[/caption]
Source: CDC/Coresight Research[/caption]