What’s the Story?
5G networks are being turned up in the US (with major carrier having most recently launched 5G wireless services in August 2020, following Verizon in April 2019 and AT&T in December 2018) and around the world. Stakeholders in supply chains can now begin to leverage the capabilities of these leading-edge networks to make their operations smarter and more efficient.
Why It Matters
Of the major
benefits that 5G technology offers for retailers and consumers—higher capacity, greater bandwidth, lower latency and lower power consumption—capacity is key, since it enables a larger number of items to be connected to the network. The technology offers more robust product-tracking capabilities, from the factory to the transportation vehicles to the physical store.
While there are deployments of fixed 5G broadband services for indoor use, there are other, cheaper technologies available. For example, Wi-Fi chips cost a couple of dollars, compared to the $70–80 cost of 5G chips in mid-2020 (although this price has decreased steadily and is expected to continue to fall, according to
DigiTimes. However, an obvious but essential feature of 5G (and all wireless services) is that it is a mobile technology, enabling devices in virtually any location, indoors or outdoors, to connect to the network and benefit from its capabilities.
5G Wireless in the Supply Chain: In Detail
Capacity Is Key
5G technology complements and enables the Internet of Things (IoT), which refers to the network of physical objects that enable technologies to connect to the Internet. 5G offers an enormous increase in the number of devices that can be connected to the network—to 1 million devices versus around 4,000 in a 4G network. This enables a wide variety of objects (including inventory and vehicles) to connect with and communicate within the network.
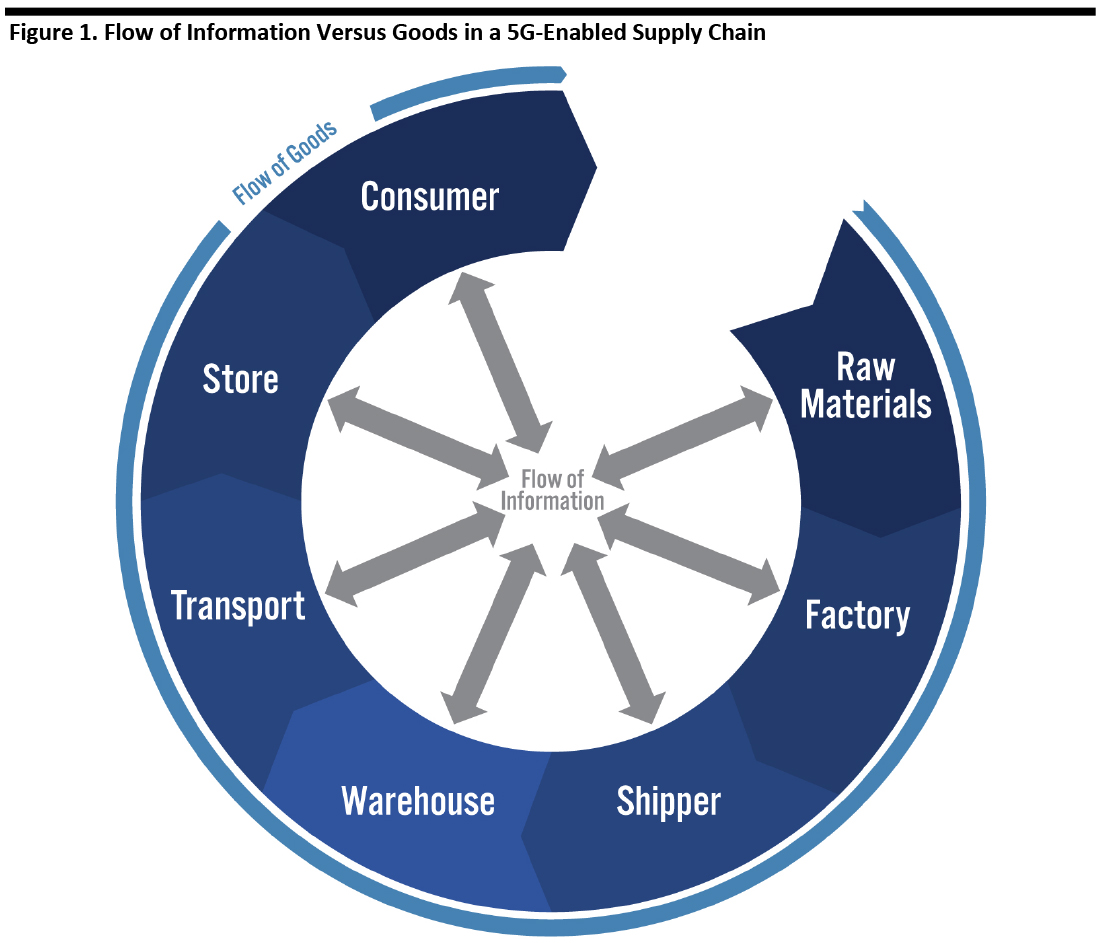
5G therefore facilitates a multidirectional flow of information within the retail supply chain, with all participants sharing data at all stages, while the raw materials are transformed into finished products by making their way through a traditional set of stages before ultimately making it to the consumer (see Figure 1).
Retailers can use the shared information through the supply chain to inform their inventory allocation and warehouse configuration. Similarly, suppliers and manufacturers are able to obtain demand forecasts from retailers, covering the initial shipment and subsequent replenishment. In the event of a disruption to manufacturing or transport, the 5G-enabled multidirectional flow of information means that the retailer can be notified in a timely manner and take action accordingly.
The enormous amount of capacity that 5G networks offers means that supply chain participants can obtain data and communicate with millions of suppliers, factories, warehouses and trucks and other delivery vehicles, in real time.
[caption id="attachment_120844" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
 Source: Coresight Research
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
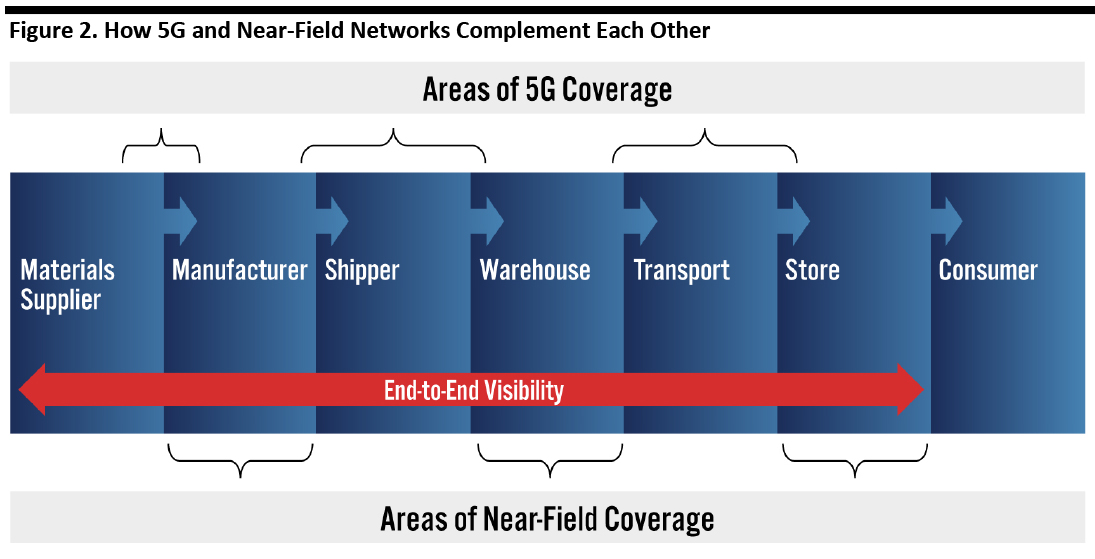
End-to-End Coverage
5G wireless, combined with other near-field technologies as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, provides end-to-end coverage of the supply chain (see Figure 2).
[caption id="attachment_120845" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
 Source: Coresight Research
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Sensors are a key component of IoT nodes, as they collect data on a variety of parameters and pass them on to inform decision-making and necessary actions. Examples of data that sensors can collect include the following:
- Location—both indoors and outdoors
- Environmental—temperature, humidity and vibration
- Materials--used in manufacturing
- Manufacturing—methods, time and equipment used
These parameters are important in areas such as grocery and pharmaceuticals, where the cold chain must be monitored and maintained, and tracking the location of vehicles is integral to loss prevention.
Additional Benefits
5G technology offers additional benefits to retailers and supply chain participants beyond the supply chain:
- The high bandwidth of 5G wireless enables video monitoring of inventory, assets and employees.
- Cities are evaluating the use of 5G for real-time traffic management, which would enable a reduction in transport times, thus benefiting retailers.
- The lower latency of 5G networks is beneficial for time-sensitive applications—such as the transport of temperature-sensitive goods (e.g., vaccinations packed in dry ice).
Outlook for 5G-Enabled Supply Chains
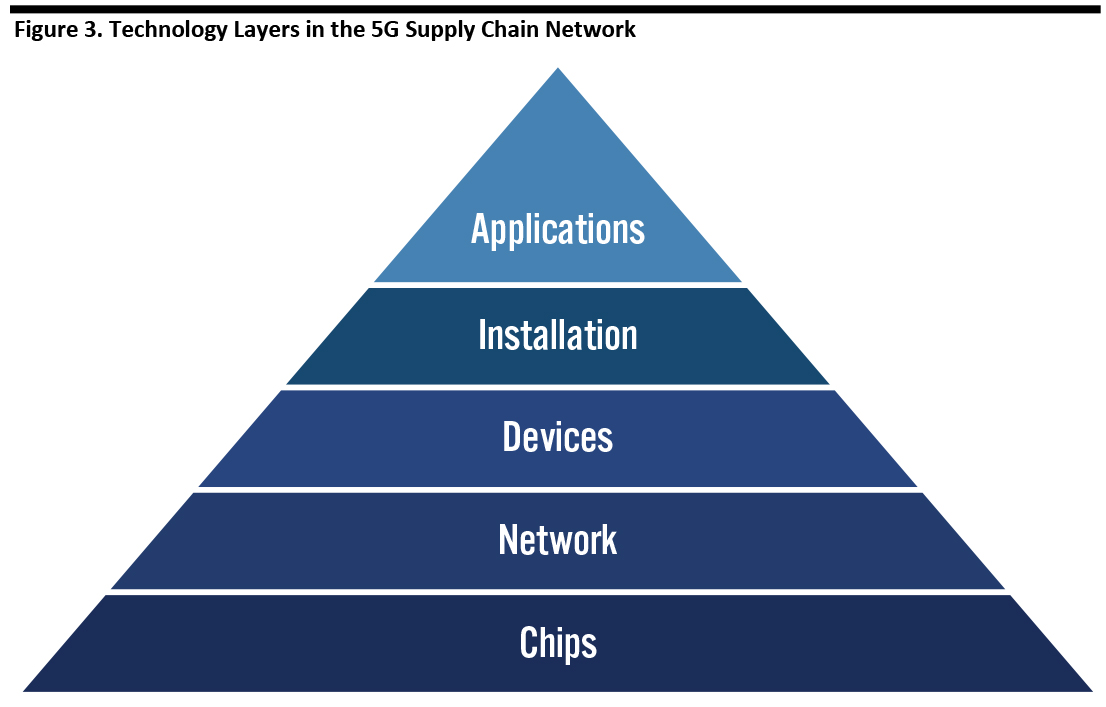
There are five layers of technology in a 5G supply chain network: chips, network, devices, installation and applications. Thus far, the chips have been developed, and the networks have been turned on. Devices are also now available (i.e., handsets are now available for consumers, although transportation-industry experts expect it to take a couple of years before vehicle fleets are fully covered by 5G). Now, software applications need to be developed and supply chain software needs to be updated to manage the data from the new devices.
[caption id="attachment_120846" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
 Source: Coresight Research
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
What We Think
The greater capacity of 5G networks offers enormous potential for all participants in the supply chain—including manufacturers, transporters and retailers—to gain real-time visibility into the location and state of their goods wherever they are. The network infrastructure has now largely been turned on, opening the door for the deployment of devices and software that make use of the strengths of 5G.
Implications for Brands/Retailers
- Brands and retailers need to understand the power of 5G technology in the supply chain and follow its development so as to plan for the necessary changes to IT platforms to adopt 5G once it is available.
- Brands and retailers also need to visualize the changes to business processes and data analytics that are required to benefit from new data sources.
Implications for Technology Vendors
- Since this is an emerging technology, there are still numerous opportunities for technology developers all along the value chain.
- There are opportunities for the companies developing new, previously never-before-envisioned products and business models that leverage 5G technology.

 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
End-to-End Coverage
5G wireless, combined with other near-field technologies as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, provides end-to-end coverage of the supply chain (see Figure 2).
[caption id="attachment_120845" align="aligncenter" width="700"]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
End-to-End Coverage
5G wireless, combined with other near-field technologies as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, provides end-to-end coverage of the supply chain (see Figure 2).
[caption id="attachment_120845" align="aligncenter" width="700"] Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Sensors are a key component of IoT nodes, as they collect data on a variety of parameters and pass them on to inform decision-making and necessary actions. Examples of data that sensors can collect include the following:
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Sensors are a key component of IoT nodes, as they collect data on a variety of parameters and pass them on to inform decision-making and necessary actions. Examples of data that sensors can collect include the following:
 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]