What’s the Story?
Blockchain technology is ubiquitous and low-cost, enabling the sending of funds globally without onerous transaction fees. There are several companies engaged globally in developing blockchain-based solutions to enable the billions of unbanked individuals to make electronic transactions at a low cost.
Why It Matters
Globally, there were 1.7 billion unbanked inhabitants in 2017, representing 31% of the population, according to the World Bank. The financial institution cited the top three reasons for people being unbanked as not having enough money, not believing they need an account and accounts being too expensive. The lack of access to financial services affects peoples’ ability to pay for health care and education, save or send money, or start a business.
Blockchain technology promises to include unbanked individuals. It offers myriad benefits to businesses and consumers around the world, beyond just being the engine that powers cryptocurrencies. We summarize the features and benefits of blockchain technology in Figure 1.
[caption id="attachment_116685" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
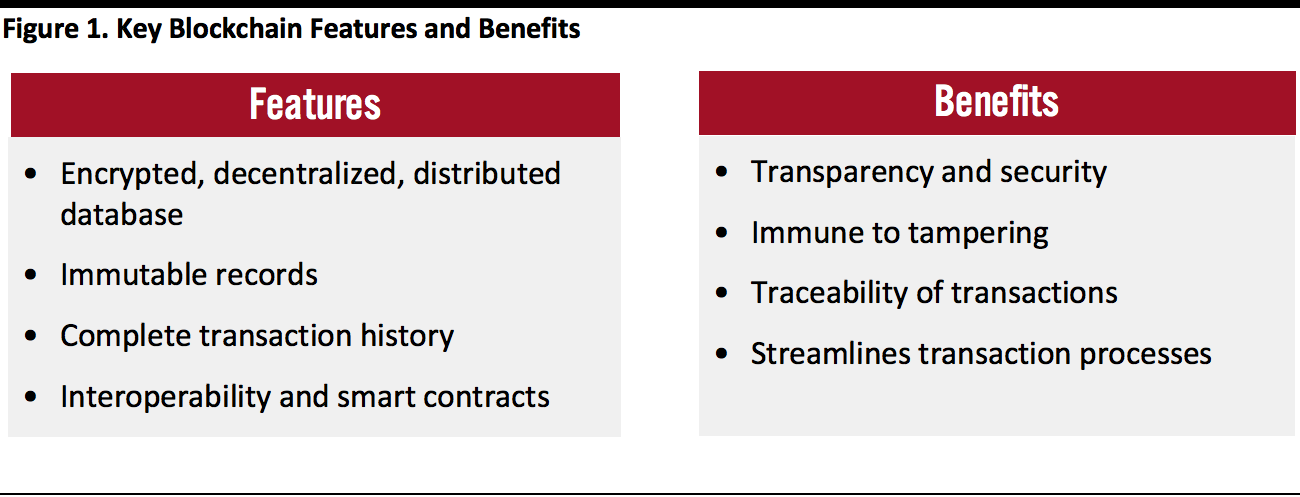 Source: Coresight Research
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Blockchain offers additional benefits for users, including lower costs and greater speed. The technology’s low cost makes it particularly suitable in developing countries, where inhabitants believe they may not be able to afford bank accounts and therefore may not have access to financial services. Other benefits include rapid settlement, streamlined account opening and providing the ability to effect payments digitally.
Companies Using Blockchain for Inclusion
There are many companies developing blockchain solutions worldwide, which can be used to bring low-cost payment services to the world’s population. We outline three examples of such companies below—one each from China, the UK and the US.
Ant Group, based in China, is an affiliate of Alibaba and the parent company of Alipay. Ant Group launched a new brand called AntChain in July 2020, which integrates the company’s existing blockchain-based solutions with other digital technologies, including artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things and secure computation. On September 25, Ant Group launched Trusple (based on “trust made simple”), an AntChain-powered trade and service platform that aims to reduce costs for small and medium-sized enterprises that sell their products and services globally, as well as for the financial institutions that serve them.
Electroneum, based in the UK, provides a digital payment ecosystem that enables anyone to store, send and receive digital funds on a smartphone. The company offers a cryptocurrency called ETN that has over 4 million registered users and is accepted by more than 2,000 merchants in over 140 countries. According to Electroneum, ETN is KYC/AML-compliant, is “one of the greenest cryptocurrencies” and is partnered with NGOs as trusted transaction validators.
Ripple, based in San Francisco, California, uses blockchain technology to enable money to be sent globally. The company’s payments network, called RippleNet, is used commercially today by more than 300 financial institutions in 40 countries across six continents. Ripple also partners with nonprofits and social entrepreneurs to support education, research and technical development, to expand the number of people who participate in the global financial system.
What We Think
Implications for Brands/Retailers
- Retailers should monitor developments in blockchain-based payments to accommodate consumers wishing to use those payment methods.
Implications for Technology Vendors
- Although blockchain technology is ubiquitous, there are still many opportunities to develop new, novel currencies, payment platforms and infrastructure.

 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Blockchain offers additional benefits for users, including lower costs and greater speed. The technology’s low cost makes it particularly suitable in developing countries, where inhabitants believe they may not be able to afford bank accounts and therefore may not have access to financial services. Other benefits include rapid settlement, streamlined account opening and providing the ability to effect payments digitally.
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Blockchain offers additional benefits for users, including lower costs and greater speed. The technology’s low cost makes it particularly suitable in developing countries, where inhabitants believe they may not be able to afford bank accounts and therefore may not have access to financial services. Other benefits include rapid settlement, streamlined account opening and providing the ability to effect payments digitally.