
DIpil Das
Introduction
What’s the Story? Coresight Research has identified the expanding metaverse as a key trend to watch in retail and a component trend of Coresight Research’s RESET framework for change. That framework provides retailers with a model for adapting to a new world marked by consumer-centricity, in 2022 and beyond (see the end of this report for more details). 5G is the fastest and most advanced cellular network yet, outperforming the latest generation of Wi-Fi. In this report, we explore how 5G is powering the metaverse and consider what brands and retailers should know about the technology. We also provide examples of notable 5G-driven strategies by major retailers. This report forms part of our Building Blocks of the Metaverse series, which presents insights into the core technological components of the retail metaverse, including important details for retailers to know in establishing a presence and operating in the virtual space. Why It Matters 5G is the fifth generation of cellular networks and the successor to 4G, 3G and 2G, which most smartphones previously connected to. Service providers began rolling out 5G globally in 2019, and the network is set to cover 75% of the global population by 2027, according to telecommunications firm Ericsson. Truly immersive AR and VR experiences that will keep users engaged for hours require extremely fast and low-latency networks. With widespread 5G coverage, metaverse users will be able to seamlessly connect to virtual worlds and experiences from anywhere, at any time, with their smartphones—even in areas where Wi-Fi is not available. Although Wi-Fi is also capable of producing powerfully immersive experiences, it can still suffer from slow data transfer rates and congestion. 5G has proven to be faster than standard Wi-Fi types in several 5G-leading countries, according to analysis by Open Signal, a mobile network analytics firm. 5G towers can also offer comparable data rates to wireline connection but can be installed much more quickly. 5G is vastly superior to previous cellular networks and will enable brands and retailers to provide customers with easily accessible, virtual shopping experiences, powering higher-quality visuals through reliable, fast connection. This could increase the amount of time users spend in the metaverse and improve interaction, loyalty and opportunities for brands to build immersive, shared communities. Metaverse and virtual world usage will drive global data usage by 20X by 2032, according to Credit Suisse. The speed of 5G connectivity will help to support this increase in data usage, and the number of 5G subscriptions—and therefore users who will be able to easily access the metaverse—is already rising rapidly and is set to total nearly 3 billion by 2025, according to Ericsson (see Figure 1).Figure 1. Estimated Global 5G Subscriptions (Mil.) [caption id="attachment_146931" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
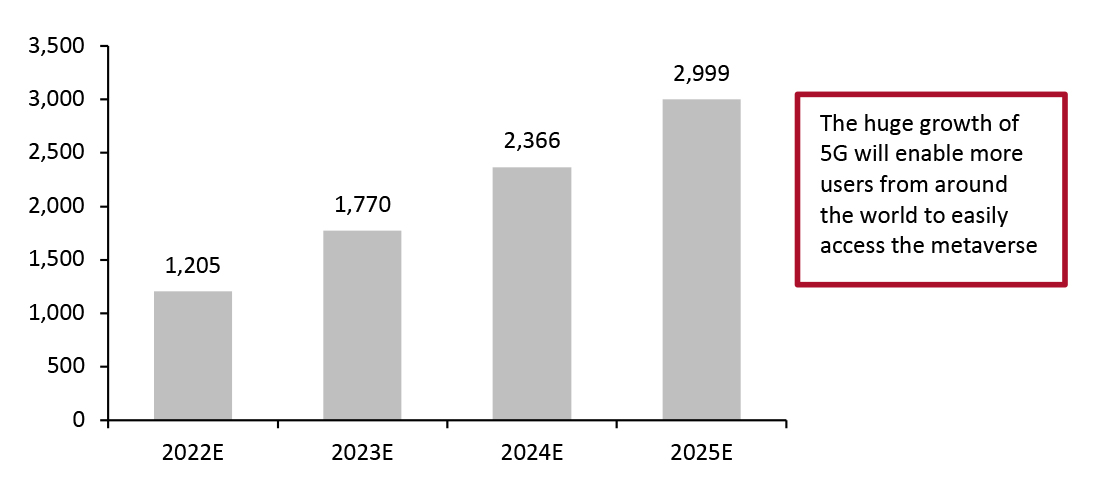 Source: Ericsson[/caption]
Source: Ericsson[/caption]
Building the Metaverse—5G: Coresight Research Analysis
Benefits of 5G in the Metaverse We believe that the global metaverse ecosystem will benefit from 5G in three critical ways:- Simplifying access—Faster data-transfer rates and the use of satellites will enable widespread connectivity and access for users wherever they are, not just in Wi-Fi-accessible areas, leading to growth in the number of metaverse users.
- Powering real-time experiences—5G digital twins will allow developers to replicate physical locations in perfect detail, powering AR experiences. Low latency and high data rates will also support more powerful visuals in AR and VR experiences.
- Supporting increased global data usage—As more users begin to explore the metaverse and build their virtual identities, 5G will also help to combat huge energy consumption amid soaring data usage over the next decade.
- For more about headset and immersive technology, read the previous report in this series, Building Blocks of the Metaverse: Immersive Technologies.
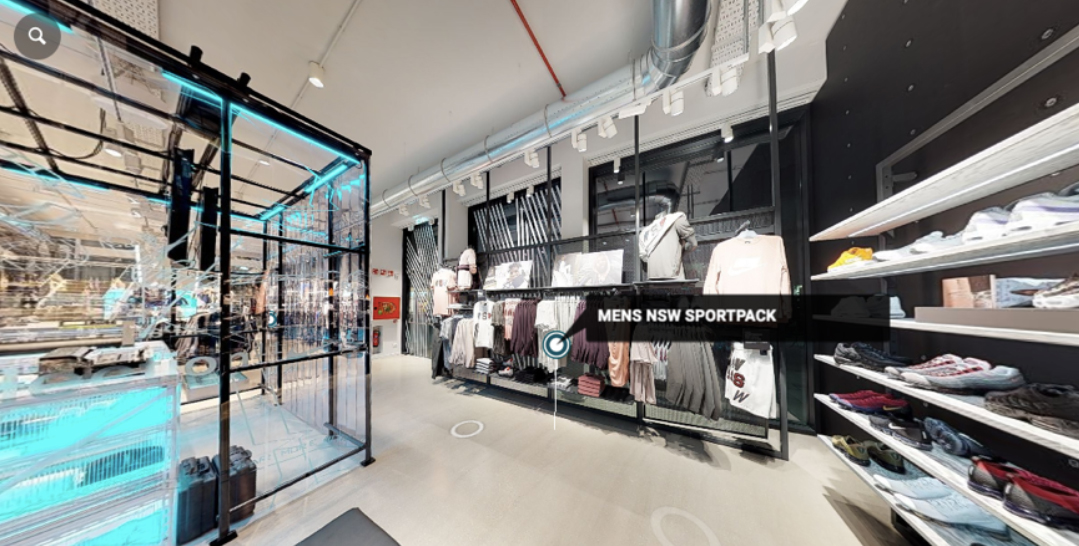 Virtual 3D version of a NIKE store in Milan using 5G digital twins
Virtual 3D version of a NIKE store in Milan using 5G digital twins Source: Matterport [/caption] Supporting Increased Global Data Usage As more people continue to invest more time in digital and virtual environments, global data usage is going to increase significantly. 5G cellular technology has proven to be 90% more energy efficient than 4G networks in terms of energy consumption per unit of traffic, according to Ericsson. Screen time will continue to increase as more users spend hours at a time immersed within virtual experiences. Additionally, while the average person is acclimating to the idea of spending time within a virtual world, the number of avid gamers continues to grow. Global revenue from VR gaming is set to increase from an estimated $1.6 billion in 2022 to $2.4 billion in 2024, according to PwC and Omdia—driving the need for the advanced connectivity and access of 5G. 5G will likely be capable of supporting the metaverse’s data needs over the next decade, but as the total user base grows and use cases evolve along with metaverse technologies and trends, 6G—enabled by 5G—will eventually become available to support even more data usage. Background of 5G and Associated Metaverse-Enabling Technologies General research in 5G technology began as early as 2008, but in 2013, electronics companies Samsung and Huawei both announced major plans to invest heavily in 5G development. In 2016, Verizon began running tests for 5G networks, and soon after, many telecommunications and service companies began forming partnerships to start building out the global 5G network, which started providing coverage in 2019. Although each cellular network generation was a technological marvel at its time, successors have always been much more advanced. 5G has significantly higher transfer speeds than previous cellular networks (see Figure 2).
Figure 2. Comparison of Cellular Network Speeds [wpdatatable id=1963 table_view=regular]
*Megabits per second (one megabit is the equivalent of 1,000 kilobits) **Kilobits per second Source: Coresight Research/Verizon/Qualcomm If the trend holds, 6G should be released sometime around 2030. The 5G buildout will be crucial for enhanced global data-transfer speeds and will provide the building blocks for the eventual 6G network, which could be up to 100 times as fast as 5G. Both networks will support increased global data usage as metaverse activity continues to increase. 5G is made possible by several technologies, including OFDM (orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing) and MIMO (multiple input, multiple output). OFDM OFDM is a form of digital modulation, a method for transmitting data used by cellular networks such as 5G and 4G LTE. In cellular networks using OFDM, information streams are spread among closely spaced narrowband frequencies that are overlapping, rather than a single wideband frequency. In traditional single carrier systems, such as CDMA (code-division multiple access, which previous networks such as 3G are based on), only a single radio frequency is used to transfer bits of information, sent sequentially after one another. With overlapping frequencies in OFDM, users are able to send multiple bits of information across different frequencies, reducing latency and multi-path distortion, and improving efficiency. These factors will be crucial for the metaverse with countless platforms and users interacting—transmitting data—in real time, allowing for multi-user access. 5G will differ from 4G LTE in that it features a specification, 5G NR (New Radio), for a 5G radio access network (RAN) which connects devices such as smartphones to the cloud. 5G NR, using OFDM, will also cover spectrums of waves not utilized by 4G LTE technology, significantly increasing bandwidth to support the increased data usage caused by the metaverse. 5G networks will not solely be limited to new radio waves; they will be homogeneous, making use of both licensed (owned by companies) and unlicensed (free for anyone) bands, improving instantaneous connectivity, interaction and communication in the metaverse. MIMO MIMO is a type of antenna technology that tower companies have been purchasing in large quantities to support 5G infrastructure. Critical for 5G’s speed, MIMO antennas strengthen the link between devices and 5G RANs by using multiple pathways to send OFDM signals. The pathways are not correlated with one another, meaning that networks using MIMO antennas provide the opportunity to transmit several data streams at once. 4G LTE towers operate on basic MIMO technology, whereas antennas in 5G towers will have more components. More complex antennas create a technology known as massive MIMO, a significant increase in spectrum efficiency (he rate at which bits of data can be transmitted to a given number of end users while ensuring quality is maintained). Higher spectrum efficiency will be crucial for improving immersion in the metaverse as many users connect to platforms and experiences from various locations. [caption id="attachment_146933" align="aligncenter" width="699"]
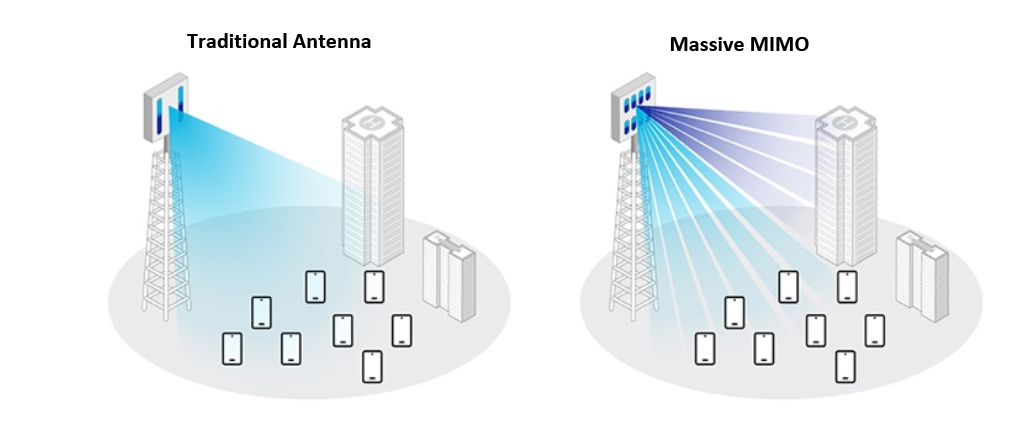 MIMO antenna versus traditional antenna
MIMO antenna versus traditional antenna Source: Samsung [/caption] What Retailers Should Know 5G will make widespread Internet and metaverse access possible for impoverished and rural communities, which previously had not experienced fast-enough data rates for meaningful virtual experiences. The 5G network will also significantly increase the pool of digital customers to areas that were, for whatever reason, previously inaccessible to brands and retailers, transforming the way they shop. New digital customers (from all areas) will also enjoy a number of benefits, all of which support increased virtual and metaverse shopping activity (see Figure 3).
Figure 3. Benefits of 5G for the Digital Customer
| Higher Capacity | Devices in the home, vehicle and pocket can be connected to smart grids in cities to offer benefits for safety, convenience, environmental concerns and easing traffic congestion as users connect to various platforms from wherever they please. |
| Greater Bandwidth | Consumers can download movies and music much more quickly on their phones and make greater use of AR/VR. |
| Lower Latency | The greater responsiveness of virtual worlds will enable new games and improve the gaming experience. |
| Lower Power Consumption | 5G networks promise to offer a 90% reduction in power usage, offering longer battery life and more time to connect to experiences. |
 Data as of May 2, 2022
Data as of May 2, 2022 Source: nPerf [/caption] Examples of Brands and Retailers Leveraging 5G Technology Many retailers have started partnering with service and telecommunications companies to power 5G-enabled AR and VR experiences for customers.
- Dior
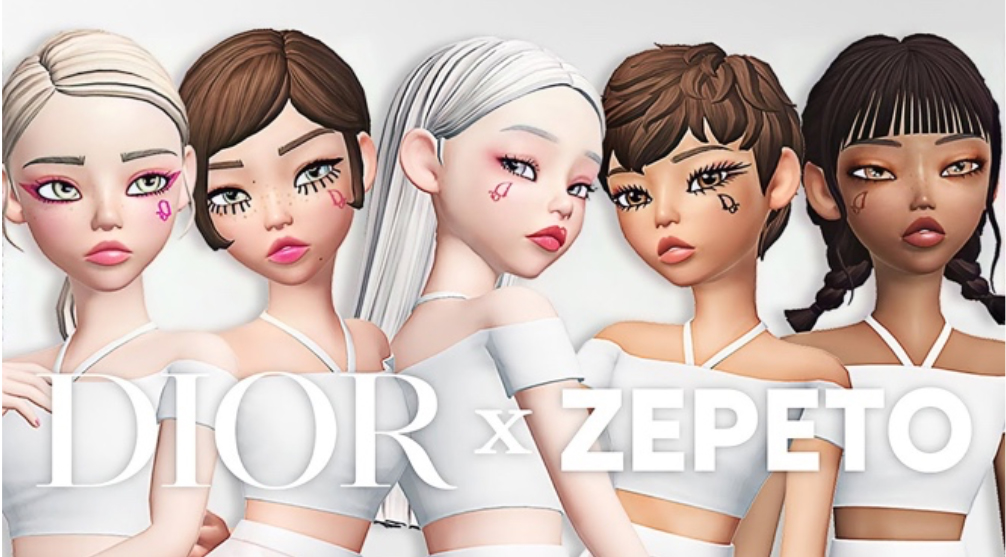 Preview of a Dior makeup tutorial hosted by a Zepeto virtual human
Preview of a Dior makeup tutorial hosted by a Zepeto virtual human Source: Zepeto’s Kaily Idol [/caption] In October 2020, Dior had also formed a partnership with social platform Snap, through which Snapchat users can try on sneakers in an AR experience. After testing the shoes, users are either directed to Dior’s Snapchat profile for more information or directly to its website to make a purchase. As 5G continues to expand, a growing number of digital customers will interact with retailers and brands that do not have physical presences near these customers.
- Lowe’s
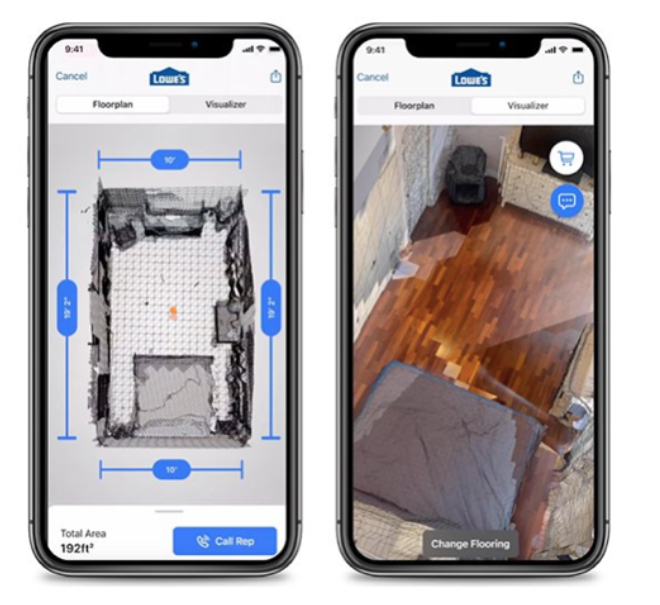 Lowe’s Innovation Labs’ iOS application
Lowe’s Innovation Labs’ iOS application Source: Lowe’s [/caption] In partnership with Microsoft, the lab is also developing in-store project visualization and offering customers the opportunity to visualize theoretical projects using Microsoft’s HoloLens VR headset. 5G networks, faster than even the fastest Wi-Fi networks, will be able to overlay augmented elements and offer project visualization with more accuracy and less delay, and bring this opportunity to distant customers in rural areas. In the future, if the metaverse—as well as cryptocurrencies—continues to gain significant traction, experiences will be interoperable. Customers will be able to maintain elements of their digital identities, tied to cryptocurrency wallets, from AR and VR experiences based on the real world, such as what Lowe’s offers, to fully immersive gaming experiences such as Decentraland or The Sandbox.
What We Think
5G is a powerful cellular network that will enable the metaverse in multiple ways. Its technology will reduce barriers to access for users, power new types of real-time and virtual shopping experiences and support the increase in global data usage that is likely to come with increased virtual activity. Without it, connecting to a virtual experience or world becomes a time-consuming, arduous task that, ultimately, will be a significant hurdle to metaverse user growth. 5G will enable shared community experiences involving consumers all over the world, which increase brand loyalty and interaction and could be completely reinvented through AR and VR experiences. Although cellular network technology is rapidly evolving, with 6G on the horizon, 5G coverage will continue to be important for decades to come, as emerging countries and users in rural areas connect to the Internet at rapid rates for the first time. 5G will connect a massive pool of customers to the global metaverse ecosystem, and understanding how to utilize 5G technology for customer offerings will be crucial for brands and retailers to accessing them instantaneously in virtual settings, no matter where the brand or retailer operates from. We believe 5G will unlock Internet access, increasing the global number of accessible digital customers, by offering faster data speeds. Many retailers and brands are beginning to take advantage of the technology by partnering with telecommunications companies to power virtual 5G experiences for customers. The number of 5G subscriptions—and therefore the number of potential metaverse users—continues to climb, and brands and retailers should begin to study how the technology can help them to access a massive pool of global customers with AR and VR offerings.Appendix: About Coresight Research’s RESET Framework
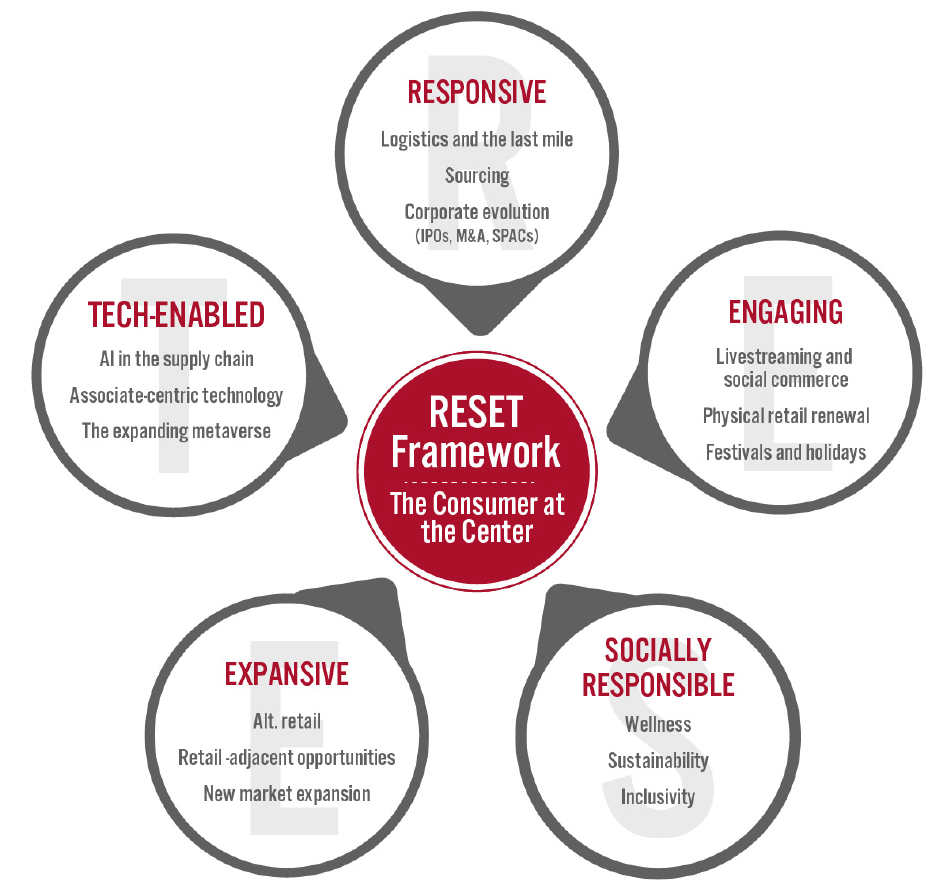
Coresight Research’s RESET framework for change in retail serves as a call to action for retail companies. The framework aggregates the retail trends that our analysts identify as meaningful for 2022 and beyond, as well as our recommendations to capitalize on those trends, around five areas of evolution. To remain relevant and stand equipped for change, we urge retailers to be Responsive, Engaging, Socially responsible, Expansive and Tech-enabled. Emphasizing the need for consumer-centricity, the consumer sits at the center of this framework, with their preferences, behaviors and choices demanding those changes. RESET was ideated as a means to aggregate more than a dozen of our identified retail trends into a higher-level framework. The framework enhances accessibility, serving as an entry point into the longer list of more specific trends that we think should be front of mind for retail companies as they seek to maintain relevance. Retailers can dive into these trends as they cycle through the RESET framework. The components of RESET serve as a template for approaching adaptation in retail. Companies can consolidate processes such as the identification of opportunities, internal capability reviews, competitor analysis and implementation of new processes and competencies around these RESET segments. Through 2022, our research will assist retailers in understanding the drivers of evolution in retail and managing the resulting processes of adaptation. The RESET framework’s constituent trends will form a pillar of our research and analysis through 2022, with our analysts dedicated to exploring these trends in detail. Readers will see this explainer and the RESET framework identifier on further reports as we continue that coverage.Appendix Figure 1. RESET Framework [caption id="attachment_143517" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]