
DIpil Das
Introduction
What’s the Story?
Coresight Research has identified the expanding metaverse as a key trend to watch in retail and a component trend of Coresight Research’s RESET framework for change. That framework provides retailers with a model for adapting to a new world marked by consumer-centricity, in 2022 and beyond (see the appendix of this report for more details).
In this report, we explore the Internet of Things (IoT), covering its key technologies and relationship with the metaverse.
This report forms part of our Building Blocks of the Metaverse series, which presents insights into the core technological components of the retail metaverse, including important details for retailers to know in establishing a presence and operating in the virtual space.
Why It Matters
IoT describes the network of physical items (such as objects fitted with sensors) that amasses and exchanges massive amounts of real-time data over the Internet. Sensors may include haptic sensors, sound sensors, GPS and cameras. IoT devices are prevalent in the world today, from smart home systems to wearable technology and even connected smart cities. In the metaverse, they will be the crucial link between the virtual and real worlds. Devices fitted with IoT sensors that are connected to 5G networks can help brands and retailers recreate real-world locations in detail and providing immersive virtual experiences.
The global IoT software and hardware industry has been steadily growing in recent years, and is projected to total $525 billion in 2027, according to IoT data provider IoT Analytics (see Figure 1). There are set to be around 25 billion IoT-connected devices worldwide by 2030—up from less than 12 billion today—according to Transforma Insights.
Figure 1. Global IoT Services and Hardware Market (USD Bil.) [caption id="attachment_153323" align="aligncenter" width="701"]
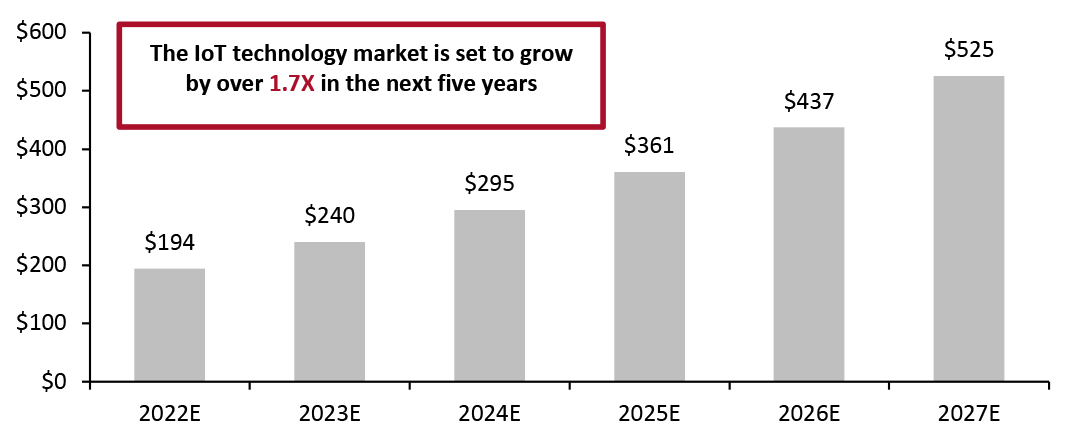 Source: IoT Analytics[/caption]
Source: IoT Analytics[/caption]
Although IoT technology can be complex to understand, brands and retailers that familiarize themselves with it will be best positioned to reap its potential rewards in the near future. Many retailers have already begun experimenting with “digital twin” stores, warehouses and factories, which can significantly improve operational efficiency and reduce waste in the value chain (supporting sustainability). By simulating operations in the metaverse, businesses of all types can be significantly more sustainable and save costs.
As technologies such as 5G wireless connectivity and the blockchain continue to improve accessibility, connectivity and efficiency for global and digital economies, there is a major opportunity for brands and retailers to use IoT devices to tap a new base of digitally connected customers.
Building Blocks of the Metaverse—IoT
IoT’s Connection with the Metaverse
The typical concept of the metaverse is a fully immersive virtual environment, such as Decentraland or The Sandbox. However, metaverse spaces can be virtual representations of the real world. IoT digital twins give brands and retailers the opportunity to provide real-time shopping experiences for customers no matter where they are located, as well as simulate production to support sustainability initiatives. We discuss these two benefits of IoT’s integration with the metaverse below.
1. Real-World Locations
Flagship stores and iconic retail experiences can be recreated in virtual settings using real-time data provided by IoT digital twins. In virtual settings, retailers and brands have the opportunity to enhance the shopping experience, adding information about product history, quality, origin and availability, as well as incorporating augmented elements to improve visual aesthetics. With camera technology, digital-twin recreations of outdoor spaces and entire cities are possible. Digital twins can also capture real-time store and visual data, allowing businesses to recreate locations in the metaverse with greater detail.
As digital sales channels and online stores grow in popularity, the interactivity of these types of stores will increase global customer bases and may provide alternatives for brands and retailers to opening new locations in unfamiliar countries and areas.
Many large technology companies are offering digital-twin services in some capacity, including Autodesk, IBM, Microsoft, Nvidia and Siemens. Matterport is one of the leaders in creating virtual stores for customers based on digital twins. Food and restaurant retailers use Matterport digital twins to capture actionable real-time data from their stores. Although many brands and retailers have not used digital twins to replicate stores for the metaverse yet, they now have the ability and the means to accurately create them.
Figure 2. Brands and Retailers Utilizing Matterport Digital Twins [wpdatatable id=2179 table_view=regular]
Source: Coresight Research
Online and virtual stores have been gaining significant popularity for their versatility, flexibility and added elements for customer experience. Among US consumers who have visited an online store, 70% have purchased an item, according to a survey conducted in December 2021 by virtual shopping platform Obsess. Additionally, 93% of US consumers expressed their intention to shop at an online store, although 70% miss the physical experience when doing so, according to a 2020 Matterport survey of US consumers—showcasing the need for IoT-enabled digital stores that can replicate the brick-and-mortar experience. Digital twins give brands and retailers the opportunity to recreate locations in the metaverse (or virtual setting), offering a “phygital” (physical-digital) experience.
In the future, as technology continues to develop, virtual store and warehouse operations will be more immersive, with IoT sensors also encompassing haptic sensors to simulate the sense of touch and even sound sensors that transport sound waves by converting them to electric signals. Advanced camera sensors will help to integrate IoT and other immersive technologies, such as augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR).
- For more information about AR/VR and haptic technologies, read our separate report, Building Blocks of the Metaverse: Immersive Technologies.
2. Sustainability
Simulating production in warehouses in the metaverse using digital twins can help retailers and merchants significantly increase operational efficiency, reduce waste and reduce overhead costs.
Digital twins are also being used in 3D collaborative tools, which help businesses and organizations simulate operations and factory operations for optimal production. By simulating operations in the metaverse or virtual settings using digital twins, brands and retailers can reduce inventory drag and overhang, efficiently allocate resources, identify bottlenecks and constraints, and reduce general waste.
Nvidia’s Omniverse is one digital-twin platform that is helping retailers and brands with complex factory operations to streamline production by modeling it in the metaverse (see Figure 3).
Figure 3. Brands and Retailers Using Nvidia’s Omniverse [wpdatatable id=2180 table_view=regular]
Source: Coresight Research
- For more on brands and retailers that are leveraging IoT digital twins, read our report, Metaverse Latest: The Race To Build IoT Digital Twins and the Power of 3D Game Engines.
Components of IoT
Digital twins are typically created by gathering data and creating computational and mathematical models for testing. This process includes a link between the physical model of the object or item (often sensors) and its digital copy to send and receive real-time data and feedback.
IoT comprises several pieces of technology that function together to create the link between the physical object and its digital twin. The most basic, and the most important, are the wireless sensors, the connection to the cloud and storage, and the end users/interfaces, as shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4. Crucial IoT Components [wpdatatable id=2181 table_view=regular]
Source: Coresight Research
- For more about IoT digital twins and 5G’s importance as a complementary technology, please refer to Building Blocks of the Metaverse: 5G.
Considerations When Setting up a Digital Twin
In the long-term, incorporating each IoT component will help brands and retailers to set up digital twins for metaverse simulations of stores and operations. To properly configure an IoT digital twin, brands and retailers should understand how data processing and modeling can help to link physical and virtual objects.
Data and Modeling
Information must be processed after being sent to the cloud; the data can represent many different features of product information, including lifecycle, design specifications, production information, equipment, materials, historical analysis and real-time feedback. After the link between the physical and virtual object is set up and the data is processed, the end user (customer or employee) can make a decision on what action to perform next as they receive real-time data and information.
After collecting massive amounts of data, retailers and brands can begin to create analytical and digital twin models of stores, warehouse, factories or any real-world location that could benefit in some manner from simulating operations. In doing so, they will be able to create perfect replicas of real-world locations and simulate thousands of production scenarios before they determine most efficient strategies and resource allocation.
Linking
Using the combined findings from multiple digital twins that can be linked with one another, brands and retailers can create digital-twin factories or stores. The links between physical and virtual objects are enabled by cellular networks and Wi-Fi, allowing devices to communicate with their twins in real time.
In the future, as more assets come to be represented as non-fungible tokens (NFTs), IoT digital twins may eventually be tied to specific NFTs, and brands and retailers may consider incorporating blockchain and cryptocurrency infrastructure to facilitate smooth cross-border payments and instantaneous transactions for their digital-twin stores. In warehouses and factories, NFTs tied to digital twins can improve traceability and help retailers identify supply chain constraints and bottlenecks.
- For more about how the blockchain unlocks cross-border payments, read our report, Building Blocks of the Metaverse: The Blockchain.
- For more about benefits of adopting cryptocurrencies for retailers, read our report, Building Blocks of the Metaverse: Cryptocurrencies.
Benefits
Brands and retailers leveraging IoT digital twins have been able to improve efficiency in a number of aspects of their businesses. We discuss the benefits of risk assessment, remote monitoring and maintenance in Figure 5.
Figure 5. Benefits of Incorporating IoT Digital Twins [wpdatatable id=2182 table_view=regular]
Source: Coresight Research
What We Think
IoT is a broad field with many practical purposes, and many elements of their technologies will be crucial for brands and retailers to incorporate as they look to establish a footing in Web 3.0. By linking the physical and virtual worlds through digital twins, brands and retailers can offer flagship locations and experiences to customers all over the world and simulate operations, significantly expanding their global reach and customer base, as well as reducing costs and improving sustainability initiatives.
Setting up a digital twin can be time-consuming, but we believe that the technology can help retailers build a stronger and more efficient organization that quickly responds to changing consumer tastes. It is crucial to understand how digital-twin technology incorporates sensors to amass massive amounts of data, model scenarios, and link the physical and digital worlds.
Appendix: About Coresight Research’s RESET Framework
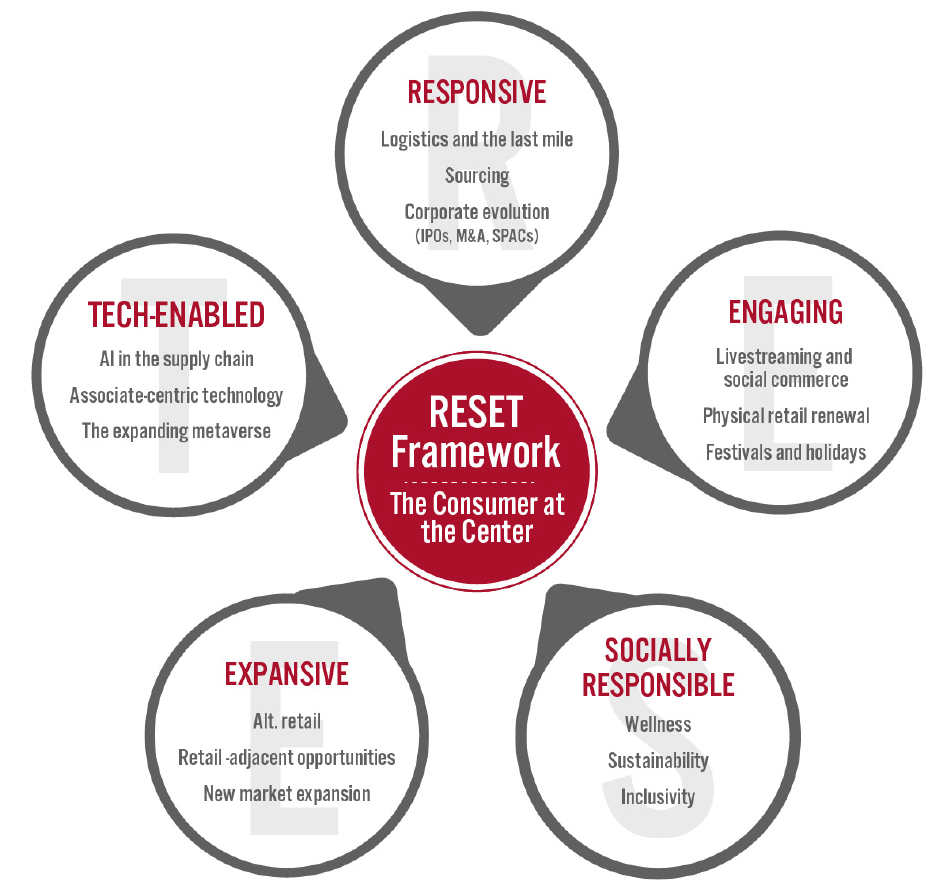
Coresight Research’s RESET framework for change in retail serves as a call to action for retail companies. The framework aggregates the retail trends that our analysts identify as meaningful for 2022 and beyond, as well as our recommendations to capitalize on those trends, around five areas of evolution. To remain relevant and stand equipped for change, we urge retailers to be Responsive, Engaging, Socially responsible, Expansive and Tech-enabled. Emphasizing the need for consumer-centricity, the consumer sits at the center of this framework, with their preferences, behaviors and choices demanding those changes.
RESET was ideated as a means to aggregate more than a dozen of our identified retail trends into a higher-level framework. The framework enhances accessibility, serving as an entry point into the longer list of more specific trends that we think should be front of mind for retail companies as they seek to maintain relevance. Retailers can dive into these trends as they cycle through the RESET framework.
The components of RESET serve as a template for approaching adaptation in retail. Companies can consolidate processes such as the identification of opportunities, internal capability reviews, competitor analysis and implementation of new processes and competencies around these RESET segments.
Through 2022, our research will assist retailers in understanding the drivers of evolution in retail and managing the resulting processes of adaptation. The RESET framework’s constituent trends will form a pillar of our research and analysis through 2022, with our analysts dedicated to exploring these trends in detail. Readers will see this explainer and the RESET framework identifier on further reports as we continue that coverage.
Appendix Figure 1. RESET Framework [caption id="attachment_143517" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]