
albert Chan
Introduction
What’s the Story?
Coresight Research has identified the expanding metaverse as a key trend to watch in retail and a component trend of Coresight Research’s RESET framework for change. That framework provides retailers with a model for adapting to a new world marked by consumer-centricity, in 2022 and beyond (see the appendix of this report for more details).
In this report, we explore digital payments in the metaverse, covering the underlying technologies as well as payment solutions and channels.
This report forms part of our Building Blocks of the Metaverse series, which presents insights into the core technological components of the retail metaverse, including important details for retailers to know in establishing a presence and operating in the virtual space.
Why It Matters
In recent years, many new and highly technical payment methods for retailers, brands and businesses have emerged to increase efficiency, reduce costs and help unlock trade barriers. As consumers continue their shift toward a digital life, payment systems and solutions are evolving at a rapid pace—and have been accelerated by the emergence of the metaverse and Web 3.0. Unless metaverse and virtual economy payment infrastructure is secure, fast and reliable, retailers and brands will be less likely to use it as a new channel for sales and customer interaction.
The blockchain is a distributed ledger that will power cryptocurrencies (the currency of the metaverse) and digital assets, such as non-fungible tokens (NFTs). However, the payment channels and methods by which transactions are completed and funds are received can vary significantly by blockchain and payment solution, and are crucial components of metaverse infrastructure. Without speed and reliability, the potential of joining a virtual economy and ecosystem, accessing customers from distant corners of the world seamlessly, is diminished.
Web 3.0 technologies, such as cryptocurrencies, NFTs and the blockchain, are experiencing volatility (as is the rest of the world economy), as of the midway point of 2022. Still, as access to technology (such as smartphones and 5G connectivity) continues to improve, global digital payments will increase at a rapid pace (see Figure 1)—and developers continue to improve upon payment solutions.
Figure 1. Digital Commerce and Mobile Payment Transaction Value (USD [caption id="attachment_150715" align="aligncenter" width="550"]
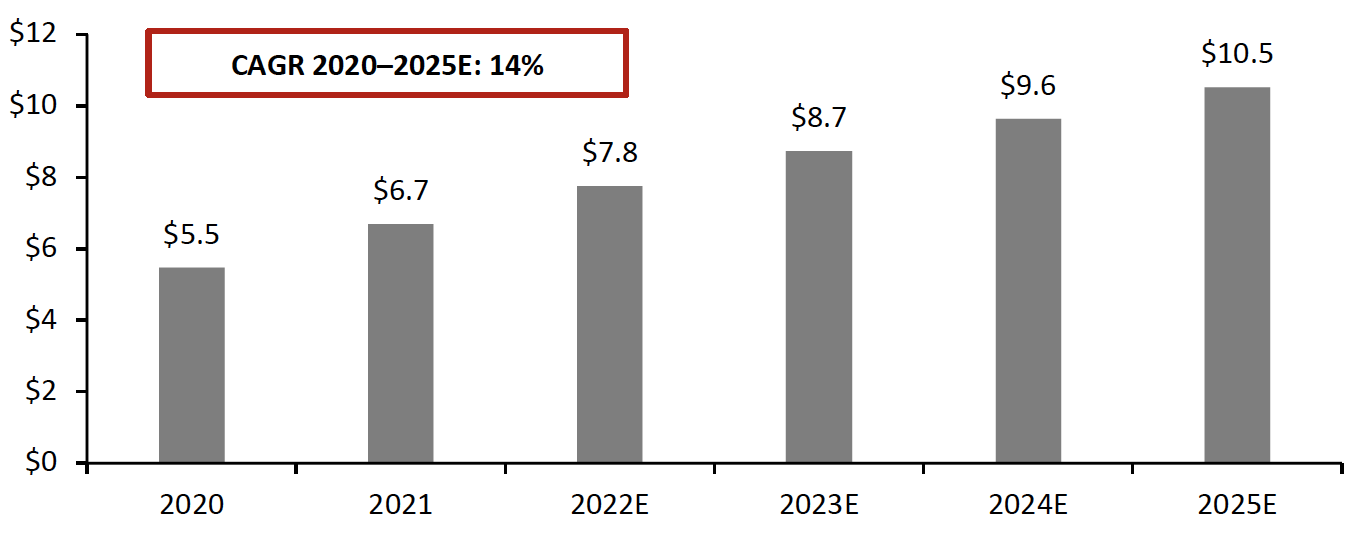 Source: Statista[/caption]
Source: Statista[/caption]
Metaverse-specific crypto tokens, such as Decentraland’s MANA or The Sandbox’s SAND, used as currency and for payments by users on the platforms and in respective marketplaces, can also be used gauge financial health. Metaverse tokens have not been immune to the recent price crash of cryptocurrencies, but, with little interoperability (transferability of assets between platforms), their individual prices should not matter, as payment processors allow for immediate conversion to fiat currencies.
Whether Web 3.0 technologies, such as cryptocurrencies and NFTs, are adopted rapidly in the near term or slowly over the course of decades, metaverse and digital activities continue to increase on a global basis, as does access to metaverse-related technologies. It will be essential for brands and retailers to incorporate efficient payment systems that allow them to adequately handle the increase in customers that Web 3.0’s connectivity will bring.
Building Blocks of the Metaverse—Payments: Coresight Research Analysis
Components of Metaverse Payments
Metaverse payments require multiple components, with the most essential being the following:
- Blockchain, cryptocurrencies and NFTs (non-fungible tokens) to achieve decentralization
- Digital wallets to send/receive funds and hold assets
- Crypto payment gateways to process digital transfers and funds (for businesses, brands and retailers)
We explore each in detail below.
Blockchain, NFTs and Cryptocurrencies
The blockchain is a system in which multiple nodes (computers) work together to form a peer-to-peer network which is responsible for maintaining a ledger of digital transactions; this is similar to a bank’s ledger, but no one entity has control to manipulate or change transactions, making the system decentralized. Cryptocurrencies and NFTs, which will eventually come to represent all metaverse assets and unique products, are powered by the blockchain and are essential for establishing in-world metaverse economies.
Despite the ongoing plummet in NFT prices, transaction volume is somewhat steady and still spikes on days in which popular collections are released. As the world continues to move toward Web 3.0 and retailers find new and innovative ways to utilize the blockchain’s security, verification and efficiency through NFT-related strategies, blockchain systems are becoming more and more important for supporting increased transaction volume.
Within each virtual world, users and customers will pay for assets and virtual products (held in the form of NFTs) for their avatars and personal virtual spaces by using the world’s cryptocurrency token.
Digital Wallet
Cryptocurrency and digital wallets, such as Coinbase Wallet, NFT- and metaverse-specific wallets MetaMask and Meta Pay, BlockFi and Crypto.com will be crucial for payments in the metaverse. Both users and creators as well as smaller businesses, retailers and brands will use these wallets as a means to store cryptocurrency funds and NFTs, engaging in direct trade with customers within virtual worlds. In addition, exclusive access to NFTs is available in the wallets, along with the private and public keys to send, receive and unlock cryptocurrency payments.
Although the number of active wallets has crashed from its peak at the start of 2022, there is still a steady number of daily wallet and NFT unit sales (see Figure 2).
Figure 2. NFT Transaction Volume (Daily Unit Sales) and Active Market Wallets, 2022 YTD
[caption id="attachment_150716" align="aligncenter" width="700"]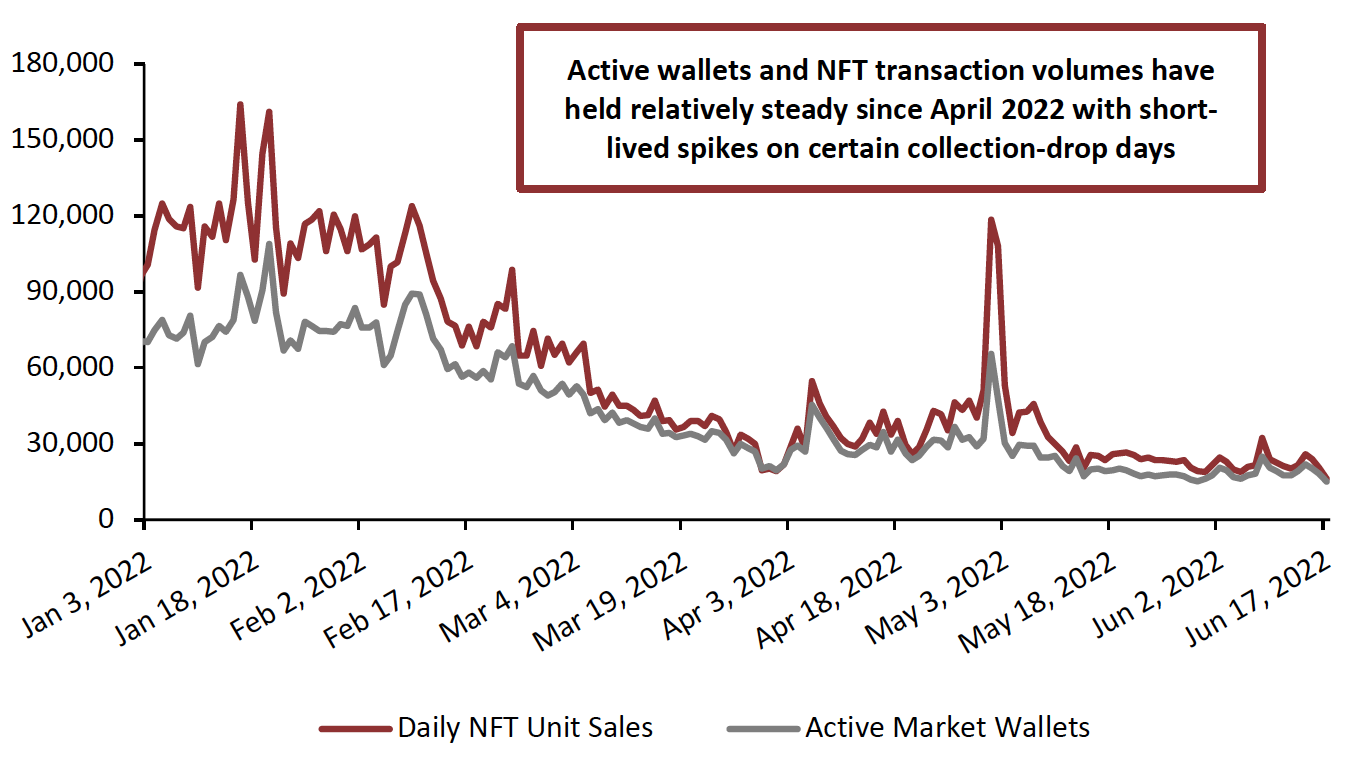 Source: Non-Fungible[/caption]
Meta Platforms, of one Web 3.0’s earliest pioneers, announced on June 27, 2022, that it was developing a digital wallet, Meta Pay, specifically for customers to tie to their digital identities and purchase virtual assets and digital products. Similar to MetaMask, Meta Pay will focus on two important aspects of virtual economies: securing digital ownership and providing easily accessible digital assets.
Using crypto wallets, retailers, businesses and customers can enjoy the benefits of the blockchain, including security, immutability, immediate transfer and anonymity, which allow trade within virtual worlds and economies to flourish. However, while blockchains are generally secure, wallets and companies operating those wallets are not necessarily reliable and may be prone to breaches and hacks. It is important for retailers to choose a wallet that has sufficient safeguards against theft of funds and potential breaches of data. BlockFi Wallet, for example, does not operate with its own token and has opened itself up for federal regulation; as a result, it has not yet reported a significant theft (though it has had a data breach).
Given the recent price crash in cryptocurrencies, it is understandable that many retailers and brands are still hesitant to adopt these technologies. To help remove the barriers to digital trade and entering virtual worlds, fintech giants such as MasterCard have filed patents for virtual credit and debit cards in the metaverse, and Visa and Amex are not far behind in metaverse-related consulting. It may soon be possible for retailers to access a larger customer base through the metaverse without adopting crypto, although they would not enjoy any of the blockchain’s benefits.
Source: Non-Fungible[/caption]
Meta Platforms, of one Web 3.0’s earliest pioneers, announced on June 27, 2022, that it was developing a digital wallet, Meta Pay, specifically for customers to tie to their digital identities and purchase virtual assets and digital products. Similar to MetaMask, Meta Pay will focus on two important aspects of virtual economies: securing digital ownership and providing easily accessible digital assets.
Using crypto wallets, retailers, businesses and customers can enjoy the benefits of the blockchain, including security, immutability, immediate transfer and anonymity, which allow trade within virtual worlds and economies to flourish. However, while blockchains are generally secure, wallets and companies operating those wallets are not necessarily reliable and may be prone to breaches and hacks. It is important for retailers to choose a wallet that has sufficient safeguards against theft of funds and potential breaches of data. BlockFi Wallet, for example, does not operate with its own token and has opened itself up for federal regulation; as a result, it has not yet reported a significant theft (though it has had a data breach).
Given the recent price crash in cryptocurrencies, it is understandable that many retailers and brands are still hesitant to adopt these technologies. To help remove the barriers to digital trade and entering virtual worlds, fintech giants such as MasterCard have filed patents for virtual credit and debit cards in the metaverse, and Visa and Amex are not far behind in metaverse-related consulting. It may soon be possible for retailers to access a larger customer base through the metaverse without adopting crypto, although they would not enjoy any of the blockchain’s benefits.
Crypto Payment Gateways
There are many reputable crypto payment gateways (processors) currently on the market, including BitPay, Coinbase, CoinGate, Crypto.com and Flexa, as well as processors focusing on metaverse payments, such as MoonPay. Businesses could use wallets to send and receive funds from customers, but payment gateways remove the extra work of exchanging currencies and managing multiple wallets across various platforms and applications. The customer makes a crypto payment in the metaverse, in-store or on mobile. The amount paid is equivalent to the crypto's fair market value (in fiat currency) at the time. The gateway immediately converts the cryptocurrency payment into the currency of choice, and the money is deposited into the payee’s account in intervals (decided by contract).- MoonPay
Many crypto payment gateways are actively growing their partnership ecosystem to support mass adoption of cryptocurrencies. In particular, MoonPay, founded in 2018, has employed a number of Web 3.0 and metaverse-specific initiatives.
Focused on widespread metaverse use and NFT adoption, MoonPay allows customers to purchase NFTs and cryptocurrencies with credit and debit cards and with Apple Pay and Google Pay, providing a link between the physical and virtual worlds and removing some of the barriers to cryptocurrency and NFT trading.
In April 2022, MoonPay, serving as a ramp provider (bridge from fiat to cryptocurrency), announced a partnership with metaverse-specific wallet MetaMask, simplifying the process of trading and selling digital assets and tokens and making cryptocurrency payments. Available in more than 150 countries, MoonPay is significantly increasing MetaMask’s utility and global user base. MoonPay also offers ramp services for users in Solana-backed metaverse platform Star Atlas.
MoonPay is also the official payment processor of FaZe Clan, a gaming and esports organization whose members create engaging content and compete in hundreds of immersive multiplayer games, including Call of Duty, Counterstrike, Fortnite and Rocket League. Top FaZe Clan gamers are extremely influential, setting trends within platforms; they are already in-game and real-world celebrities. MoonPay will serve FaZe Clan’s digital marketplace, and the two will work together to create NFT-related products and content that stimulates growth in virtual-world economies.
Metaverse Payment Solutions and Channels
Many individual metaverse projects, such as Decentraland, The Sandbox and Star Atlas, depending on the blockchain they use, already feature in-world payment solutions. Any brand or retailer that has opened a storefront or sold virtual products to avatars within these platforms, such as in Decentraland’s Fashion Week, has taken advantage of these payment solutions. While wallets and payment gateways provide retailers, businesses and customers with the means to send, receive and hold digital assets and currencies, the payment solutions and channels can vary significantly by each NFT or digital asset marketplace, and often sacrifice speed and efficiency for security. Mainnet blockchains, such as Ethereum and Bitcoin, never suffer from large hacks, but many blockchain payment channels are often more centralized, meaning control is less distributed in the network. Layer 2 blockchains are scaling solutions and protocols that are built on top of Mainnet blockchains (such as Ethereum, Bitcoin, Cardano, etc.); they incorporate the Mainnet’s security and help improve speed, efficiency and scalability. Sidechains, similar to Layer 2 solutions, are separate blockchain networks with their own security mechanisms that run parallel to the Mainnet; they are also being developed as scaling and speed solutions. Layer 2 and sidechain projects will typically have their own cryptocurrency token and ecosystem of projects and platforms. There are already hundreds of Layer 2 projects and sidechains for multiple blockchains. We discuss three notable examples for metaverse payments below.Immutable X
Immutable X is a Layer 2 blockchain solution developed specifically to support higher-volume NFT trade in the Ethereum Mainnet. It has its own token, IMX, which has a market capitalization of over $150 million as of July 27, 2022, according to CoinMarketCap. Despite the ongoing cryptocurrency price crash, Immutable X is still investing heavily in developing its ecosystem—it announced a $500 million developer fund on June 17, 2022. To improve scalability, speed and efficiency, Immutable X employs zero-knowledge (ZK) rollups—when blockchain solutions group a large number of transactions together, validate transactions and data with a third party off-chain (in Immutable X’s case, infrastructure provider StarkWare), and produce a single cryptographic hash for all the transactions, rather than a hash for each transaction. Immutable X covers the associated gas fee, which can vary based on network congestion and energy consumption, after moving the batch of transactions back onto the Mainnet blockchain. However, in using a third party (a much less decentralized system), Immutable X sacrifices security for efficiency. Immutable X has partnered with short-video social platform TikTok in the past to mint and sell NFTs of top TikTok moments, featuring six culturally relevant moments from top creators, including NIKE’s digital fashion division, RTFKT. Additionally, gaming retailer GameStop is working with Immutable X to create its NFT marketplace for gaming collectibles. [caption id="attachment_150717" align="aligncenter" width="550"]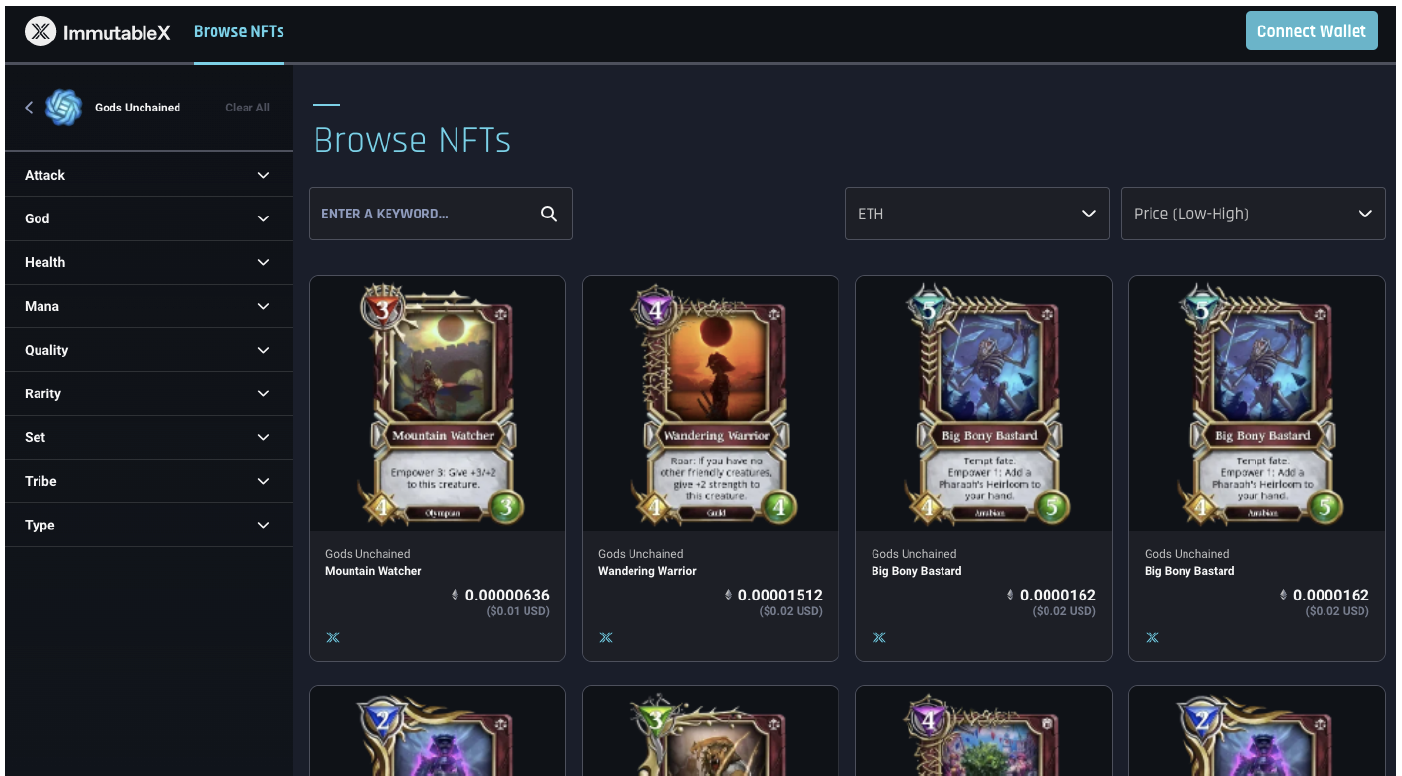 NFT marketplace for blockchain game Gods Unchained
NFT marketplace for blockchain game Gods UnchainedSource: Immutable X[/caption]
Polygon
Polygon is a Layer 2 solution for all tokens built on the Ethereum standard; it has a market capitalization of over $4 billion as of June 27, 2022, according to CoinMarketCap.
MANA and SAND, of Decentraland and The Sandbox, respectively, are tokens built on the ERC-20 token standard, backed by the Ethereum blockchain. However, because Decentraland and The Sandbox have integrated Polygon technology, users of both these platforms can enjoy Polygon’s efficiency and speed using its token, MATIC.
[caption id="attachment_150718" align="aligncenter" width="550"]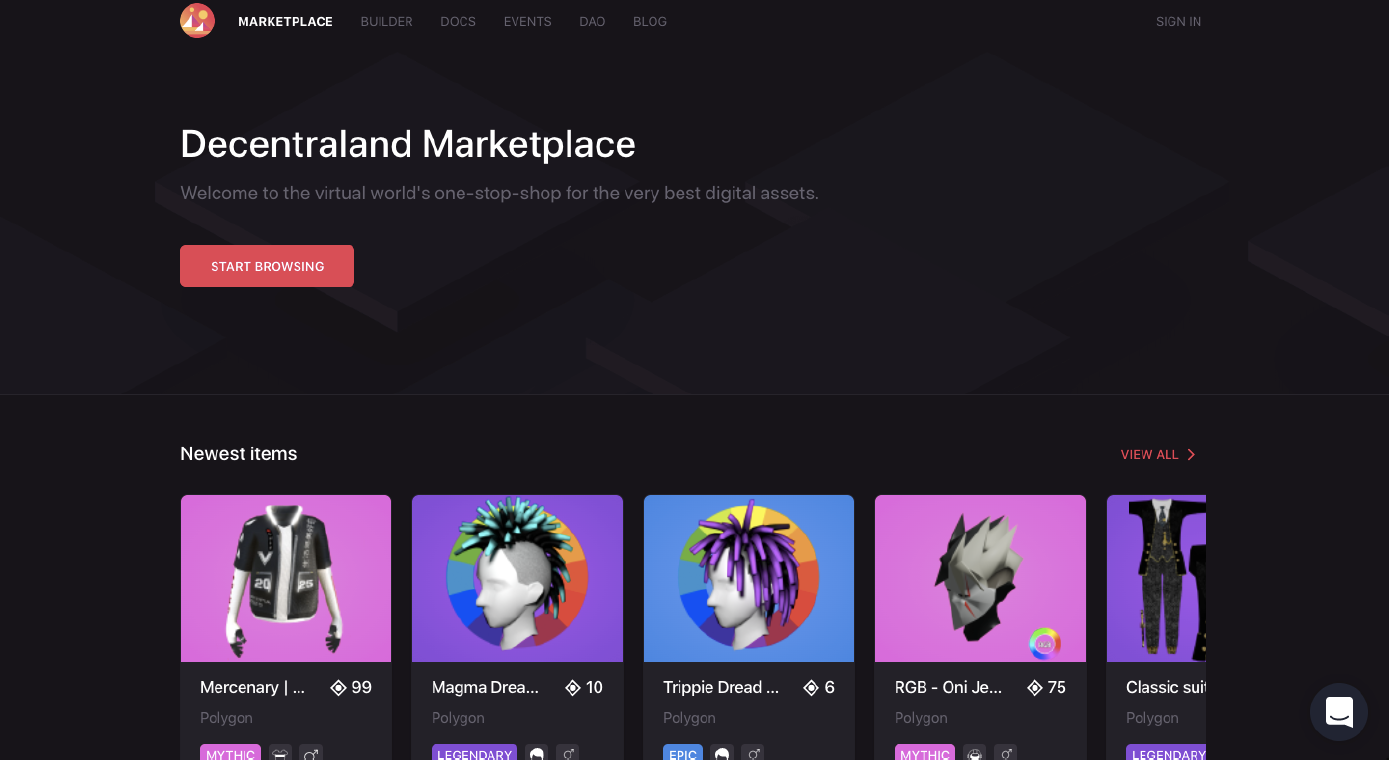 NFT marketplace for Decentraland
NFT marketplace for DecentralandSource: Decentraland[/caption] Developers building on Polygon’s proof-of-stake blockchain are able to build Ethereum-based decentralized applications as sidechains with the use of ZK rollups. Polygon technology also employs plasma chains–bundling a number of transactions into their own block on top of the Mainnet architecture and hashing it in a single submission. To support payments in blockchain-based games, Polygon also employs “optimistic rollups,” which are similar to plasma chains but for smart contract scalability (crucial for digital asset trade). Polygon claims that these Layer 2 technologies make its proof-of-stake system 99.95% more efficient than traditional proof-of-work blockchains such as Ethereum (though Ethereum is undergoing a merge with another blockchain to switch to this mechanism and will soon be as efficient on its own). Again, however, sidechains and rollups are more centralized and thus prone to hacks. Many fashion brands have recognized Polygon as a go-to blockchain for carbon-neutral NFTs:
- Luxury brand Dolce & Gabbana, active in NFT markets, minted a collection through a partnership with digital asset place UNXD and Polygon, which fetched $6 million for the brand.
- Department store Macy’s partnered with Sweets NFT Marketplace and Polygon to sell $9,500 NFTs inspired by the Macy’s Thanksgiving Day Parade.
- Sportswear brand Adidas and luxury brand Prada collaborated for an NFT collection minted on the Polygon blockchain; the collection was designed as a reward for Adidas NFT holders.
- Meta announced in May 2022 that NFTs would be coming to Instagram for creators and brands to sell digital products via a partnership with Polygon, citing its scalability and carbon-neutral footprint.
Arbitrum
Another Layer 2 blockchain solution that has been making headlines recently is Arbitrum, which is built on the Ethereum blockchain. Arbitrum utilizes a sidechain that processes transactions with the Ethereum token, meaning that it does not need a native token for its own ecosystem of developers and projects. Like Polygon, Arbitrum also uses optimistic rollups, which, as opposed to ZK rollups, do not validate transactions before batching them together (transaction verification can be disputed and resolved at a later point).
Horseracing-based metaverse platform Game of Silks announced a partnership with Arbitrum in April 2022, integrating its payments technology to improve gameplay in its in-game economy. Game of Silks chose Arbitrum for its significant ability to scale the Ethereum blockchain.
Technology platform Request Finance employs Arbitrum technology to provide crypto invoicing, payroll and expenses, allowing businesses, brands and retailers to manage, view and pay all their crypto invoices in one place. Thousands of Web 3.0 startups and companies are beginning to use the service to pay suppliers, employees and contributors in crypto—an important concept as the metaverse develops.
What We Think
Blockchain and cryptocurrencies provide efficiency, speed and security, representing the backbone of metaverse payments and allowing virtual economies to be completely decentralized. There are many other technological components to digital payments in the virtual world, including payment gateways and digital wallets. Retailers and brands can begin using, exploring and testing these technologies even before entering a metaverse platform to sell virtual products, services and experiences to customers. This would enable them to take advantage of an increasing number of digital customers who are becoming more and more connected as the metaverse and its underlying technologies evolve.
Sidechains and Layer 2 solutions for payments in the metaverse may improve efficiency, speed and scalability but will often sacrifice security. As payment technology improves and developers invest in finding better systems and mechanics, this tradeoff will likely disappear.
Understanding payment solutions and underlying technologies is crucial for brands and retailers looking to take advantage of the blockchain’s massive potential; although it is still in its earliest days and suffering from volatility and skepticism, the technology over the next five to 10 years is set to improve significantly.
Appendix: About Coresight Research’s RESET Framework
Coresight Research’s RESET framework for change in retail serves as a call to action for retail companies. The framework aggregates the retail trends that our analysts identify as meaningful for 2022 and beyond, as well as our recommendations to capitalize on those trends, around five areas of evolution. To remain relevant and stand equipped for change, we urge retailers to be Responsive, Engaging, Socially responsible, Expansive and Tech-enabled. Emphasizing the need for consumer-centricity, the consumer sits at the center of this framework, with their preferences, behaviors and choices demanding those changes.
RESET was ideated as a means to aggregate more than a dozen of our identified retail trends into a higher-level framework. The framework enhances accessibility, serving as an entry point into the longer list of more specific trends that we think should be front of mind for retail companies as they seek to maintain relevance. Retailers can dive into these trends as they cycle through the RESET framework.
The components of RESET serve as a template for approaching adaptation in retail. Companies can consolidate processes such as the identification of opportunities, internal capability reviews, competitor analysis and implementation of new processes and competencies around these RESET segments.
Through 2022, our research will assist retailers in understanding the drivers of evolution in retail and managing the resulting processes of adaptation. The RESET framework’s constituent trends will form a pillar of our research and analysis through 2022, with our analysts dedicated to exploring these trends in detail. Readers will see this explainer and the RESET framework identifier on further reports as we continue that coverage.
Appendix Figure 1. RESET Framework [caption id="attachment_143517" align="aligncenter" width="550"]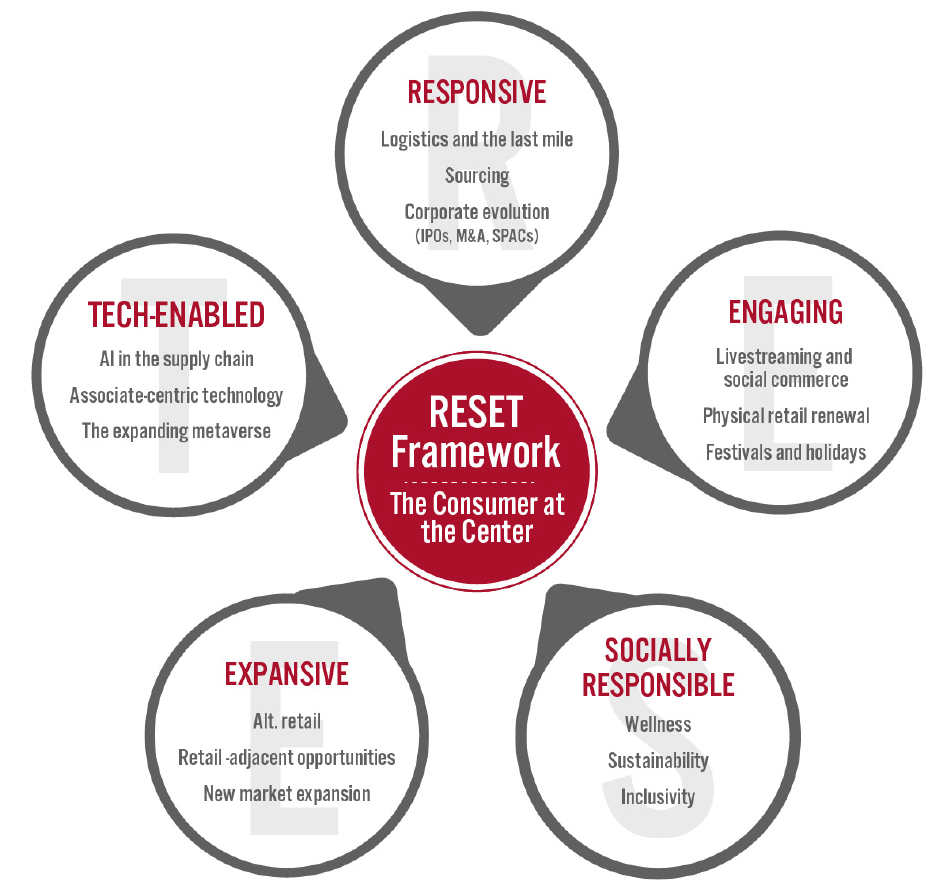 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]