
DIpil Das
In our AI in Retail series, we discuss how artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the way retailers operate and interact with customers. Our proprietary CORE framework highlights the value of AI across four key areas in retail (see Figure 1).
[caption id="attachment_103142" align="aligncenter" width="700"]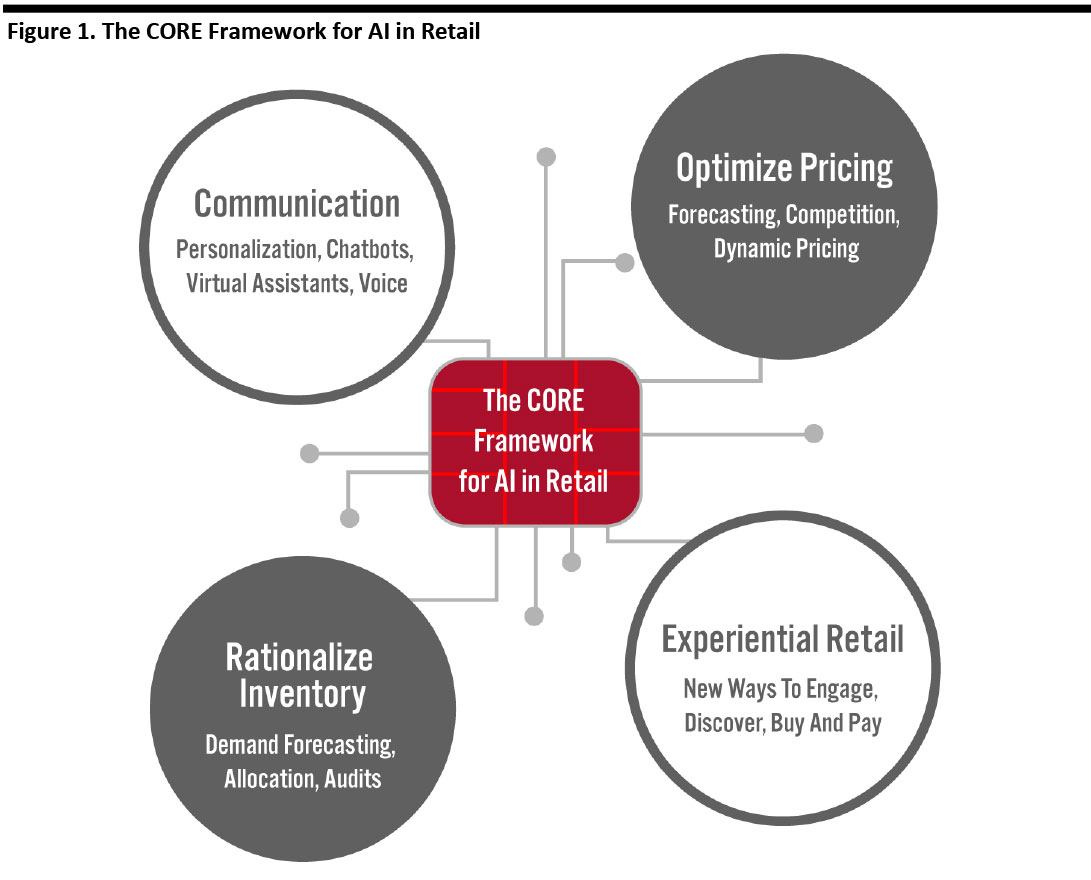 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
In this report, we look at the “R” quadrant: We show how inventory management platforms can leverage computer vision—an application of AI that automates visual information gathering and processing—and discuss the benefits of this technology for retail operations. Selected use cases illustrate that retailers are collaborating with technology providers to roll out computer vision applications.
Computer-Vision Inventory Management and the Advantages It Provides Retailers
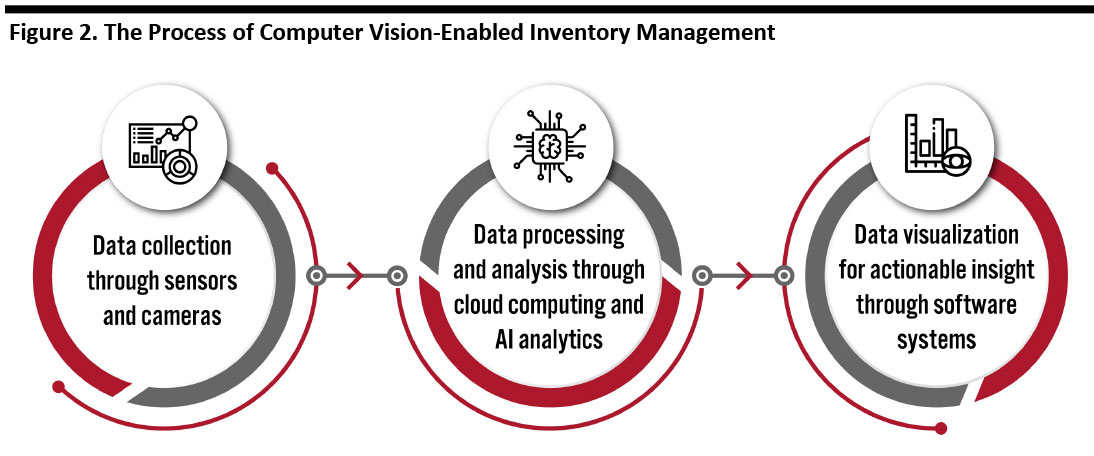
Inventory management systems that employ computer vision comprise a range of technologies:
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
In this report, we look at the “R” quadrant: We show how inventory management platforms can leverage computer vision—an application of AI that automates visual information gathering and processing—and discuss the benefits of this technology for retail operations. Selected use cases illustrate that retailers are collaborating with technology providers to roll out computer vision applications.
Computer-Vision Inventory Management and the Advantages It Provides Retailers
Inventory management systems that employ computer vision comprise a range of technologies:
 Source: Coresight Research [/caption]
By adopting systems that use computer vision, retailers can gain greater visibility of their inventory operations, which should translate into enhanced operational efficiency. Stock can be continuously monitored in real time, enabling retailers to quickly replenish out-of-stock items and track misplaced product. Moreover, the greater availability of data resulting from the use of this technology should generate insight to inform product positioning and promotional strategies.
Use Cases of Computer Vision for Inventory Management in Retail
A number of retailers have started collaborating with technology providers to integrate computer vision systems into their in-store inventory management operations.
Since 2018, Singapore-based technology company Trax has been working with domestic pharmacy chain Watsons, British grocery chain Tesco and Israeli supermarket chain Shufersal to test technology platforms for monitoring in-store stock levels. According to Israeli news source Globes, Shufersal is also planning to deploy robots developed by Trax that are equipped with computer vision technology. The robots would navigate through stores to monitor inventory, complementing the retailer’s system of fixed cameras.
According to Trax, its technology reduced the time taken for a leading grocery retailer to identify and fix out of stocks from 31 hours to nine hours. In also increased on-shelf product availability by 14% within a few weeks of the technology being rolled out.
[caption id="attachment_103144" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
Source: Coresight Research [/caption]
By adopting systems that use computer vision, retailers can gain greater visibility of their inventory operations, which should translate into enhanced operational efficiency. Stock can be continuously monitored in real time, enabling retailers to quickly replenish out-of-stock items and track misplaced product. Moreover, the greater availability of data resulting from the use of this technology should generate insight to inform product positioning and promotional strategies.
Use Cases of Computer Vision for Inventory Management in Retail
A number of retailers have started collaborating with technology providers to integrate computer vision systems into their in-store inventory management operations.
Since 2018, Singapore-based technology company Trax has been working with domestic pharmacy chain Watsons, British grocery chain Tesco and Israeli supermarket chain Shufersal to test technology platforms for monitoring in-store stock levels. According to Israeli news source Globes, Shufersal is also planning to deploy robots developed by Trax that are equipped with computer vision technology. The robots would navigate through stores to monitor inventory, complementing the retailer’s system of fixed cameras.
According to Trax, its technology reduced the time taken for a leading grocery retailer to identify and fix out of stocks from 31 hours to nine hours. In also increased on-shelf product availability by 14% within a few weeks of the technology being rolled out.
[caption id="attachment_103144" align="aligncenter" width="700"]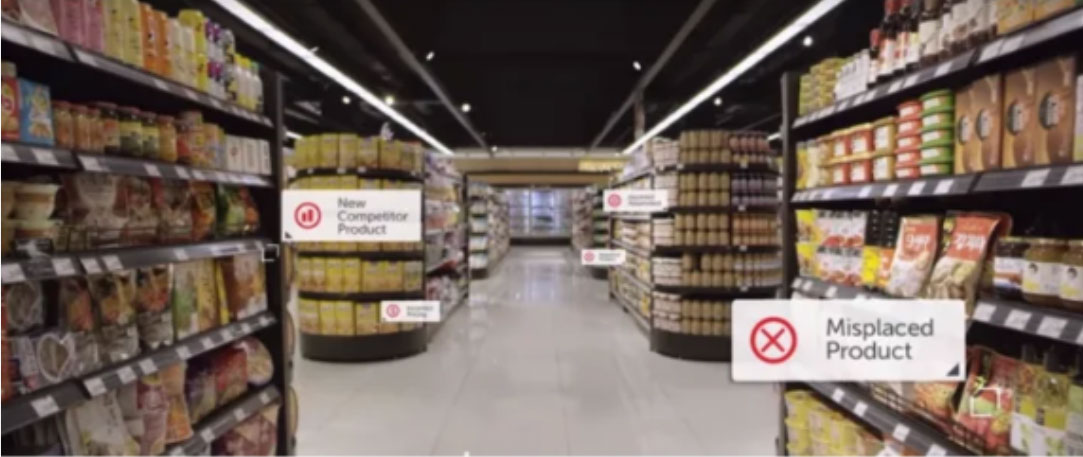 Real-time monitoring of products on shelves through computer vision
Real-time monitoring of products on shelves through computer vision
Source: Trax [/caption] Other notable retailers and technology providers that are testing similar computer vision systems are as follows:
 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
In this report, we look at the “R” quadrant: We show how inventory management platforms can leverage computer vision—an application of AI that automates visual information gathering and processing—and discuss the benefits of this technology for retail operations. Selected use cases illustrate that retailers are collaborating with technology providers to roll out computer vision applications.
Computer-Vision Inventory Management and the Advantages It Provides Retailers
Inventory management systems that employ computer vision comprise a range of technologies:
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
In this report, we look at the “R” quadrant: We show how inventory management platforms can leverage computer vision—an application of AI that automates visual information gathering and processing—and discuss the benefits of this technology for retail operations. Selected use cases illustrate that retailers are collaborating with technology providers to roll out computer vision applications.
Computer-Vision Inventory Management and the Advantages It Provides Retailers
Inventory management systems that employ computer vision comprise a range of technologies:
- Cameras and sensors collect relevant data—for example, images of product displays on shelves in store.
- This information is transmitted to the cloud for storing and processing.
- AI-powered analytics software makes sense of the data collected.
- Data visualization platforms show the results of this analysis to the decision-makers in retail operations, who can access the information through desktop computers or portable devices such as smartphones.
 Source: Coresight Research [/caption]
By adopting systems that use computer vision, retailers can gain greater visibility of their inventory operations, which should translate into enhanced operational efficiency. Stock can be continuously monitored in real time, enabling retailers to quickly replenish out-of-stock items and track misplaced product. Moreover, the greater availability of data resulting from the use of this technology should generate insight to inform product positioning and promotional strategies.
Use Cases of Computer Vision for Inventory Management in Retail
A number of retailers have started collaborating with technology providers to integrate computer vision systems into their in-store inventory management operations.
Since 2018, Singapore-based technology company Trax has been working with domestic pharmacy chain Watsons, British grocery chain Tesco and Israeli supermarket chain Shufersal to test technology platforms for monitoring in-store stock levels. According to Israeli news source Globes, Shufersal is also planning to deploy robots developed by Trax that are equipped with computer vision technology. The robots would navigate through stores to monitor inventory, complementing the retailer’s system of fixed cameras.
According to Trax, its technology reduced the time taken for a leading grocery retailer to identify and fix out of stocks from 31 hours to nine hours. In also increased on-shelf product availability by 14% within a few weeks of the technology being rolled out.
[caption id="attachment_103144" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
Source: Coresight Research [/caption]
By adopting systems that use computer vision, retailers can gain greater visibility of their inventory operations, which should translate into enhanced operational efficiency. Stock can be continuously monitored in real time, enabling retailers to quickly replenish out-of-stock items and track misplaced product. Moreover, the greater availability of data resulting from the use of this technology should generate insight to inform product positioning and promotional strategies.
Use Cases of Computer Vision for Inventory Management in Retail
A number of retailers have started collaborating with technology providers to integrate computer vision systems into their in-store inventory management operations.
Since 2018, Singapore-based technology company Trax has been working with domestic pharmacy chain Watsons, British grocery chain Tesco and Israeli supermarket chain Shufersal to test technology platforms for monitoring in-store stock levels. According to Israeli news source Globes, Shufersal is also planning to deploy robots developed by Trax that are equipped with computer vision technology. The robots would navigate through stores to monitor inventory, complementing the retailer’s system of fixed cameras.
According to Trax, its technology reduced the time taken for a leading grocery retailer to identify and fix out of stocks from 31 hours to nine hours. In also increased on-shelf product availability by 14% within a few weeks of the technology being rolled out.
[caption id="attachment_103144" align="aligncenter" width="700"] Real-time monitoring of products on shelves through computer vision
Real-time monitoring of products on shelves through computer vision Source: Trax [/caption] Other notable retailers and technology providers that are testing similar computer vision systems are as follows:
- US retail giant Walmart is developing proprietary computer vision technology for inventory management.
- US supermarket operator Giant Eagle is collaborating with technology provider Simbe Robotics to introduce inventory-monitoring robots in stores.
- At NRF 2020, technology company Sensormatic showcased its system of cameras powered by computer vision, which it claims helps store associates to monitor the level of stock on shelves in real time.