
Nitheesh NH
CES 2021, an event held by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA), is taking place on January 11–14 and is a virtual event for the first time. Key tech trends at this year’s CES include digital health, robotics and drones, 5G connectivity, digital transformation, vehicle technology and smart cities.
The Coresight Research team is presenting takeaways from the three-day event in three reports. In this report, we offer 10 key insights from day two.
 Delivery of final group of GM ventilators to US Department of Health and Human Services
Delivery of final group of GM ventilators to US Department of Health and Human Services
Source: GM[/caption] 3. Processor-PC Maker Partnerships Drive Innovation in Computing and Gaming Gaming is steadily pushing the limits of processing power and computer graphics and drives the direction of PC hardware development. AMD, in addition to providing processors for high-performance laptops and desktops, has worked closely with the makers of gaming consoles, specifically Microsoft and Sony. AMD produces custom SOCs (systems on a chip) that leverage its Ryzen processor and Radeon graphics chip technologies to provide higher frame rates (the number of screen refreshes per second), higher resolution (more pixels) and immersive experiences. At CES 2021, AMD offered a testimonial from Industrial Light and Magic, the creator of the Star Wars movies, which discussed AMD’s hardware enabling the playback of 4K, 8K and even 16K content in real time. At the show, AMD unveiled its new Ryzen 5000 series mobile processors, which are based on its “Zen 3” core and offer a combination of high performance and power efficiency. [caption id="attachment_121694" align="aligncenter" width="700"] AMD CEO Lisa Su announces the new Ryzen 5000 processor
AMD CEO Lisa Su announces the new Ryzen 5000 processor
Source: AMD[/caption] 4. Computer Gaming Is a Major Part of Many Consumers’ Everyday Lives In addition to being a driving force behind innovation in processing and computer graphics, computer gaming has become a major part of many consumers’ everyday lives—including playing, watching and talking about games—due to more time being spent at home and a dramatic increase in interest in esports. During the AMD keynote, CEO Lisa Su offered several interesting statistics about computer gaming from NPG Group and DFC Intelligence: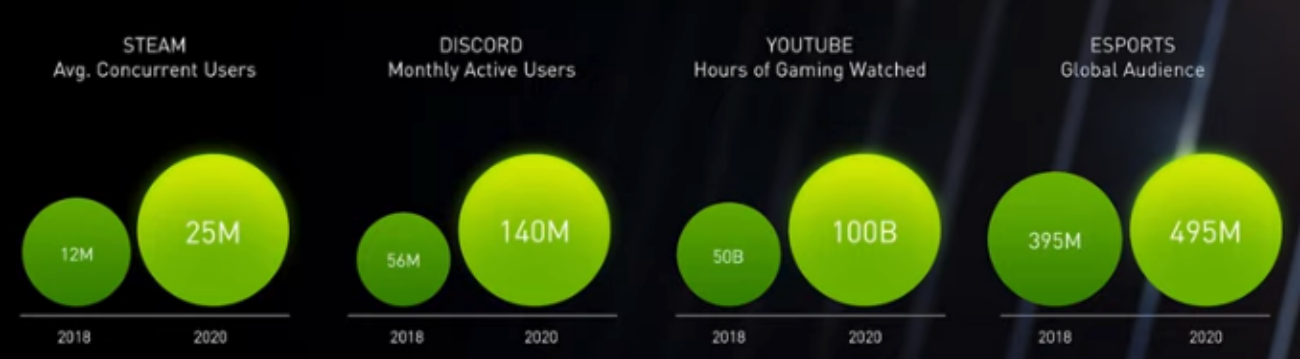 Dramatic increases in the consumption of video-game content in 2020
Dramatic increases in the consumption of video-game content in 2020
Source: Nvidia[/caption] 5. Companies’ Efforts in Diversity and Inclusion Should Focus on Talent Retention Tiffany Moore, Senior Vice President, Political and Industry Affairs, at CTA, moderated a session entitled “Keys to Success, How D&I Helped US to Survive 2020.” During the session, Intel Corporation was one of the companies to share diversity and inclusion insights. Intel, a pioneer in championing an inclusive and diverse workforce, made a commitment in 2015 for equal representation. The company achieved its 2020 goal of reaching full representation of women and under-represented minorities in its US workforce two years ahead of schedule. In January 2019, Intel also announced that it achieved 100% gender-pay equality globally by closing the gap in average pay between employees of different genders in the same or similar roles. Dawn Jones, Chief Diversity and Inclusion Officer a Intel Corporation, said that reaching full representation was a huge milestone. She added, “You cannot hire your way into diversity and inclusion; hire in good talent and focus on keeping them.” Intel has pledged in its 2030 goals that it will advance diversity and inclusion, including doubling the number of women and under-represented minorities in senior leadership roles. The company also aims to increase diversity in technical roles by 40% to ensure it offers its workforce an inclusive environment. 6. The Future of Vehicles: All-Electric Offers Sustainability, Quality of Life and Safety GM believes that electric vehicles (EVs) offer the solution for reducing emissions, congestion and car crashes. The company has been a pioneer in EV technology, announcing the Chevy Volt at the 2016 CES show, yet EV penetration globally is just 3%. GM believes that this penetration rate is about to change and intends to lead the way to all-electric. There are three areas of technology advancement that GM expects to accelerate the EV market: battery architecture, electrical propulsion systems and higher-energy battery cells. GM is engaged in a joint venture with LG Chem, for a total investment of $2.3 billion in a new battery plant located in Kokomo, Indiana. GM’s advances in battery architecture include a stackable battery design that reduces the space between cells and also uses aluminum, a more commonplace element than cobalt, which is typically used in lithium-ion batteries. Separately, GM announced a new business called BrightDrop on the second day of CES 2021. BrightDrop offers an ecosystem of electric first-to-last-mile products, software and services to empower delivery and logistics companies to move goods more efficiently. These solutions aim to offer businesses lower costs, maximize productivity, improve employee safety and freight security, and support overall sustainability efforts. [caption id="attachment_121696" align="aligncenter" width="700"]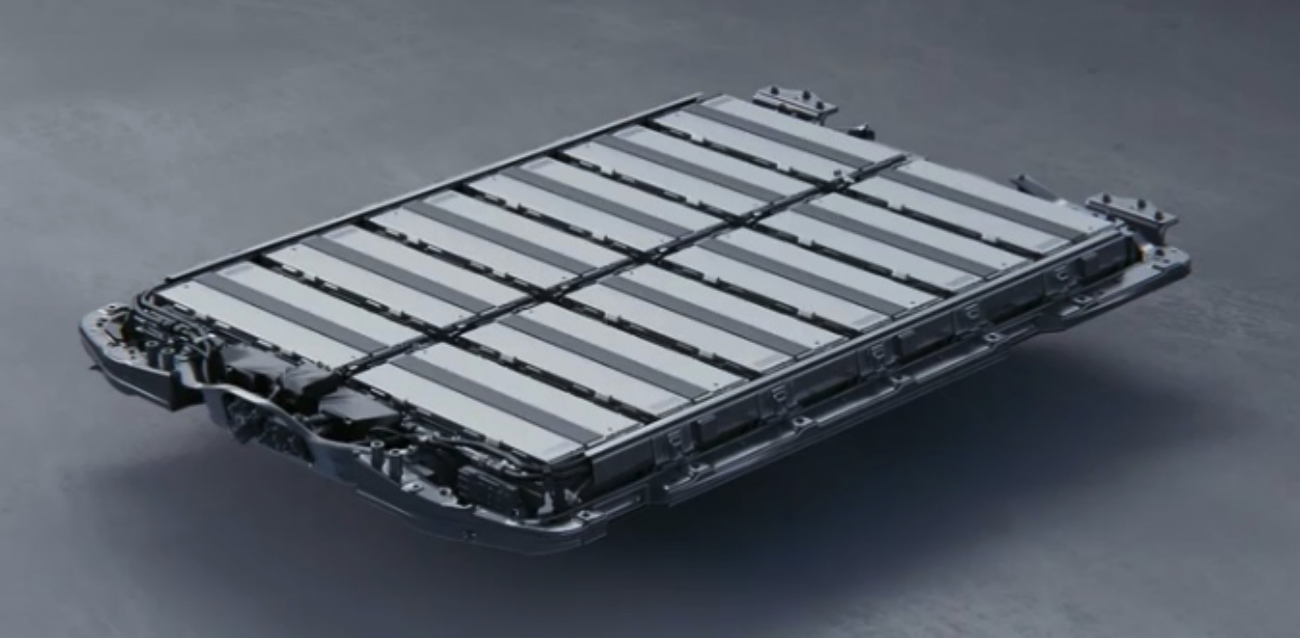 Stackable battery module
Stackable battery module
Source: GM[/caption] 7. The Future of Retailing Is To Agnostically Meet Consumers Wherever They Are At CES 2021, Best Buy CEO Corie Barry discussed her vision for the future of tech. Barry said that after the Covid-19 pandemic hit, consumer demand for technology became a near-immediate need as consumers staying at home required products for entertainment, cooking and connecting, for example. Best Buy adapted to the environment by implementing a curbside-pickup model within three weeks of the outbreak in the US (in March), and Barry emphasized that the entire company became more flexible in how it operated and responded to meet consumers—for example, job responsibilities flexed and changed in order to fulfill curbside orders, fulfill inventory requests and meet changing daily requirements. When asked how Best Buy could compete with online retailers, Barry said that the company had seen online sales growth of about 175% year over year, yet 40% of consumers still sought to pick up their orders in-store or at the curbside. “They wanted it [order fulfillment] when they wanted it, where they wanted it, as fast as they wanted it. The customer is in control. Agnostically meet the customer wherever they are; that is the future of retailing,” Barry explained. The future of the physical store will be broader and will play a massive role in fulfillment as a fulfillment epicenter, she added. The Best Buy physical store will also be important for more complex sales, as many consumers come to the stores for support and help. 8. Companies Can Achieve Inclusion via Suppliers, Startups and Employees in Other Geographies The Mastercard session on the second day of CES 2021 comprised a moderated discussion with the CEOs of professional services company Accenture (Julie Sweet) and financial services corporation Mastercard (Michael Miebach). The discussion covered two main topics: technology and inclusion. In terms of technology, Accenture outlined two pivots that are here to stay. The first is the move to the cloud, with rate of shift averaging 20% across industries prior to the Covid-19 pandemic but increasing to reach 80% by 2025, according to Accenture. The second is the role of AI, particularly in terms of enterprise resilience due to the widening gap between companies that have digital working capability and those that do not. Mastercard highlighted blockchain as a technology that has built-in trust and can be used to ensure trust in financial services globally. Both Accenture and Mastercard have undertaken public measures to improve racial inclusivity:
CES Day Two: 10 Key Insights
The second day of CES 2021 saw keynote addresses by major technology companies in addition to panel discussions on key technology topics. The day focused on initiatives launched, and progress made, by technology companies to benefit society in light of the Covid-19 pandemic, as well as video gaming as a driver of technology. Sustainability, diversity and inclusion also emerged as key themes. 1. The Tech Industry Provides Substantial Resources for Covid-19 Vaccine Development As part of AMD’s Covid-19 HPC (high-performance computing) Fund, the global tech company donated a 12 petaflops (12 × 1015 floating-point operations) of computing resources in two rounds to support Covid-19 research. The fund had 18 initial partners, including Penguin Computing and US universities Massachusetts Institute of Technology, New York University and Rice University, Texas. The second round in September 2020 brought the number of participating institutions to 21, including Oxford University and the Stanford School of Medicine. 2. Companies Leverage Manufacturing Capacity To Produce PPE amid Covid-19 General Motors (GM) announced in March 2020 that it would partner with Ventec Lift Systems to build critical-care ventilators in its Kokoma, Indiana facility, with capacity ramping up to 10,000 units per month. The company also announced that it would manufacture Level 1 surgical masks in its Warren, Michigan facility, with the initial capacity of 50,000 masks per day ramping up to 100,000 masks per day. In September 2020, GM announced that it had delivered its 30,000th ventilator to the US Department of Health and Human Services. [caption id="attachment_121693" align="aligncenter" width="700"] Delivery of final group of GM ventilators to US Department of Health and Human Services
Delivery of final group of GM ventilators to US Department of Health and Human ServicesSource: GM[/caption] 3. Processor-PC Maker Partnerships Drive Innovation in Computing and Gaming Gaming is steadily pushing the limits of processing power and computer graphics and drives the direction of PC hardware development. AMD, in addition to providing processors for high-performance laptops and desktops, has worked closely with the makers of gaming consoles, specifically Microsoft and Sony. AMD produces custom SOCs (systems on a chip) that leverage its Ryzen processor and Radeon graphics chip technologies to provide higher frame rates (the number of screen refreshes per second), higher resolution (more pixels) and immersive experiences. At CES 2021, AMD offered a testimonial from Industrial Light and Magic, the creator of the Star Wars movies, which discussed AMD’s hardware enabling the playback of 4K, 8K and even 16K content in real time. At the show, AMD unveiled its new Ryzen 5000 series mobile processors, which are based on its “Zen 3” core and offer a combination of high performance and power efficiency. [caption id="attachment_121694" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
 AMD CEO Lisa Su announces the new Ryzen 5000 processor
AMD CEO Lisa Su announces the new Ryzen 5000 processorSource: AMD[/caption] 4. Computer Gaming Is a Major Part of Many Consumers’ Everyday Lives In addition to being a driving force behind innovation in processing and computer graphics, computer gaming has become a major part of many consumers’ everyday lives—including playing, watching and talking about games—due to more time being spent at home and a dramatic increase in interest in esports. During the AMD keynote, CEO Lisa Su offered several interesting statistics about computer gaming from NPG Group and DFC Intelligence:
- Four in five US consumers have played a video game in the past six months.
- The $17.4 billion gaming industry is larger than the movie and music industries combined.
- 3.1 billion people around the world play video games.
 Dramatic increases in the consumption of video-game content in 2020
Dramatic increases in the consumption of video-game content in 2020Source: Nvidia[/caption] 5. Companies’ Efforts in Diversity and Inclusion Should Focus on Talent Retention Tiffany Moore, Senior Vice President, Political and Industry Affairs, at CTA, moderated a session entitled “Keys to Success, How D&I Helped US to Survive 2020.” During the session, Intel Corporation was one of the companies to share diversity and inclusion insights. Intel, a pioneer in championing an inclusive and diverse workforce, made a commitment in 2015 for equal representation. The company achieved its 2020 goal of reaching full representation of women and under-represented minorities in its US workforce two years ahead of schedule. In January 2019, Intel also announced that it achieved 100% gender-pay equality globally by closing the gap in average pay between employees of different genders in the same or similar roles. Dawn Jones, Chief Diversity and Inclusion Officer a Intel Corporation, said that reaching full representation was a huge milestone. She added, “You cannot hire your way into diversity and inclusion; hire in good talent and focus on keeping them.” Intel has pledged in its 2030 goals that it will advance diversity and inclusion, including doubling the number of women and under-represented minorities in senior leadership roles. The company also aims to increase diversity in technical roles by 40% to ensure it offers its workforce an inclusive environment. 6. The Future of Vehicles: All-Electric Offers Sustainability, Quality of Life and Safety GM believes that electric vehicles (EVs) offer the solution for reducing emissions, congestion and car crashes. The company has been a pioneer in EV technology, announcing the Chevy Volt at the 2016 CES show, yet EV penetration globally is just 3%. GM believes that this penetration rate is about to change and intends to lead the way to all-electric. There are three areas of technology advancement that GM expects to accelerate the EV market: battery architecture, electrical propulsion systems and higher-energy battery cells. GM is engaged in a joint venture with LG Chem, for a total investment of $2.3 billion in a new battery plant located in Kokomo, Indiana. GM’s advances in battery architecture include a stackable battery design that reduces the space between cells and also uses aluminum, a more commonplace element than cobalt, which is typically used in lithium-ion batteries. Separately, GM announced a new business called BrightDrop on the second day of CES 2021. BrightDrop offers an ecosystem of electric first-to-last-mile products, software and services to empower delivery and logistics companies to move goods more efficiently. These solutions aim to offer businesses lower costs, maximize productivity, improve employee safety and freight security, and support overall sustainability efforts. [caption id="attachment_121696" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
 Stackable battery module
Stackable battery moduleSource: GM[/caption] 7. The Future of Retailing Is To Agnostically Meet Consumers Wherever They Are At CES 2021, Best Buy CEO Corie Barry discussed her vision for the future of tech. Barry said that after the Covid-19 pandemic hit, consumer demand for technology became a near-immediate need as consumers staying at home required products for entertainment, cooking and connecting, for example. Best Buy adapted to the environment by implementing a curbside-pickup model within three weeks of the outbreak in the US (in March), and Barry emphasized that the entire company became more flexible in how it operated and responded to meet consumers—for example, job responsibilities flexed and changed in order to fulfill curbside orders, fulfill inventory requests and meet changing daily requirements. When asked how Best Buy could compete with online retailers, Barry said that the company had seen online sales growth of about 175% year over year, yet 40% of consumers still sought to pick up their orders in-store or at the curbside. “They wanted it [order fulfillment] when they wanted it, where they wanted it, as fast as they wanted it. The customer is in control. Agnostically meet the customer wherever they are; that is the future of retailing,” Barry explained. The future of the physical store will be broader and will play a massive role in fulfillment as a fulfillment epicenter, she added. The Best Buy physical store will also be important for more complex sales, as many consumers come to the stores for support and help. 8. Companies Can Achieve Inclusion via Suppliers, Startups and Employees in Other Geographies The Mastercard session on the second day of CES 2021 comprised a moderated discussion with the CEOs of professional services company Accenture (Julie Sweet) and financial services corporation Mastercard (Michael Miebach). The discussion covered two main topics: technology and inclusion. In terms of technology, Accenture outlined two pivots that are here to stay. The first is the move to the cloud, with rate of shift averaging 20% across industries prior to the Covid-19 pandemic but increasing to reach 80% by 2025, according to Accenture. The second is the role of AI, particularly in terms of enterprise resilience due to the widening gap between companies that have digital working capability and those that do not. Mastercard highlighted blockchain as a technology that has built-in trust and can be used to ensure trust in financial services globally. Both Accenture and Mastercard have undertaken public measures to improve racial inclusivity:
- Accenture set a goal of having half of its senior positions occupied by women by 2025 and is currently at 25%.
- Mastercard is evaluating the inclusivity of suppliers and emerging innovators as sources to drive future inclusivity.
- Making predictions
- Automation
- Optimization, such as performance or cost enhancement