
albert Chan
Introduction
What’s the Story?
Coresight Research has identified the expanding metaverse as a key trend to watch in retail and a component trend of Coresight Research’s RESET framework for change. That framework provides retailers with a model for adapting to a new world marked by consumer-centricity, in 2022 and beyond (see the end of this report for more details).
In this report, we explore the development of cryptocurrencies, analyze their technological structure and relationship with the metaverse, and explore what retailers and brands should know as they consider adoption.
This report forms part of our Building Blocks of the Metaverse series, which presents insights into the core technological components of the retail metaverse, including important details for retailers to know in establishing a presence and operating in the virtual space.
Why It Matters
Fiat currencies, which are legal tender by government decree, have been in existence since the 10th century, first introduced in ancient China. Since then, they have dominated the basis for international and domestic trade and commerce, setting limits and restrictions on businesses and individuals and giving central banks authority to manipulate global markets.
The first concept of a digital currency, not tied to any government or institution and removing many restrictions, was developed in 1996, with e-gold, but it was shut down in 2008 by the US government. Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency—a digital currency based on a distributed ledger (blockchain)—introduced in 2009, closely following the Great Recession.
Since then, hundreds of crypto tokens have been released, gaining significant popularity. Although volatile in the short run, many of them have systems that will be crucial to the evolution and adoption of the metaverse, as they will enable unified virtual economies spanning many countries and platforms. In other words, cryptocurrencies will be the currency of the entire metaverse universe.
Because much of the current total cryptocurrency market capitalization—which has skyrocketed since 2017 (see Figure 1)—is due to speculation on future use/potential, price volatility is extreme, but over the course of the metaverse’s evolution, certain tokens will be important for establishing functioning in-world economies, gauging the financial health of platforms and unlocking active cross-border commerce for brands and retailers to connect to digital customers.
Figure 1. Combined Market Capitalization of All Cryptocurrency Tokens (USD Bil.) [caption id="attachment_148417" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
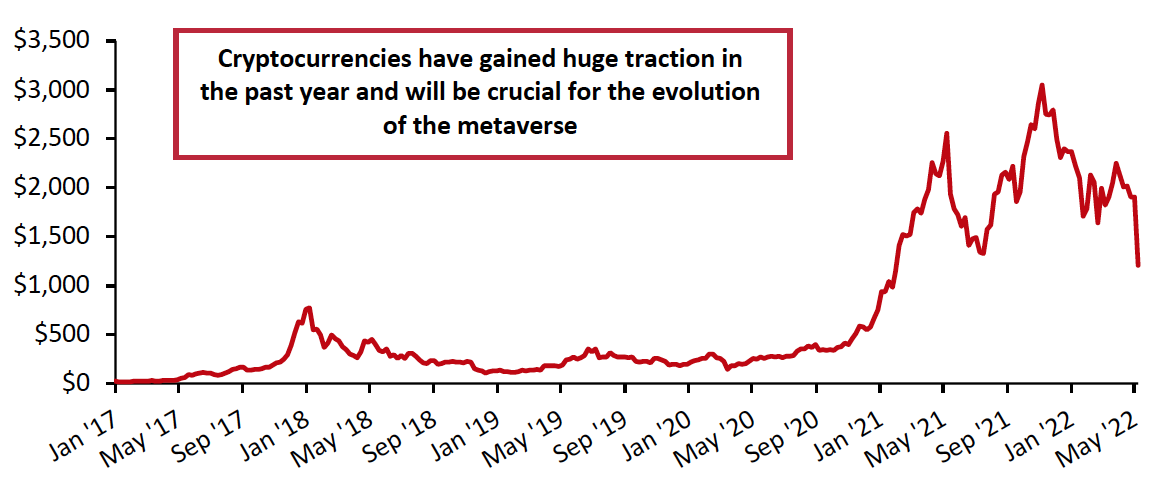 Source: BitInfoCharts/CoinGecko/Statista[/caption]
Source: BitInfoCharts/CoinGecko/Statista[/caption]
Many emerging technologies that form the basis of the metaverse, such as 5G and augmented/virtual reality are mostly available in developed countries as they are in their earlier stages of growth, but cryptocurrencies are helping impoverished communities and those living in chaotic countries with unstable currencies and governments to maintain some sense of economic stability.
As of April 2022, despite the ongoing crypto price crash, 14.6% of respondents surveyed across 27 countries active within crypto markets are still holding cryptocurrency—a rather small drop from a reported 15% in January 2022—according to a survey conducted by cryptocurrency guide Finder.
Short-term volatility can make cryptocurrencies appear to be daunting, but their technologies will be crucial for adoption of the metaverse, removing various trade barriers to support high-volume activity and providing consumers with enhanced security in functional virtual economies.
Building Blocks of the Metaverse—Cryptocurrencies: Coresight Research Analysis
Connection to the Metaverse: Two Key Benefits
The global metaverse ecosystem will benefit from cryptocurrencies in two critical ways, which we explore below.
1. Removing Trade Barriers
Virtual worlds and metaverse experiences will be easily accessible for customers all over the world, meaning that digital footfall in highly trafficked areas will be higher than physical footfall in popular real-world locations, such as New York’s Times Square. Countless brands and potentially billions of customers that were previously in-accessible (due to distance or international borders) will be interacting with one another and making transactions.
There are three features of cryptocurrencies that support high-volume trade, which we present in Figure 2 and discuss further below.
Figure 2. Features of Cryptocurrencies That Support High-Volume Trade
[wpdatatable id=2019] Source: Coresight ResearchTransaction Speed: Enabled by blockchain, cryptocurrencies are instantaneous, not delayed by third parties such as banks and currency exchanges. In the virtual world, where assets are simple to create and hundreds of thousands of experiences and products are accessible to anyone from anywhere, cryptocurrencies are crucial for securing records of transactions and supporting high-volume in-world trade and activity (both domestic and international/cross-border). Interoperability will unite the various crypto tokens and digital assets in a single ecosystem or economy.
Transaction costs: In traditional finance, transaction costs are a large issue for consumers. Around 61% of consumers globally sent international payments in 2021, with 53% of those consumers believing that fees were too high—although only 20% used cryptocurrencies for payments—according to a survey conducted in late 2021 by nonprofit blockchain company Stellar Development Foundation.
In the fourth quarter of 2022, the average global fee for remittance payments was 6.04% of the payment amount, per the World Bank. This figure can be significantly higher in emerging countries where payment infrastructure is underdeveloped. Cryptocurrencies remove these associated costs, meaning that metaverse economies should theoretically be more fluid than economies based on traditional finance.
Although some blockchains feature gas fees (fees associated with transactions that are paid to the miner and to account for energy consumption), many Layer 2 blockchain solutions and newly released blockchains are able to eliminate gas fees entirely.
Security: Once heralded as “un-hackable” by proponents, in their infancy, blockchains and cryptocurrencies have proven to be susceptible to breaches, and developers are still determining which systems for cryptocurrencies and mechanisms for validating transactions will be successful and secure moving forward.
Much like in the real world, users will be able to buy and sell virtual assets—which don’t degrade or have a production cost—despite the assets’ or users’ native environment or game. Virtual assets (such as non-fungible tokens, NFTs) do not have a traditional production cost and do not degrade in value, features that support an active virtual secondary market that significantly increases trade volume and is supported entirely by crypto tokens.
2. Establishing Functional Virtual Economies
Because token supplies for specific blockchain worlds are usually fixed, decentralized applications can drive value for users, creating functional in-world economies; token value and mechanics are also key metrics for gauging financial health and future prospects for individual worlds. Deciding which world to join is a critical decision for businesses of all types looking to establish a permanent metaverse residence.
Although crypto tokens have different supplies, many are built on the same blockchain, and in the future, tokens constructed on different blockchains will be interoperable with one another, meaning that all NFTs or digital assets can exist in the same universe. Because of these features, cryptocurrencies are crucial for creating a united metaverse in which all transactions and assets (tied to cryptocurrency wallets that are capable of supporting multiple tokens) exist. Customers will be able to purchase a digital product, or NFT, with its native blockchain token. Additionally, they will be able to instantaneously exchange one token for another at an in-world or platform exchange as they traverse the metaverse.
Each blockchain game is going to have its own unique token; these tokens are how value is created in individual environments. Different environments may be based on the same blockchain, but have different tokens. For example, Decentraland’s MANA token and The Sandbox’s SAND token are both constructed on the Ethereum blockchain, but have different circulations and supplies that depend on the specific world itself. MANA and SAND, and other tokens constructed on the Ethereum blockchain (as opposed to the currency), can be thought of as separate denominations of Ethereum.
We show the different tokens of popular blockchain games in Figure 3. The circulating supply represents the number of tokens in public hands, and the maximum supply is the total number of tokens that will ever be minted in the lifetime of the cryptocurrency—some have not yet been created and are still waiting to be entered into circulation. Much of the price run-up over the previous five years has been due solely to speculation, though these worlds have set up the fundamentals to drive value and thus establish functional in-world economies based on their tokens.
Figure 3. Popular Blockchain Games and Token Features [wpdatatable id=2020] *As of May 26, 2022 Source: CoinMarketCap/Coresight Research
Underlying Technology
Like NFTs, cryptocurrencies are enabled by blockchain, which is the basis of decentralized finance. However, the underlying mechanics relevant to cryptocurrency are important for retailers and brands to understand as they establish long-term plans for blockchain and digital currency adoption amid a turbulent time for the technologies.
Cryptography
In its simplest terms, cryptography is the process of writing secure communication and transfer techniques. The main goal of cryptocurrencies and digital currencies is to create a system in which only the intended recipient of funds can access them. In cryptocurrency, cryptography guarantees and secures the various transactions occurring on the network, controls the creation of new tokens and verifies transfer and transactions of tokens.
In a system in which no one powerful entity (such as government or banks) has significant control over commerce or money supply, and instead various anonymous entities do, cryptography provides crucial immutability and verification of transactions.
[caption id="attachment_148418" align="aligncenter" width="700"]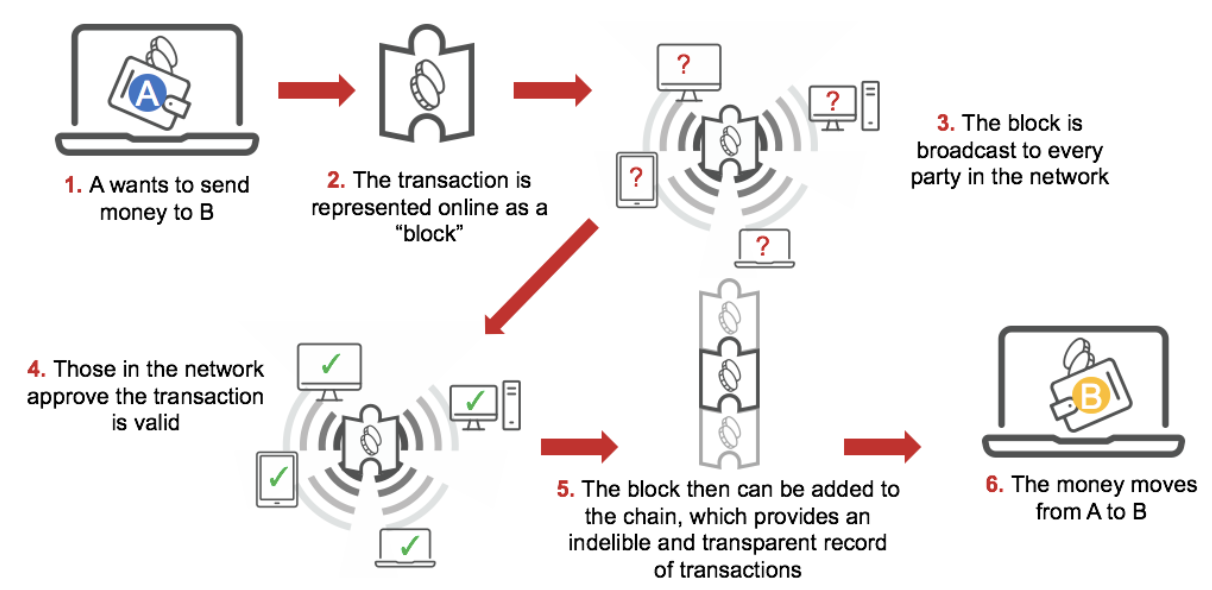 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Encryption
Encryption keys are essential, ensuring that only the authorized recipient can receive the funds—especially in the metaverse, which will feature an entirely virtual economy requiring extensive verification for ownership.
- The public key is a large number that is used to encrypt transfers and can be publicly shared safely, available to anyone. It functions as an account address and is tied to individual cryptocurrency wallets and may or may not be anonymous (users’ choice).
- The private key, which functions as a password and is located in the crypto wallet, is used to decrypt the transfer and access the funds.
Encryption and transferring funds is a three-step process:
- Funds sent to a user are encrypted with the public key, and can only be decrypted with the corresponding private key (the two are created together).
- A digital signature is generated through combining the correct private key with the encrypted funds.
- Blockchain validators automatically check and authenticate the transaction; unauthenticated transactions are rejected.
Token Standards for Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are lines of code written into the blockchain that automatically execute transactions and transfers when preset criteria are met. Token standards refer to the set of rules that smart contracts follow for how a crypto token is traded. These standards are the distinction between NFTs and cryptocurrencies and ensure that new tokens are compatible with their native blockchains.
Decentraland’s MANA and The Sandbox’s SAND, for example, are both based on the ERC-20 token standard. ERC-721 is a popular token standard for NFTs. Because multiple tokens operate on the same blockchain, Ethereum, currency and digital asset interoperability among different metaverse platforms is, in theory, a possibility, with cross-chain solutions eventually making for communication between different blockchain platforms—Ethereum and Solana for example—possible.
Most cryptocurrencies for metaverses are based on Ethereum and the ERC-20 token standard. However, newer projects based on more advanced blockchains, such as Star Atlas, powered by Solana, may function on slightly different mechanics. Each account created in the Solana chain has a unique address and is owned by a program, which enables minting, transferring and burning. The mint address for a particular token determines fungibility.
DAOs
Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) can be thought of as crypto fan clubs; they are the organizations responsible for dictating rules and governance within blockchain metaverses and token projects. These organizations can be formed in social networks such as Discord and Upstream and are able to pool resources, operating under a shared wallet and giving equal voting rights to every member in a decentralized management structure. DAOs are powered by smart contracts, which define the rules of the organization and control the treasury—no one member has access to the funds, and after member votes are tallied, decisions are automatically executed.
The most common method to gain membership and influence policy and governance decisions within particular metaverse platforms is simply owning the cryptocurrency token. In many cases, anyone owning the token, whether purchased on the secondary market (a crypto exchange) or minted themselves, can participate in voting decisions regarding that token, projects constructed on it and the allocation of funds raised in blockchain games.
What Retailers Should Know
In a metaverse setting, any retailer or brand that has minted an NFT collection or conducted commerce in a blockchain game (such as in Decentraland’s Fashion Week) has taken advantage of cryptocurrency’s benefits, transacting anonymously, instantly and securely with customers from all over the world. Before the NFT craze of 2020/2021, however, many retailers, brands and businesses had already started accepting cryptocurrency payments from customers in order to begin familiarizing themselves with the technology. Although there are many risks involved, there are ways for brands and retailers to hedge these risks.
Cryptocurrency adoption varies by country, but global firms are beginning to construct and deliver infrastructure to emerging areas, which typically suffer from frequent government issues, inflation, currency instability and poor payment infrastructure. Cryptocurrencies are also volatile, but if more global businesses begin to accept crypto payments due to their ability to remove trade barriers, this volatility will begin to settle as the world continues to learn which token and blockchain mechanics are sustainable moving forward.
[caption id="attachment_148419" align="aligncenter" width="700"]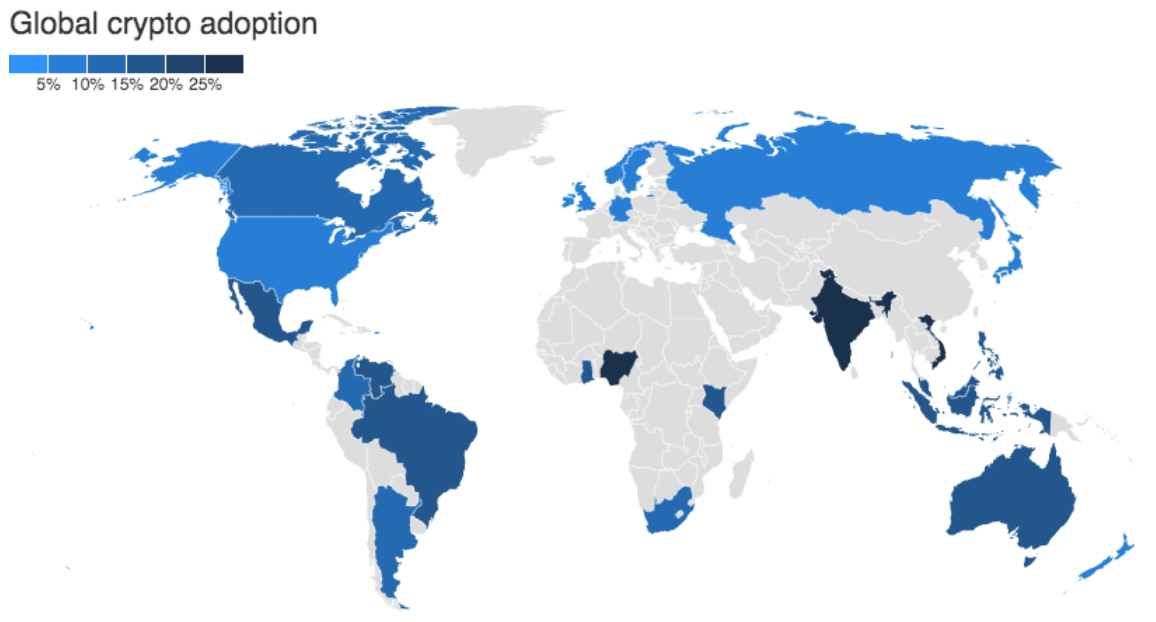 Global cryptocurrency adoption: ownership rate (%), as of May 2022
Global cryptocurrency adoption: ownership rate (%), as of May 2022Source: Finder[/caption]
Wallets and Payment Processors
As a first step to accepting cryptocurrency payments, and eventually establishing a presence in the metaverse, brands and retailers should look into cryptocurrency wallets and payment processors.
Users who do not have crypto wallets will still be free to explore, but it will be impossible to participate in economic activities in the virtual world; they will have to be redirected to websites. Similarly, retailers that want to sell directly to customers in-world and take advantage of the benefits of cryptocurrency will need to set up crypto wallets to store the game’s tokens they receive from NFT sales. Wallets are essential for storing cryptocurrency funds of any token and provide users with access to the private key. Popular wallets, such as Coinbase Wallet, Crypto.com Wallet and MetaMask, support multiple metaverse tokens, improving flexibility for both customers and businesses and opening the door for platform interoperability.
Retailers are also recreating physical experiences in perfect detail and adding augmented elements by using 5G digital twins, offering virtual experiences in real time and significantly expanding their customer base globally. Using a cryptocurrency wallet facilitates seamless cross-border payments that these types of metaverse experiences will require.
Whereas individual users may send funds and assets to one another based on public wallet addresses, for businesses (including retailers and brands), enlisting the services of a payment processor makes accepting crypto payments a seamless process for customers and businesses, similar to how payments are accepted in traditional finance. Payment processors—such as BitPay, Crypto.com, Coinbase and Flexa—also give customers and retailers flexibility, supporting multiple tokens, including Binance, Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Figure 5: Selected Companies That Accept Cryptocurrencies (Aside from NFTs)
[wpdatatable id=2021] Source: Company reports/Coresight ResearchRisks and Additional Considerations
Although their technology and potential moving forward is clear, the cryptocurrency markets are extremely volatile. As brands and retailers look to implement strategies involving cryptocurrency payments with the larger vision of establishing a long-term metaverse presence in mind, they should consider price volatility, returns and the security of certain systems and coins.
Price Volatility: The volatility of cryptocurrencies has been especially evident in the first half of 2022, but even between 2017 and 2021, during the astonishing price run-ups of Ethereum and Bitcoin (and many other tokens), volatility was always a concern. If a customer pays the US dollar equivalent in bitcoin, that amount may be worth significantly more or less in a matter of days or even hours. However, stablecoins and certain payment processors attempt to minimize price volatility risk.
- Stablecoins—Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies that, by some token system, maintain a value of $1.00. Examples include Binance USD, Dai, Tether and USD Coin. Stablecoins are supposedly extremely secure, but as they are digital currencies in their infancies, many have systems that are proving to be vulnerable to extreme volatility and price crashes in the turbulent crypto markets of 2022. Token systems such as Luna (a cryptocurrency) and Terra (a stablecoin) are examples to learn from moving forward; they recently made headlines for sizable price crashes.
- Payment Processors—To eliminate price volatility, many payment processors (including Flexa) offer brands and retailers the opportunity to immediately convert cryptocurrency payments to fiat currencies after the transaction is completed.
Security: Large blockchains are generally secure from large hacks and data breaches, but individual crypto wallets are prone to hacks, and exchanges may also freeze funds, meaning that users do not have total control. It will be important for businesses accepting crypto payments to ensure the exchanges and wallets they select have protocols and safeguards in place to prevent against attacks and sudden price drops.
Returns: Brands and retailers may also want to consider returns. For example, if a customer spends 1 ETH (Ethereum) on an item online, in the metaverse or for an NFT and wishes to make a return after a week or a month, the price could be significantly different. Because the blockchain is decentralized and no one entity has control over transactions, barring crypto regulation significantly, the merchant ultimately has the final say on what return to authorize—whether it be in the original US dollar amount or the token amount.
What We Think
Cryptocurrencies, with limited supplies, are the currency of the metaverse, forming the foundation of virtual economies by driving demand and value. In a virtual world where thousands of experiences will be accessible by billions of potential users, the security and immutability that the blockchain and cryptocurrencies provide will be crucial to ensuring that trade between all parties is smooth and seamless, eliminating transaction fees and the need for third parties such as banks or currency exchanges.
The blockchain is the basis of all cryptocurrencies, making it possible for decentralized ledgers and networks to form and hold records of encrypted transactions. NFTs and cryptocurrencies both operate on the blockchain, but NFTs are transferred on the basis of non-fungible token standards. Although adopting crypto payments is daunting, brands and retailers should at least start to study their mechanics, as ownership in metaverse tokens allows for participation in governance and policy decisions for decentralized applications.
Many people in the world live in chaotic countries with unstable and untrustworthy governments and fiat currencies. Over the long term, as crypto tokens’ values come to be determined by supply and demand instead of speculation about future use cases and market capitalizations, volatility will settle. Brands and retailers should look to establish cryptocurrency and metaverse strategies that consider which exchanges, wallets and payment processors are safest and most secure.
Appendix: About Coresight Research’s RESET Framework
Coresight Research’s RESET framework for change in retail serves as a call to action for retail companies. The framework aggregates the retail trends that our analysts identify as meaningful for 2022 and beyond, as well as our recommendations to capitalize on those trends, around five areas of evolution. To remain relevant and stand equipped for change, we urge retailers to be Responsive, Engaging, Socially responsible, Expansive and Tech-enabled. Emphasizing the need for consumer-centricity, the consumer sits at the center of this framework, with their preferences, behaviors and choices demanding those changes.
RESET was ideated as a means to aggregate more than a dozen of our identified retail trends into a higher-level framework. The framework enhances accessibility, serving as an entry point into the longer list of more specific trends that we think should be front of mind for retail companies as they seek to maintain relevance. Retailers can dive into these trends as they cycle through the RESET framework.
The components of RESET serve as a template for approaching adaptation in retail. Companies can consolidate processes such as the identification of opportunities, internal capability reviews, competitor analysis and implementation of new processes and competencies around these RESET segments.
Through 2022, our research will assist retailers in understanding the drivers of evolution in retail and managing the resulting processes of adaptation. The RESET framework’s constituent trends will form a pillar of our research and analysis through 2022, with our analysts dedicated to exploring these trends in detail. Readers will see this explainer and the RESET framework identifier on further reports as we continue that coverage.
Appendix Figure 1. RESET Framework
[caption id="attachment_143517" align="aligncenter" width="700"]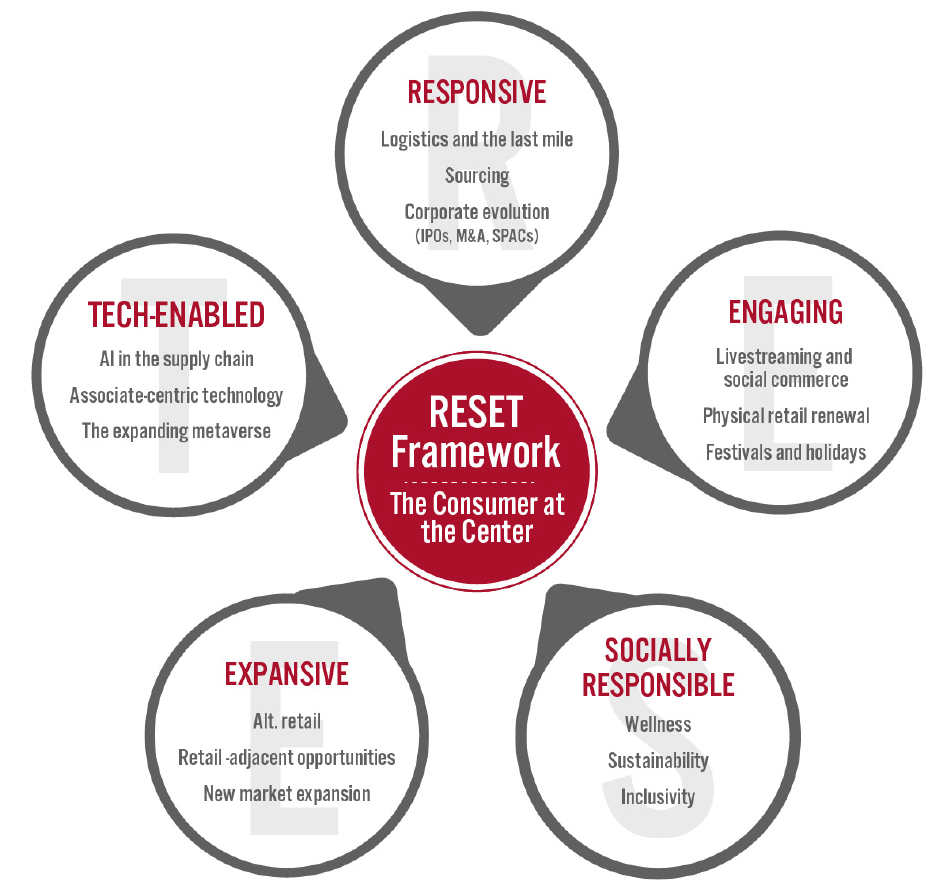 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]