
Nitheesh NH
The upcoming 5G technology—the fifth generation of mobile connectivity—is promising to deliver faster speeds and more capacity and responsiveness compared with previous generations of mobile technology. 5G will offer peak speeds of 10–20 gigabits per second, plus latency—the amount of time between the command and the related action—of less than
1 millisecond and the ability to connect one million devices per square kilometer (the equivalent of 0.39 square miles).
[caption id="attachment_82866" align="aligncenter" width="720"]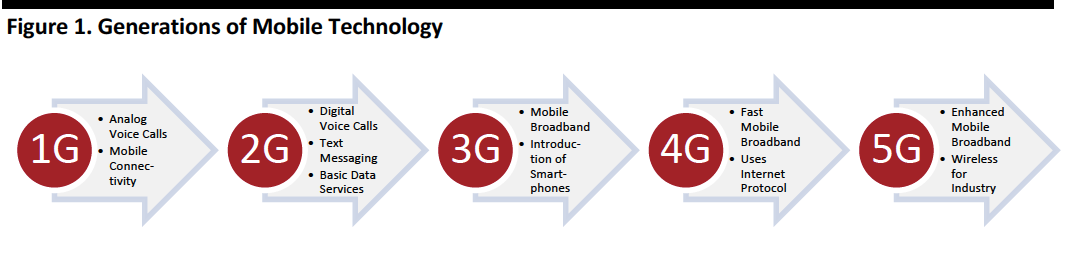 Source: Ofcom[/caption]
5G’s technical characteristics should make it extremely fast and reliable, improving dramatically the existing uses of mobile connectivity and enabling new applications. The increased efficiency also means that 5G will require less energy consumption than previous mobile technologies to run the same functions, resulting in cost reductions.
[caption id="attachment_82868" align="aligncenter" width="720"]
Source: Ofcom[/caption]
5G’s technical characteristics should make it extremely fast and reliable, improving dramatically the existing uses of mobile connectivity and enabling new applications. The increased efficiency also means that 5G will require less energy consumption than previous mobile technologies to run the same functions, resulting in cost reductions.
[caption id="attachment_82868" align="aligncenter" width="720"]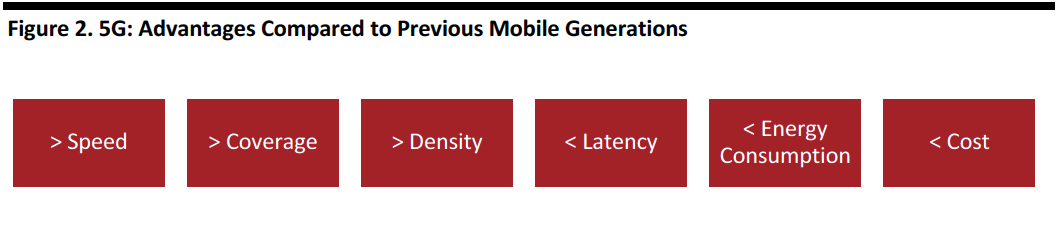 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Impact of 5G in Retail: Improved Operations and New Use Cases to Generate Additional Revenue
5G promises to have a significant impact on retail, improving and expanding existing applications and powering new use cases. The application of the technology to retail operations is expected to translate into additional revenue for the industry—particularly from e-commerce operations, in which the enhanced connectivity will lead to more straightforward online shopping journeys, but also from a more extensive and efficient use of in-store technology, which should also encourage sale conversion.
A Boost for E-Commerce
5G will make the Internet more accessible, making it easier, more efficient and convenient to shop online. More shoppers will be able to browse e-commerce websites faster. E-commerce portals will become more engaging and visual, with greater use of images and short videos. Mobile commerce will become particularly convenient as the improved speed, reduced latency and increased connection density delivered by the technology will enable consumers to shop on the go more easily.
Delivering an efficient and hassle-free mobile shopping experience is becoming increasingly important for retailers, as mobile commerce is gaining a growing share of e-commerce while browsing visits are becoming shorter: Retailers need to deliver information instantly to prompt a shopping decision and provide a straightforward checkout. In the US, online visits through smartphones grew 89% in the three-year period through 2017, compared to a decline of 17% and 30% in visits through desktop computers and tablets, respectively, according to technology firm Adobe. At the same time, smartphone visits are becoming shorter—by almost 10% in the US in the period 2015–17, according to Adobe—making it even more pressing to optimize the browsing experience.
Because of 5G’s improved access and connectivity, more shoppers are expected to be online and to complete purchases faster. Adobe notes that there is a proven relationship between online conversion and connection speed. Faster speed should translate into a boost of revenue for e-commerce. The tech firm estimates that 5G could bring US online retailers an additional
$12 billion per year by 2021.
[caption id="attachment_82870" align="aligncenter" width="720"]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Impact of 5G in Retail: Improved Operations and New Use Cases to Generate Additional Revenue
5G promises to have a significant impact on retail, improving and expanding existing applications and powering new use cases. The application of the technology to retail operations is expected to translate into additional revenue for the industry—particularly from e-commerce operations, in which the enhanced connectivity will lead to more straightforward online shopping journeys, but also from a more extensive and efficient use of in-store technology, which should also encourage sale conversion.
A Boost for E-Commerce
5G will make the Internet more accessible, making it easier, more efficient and convenient to shop online. More shoppers will be able to browse e-commerce websites faster. E-commerce portals will become more engaging and visual, with greater use of images and short videos. Mobile commerce will become particularly convenient as the improved speed, reduced latency and increased connection density delivered by the technology will enable consumers to shop on the go more easily.
Delivering an efficient and hassle-free mobile shopping experience is becoming increasingly important for retailers, as mobile commerce is gaining a growing share of e-commerce while browsing visits are becoming shorter: Retailers need to deliver information instantly to prompt a shopping decision and provide a straightforward checkout. In the US, online visits through smartphones grew 89% in the three-year period through 2017, compared to a decline of 17% and 30% in visits through desktop computers and tablets, respectively, according to technology firm Adobe. At the same time, smartphone visits are becoming shorter—by almost 10% in the US in the period 2015–17, according to Adobe—making it even more pressing to optimize the browsing experience.
Because of 5G’s improved access and connectivity, more shoppers are expected to be online and to complete purchases faster. Adobe notes that there is a proven relationship between online conversion and connection speed. Faster speed should translate into a boost of revenue for e-commerce. The tech firm estimates that 5G could bring US online retailers an additional
$12 billion per year by 2021.
[caption id="attachment_82870" align="aligncenter" width="720"]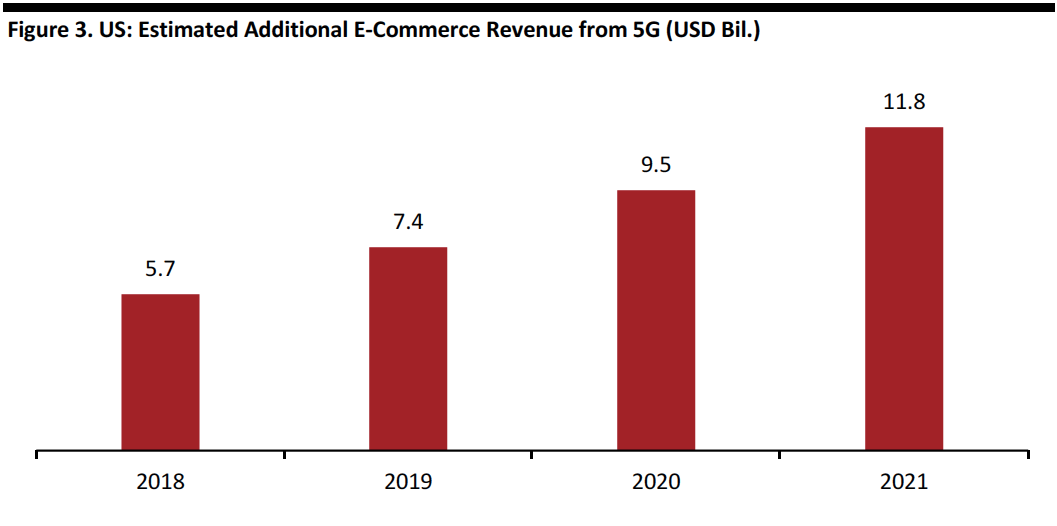 Source: Adobe Analytics[/caption]
Unleashing IoT Capabilities
Source: Adobe Analytics[/caption]
Unleashing IoT Capabilities
 Source: GSMA[/caption]
The increased density promised by 5G technology will enable connectivity of larger IoT ecosystems. 5G’s faster speed and reduced latency will improve existing IoT systems and give rise to new use cases such as fully automated ecosystems in which self-driving vehicles will operate effectively.
5G is likely to support a new generation of IoT systems in which connected devices that communicate within the network will work together with intelligent IoT nodes that will use AI and machine learning to make autonomous decisions based on the information transmitted by other nodes within the system.
In retail, such 5G-powered IoT systems will be able to support operations including smart manufacturing, sourcing, supply chain, fulfillment, last-mile delivery and technology deployment in brick-and-mortar stores.
[caption id="attachment_82873" align="aligncenter" width="720"]
Source: GSMA[/caption]
The increased density promised by 5G technology will enable connectivity of larger IoT ecosystems. 5G’s faster speed and reduced latency will improve existing IoT systems and give rise to new use cases such as fully automated ecosystems in which self-driving vehicles will operate effectively.
5G is likely to support a new generation of IoT systems in which connected devices that communicate within the network will work together with intelligent IoT nodes that will use AI and machine learning to make autonomous decisions based on the information transmitted by other nodes within the system.
In retail, such 5G-powered IoT systems will be able to support operations including smart manufacturing, sourcing, supply chain, fulfillment, last-mile delivery and technology deployment in brick-and-mortar stores.
[caption id="attachment_82873" align="aligncenter" width="720"]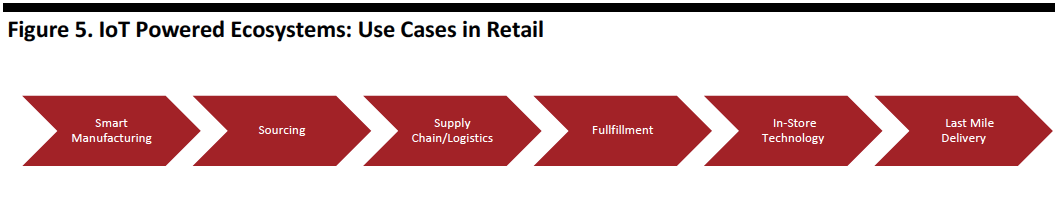 Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
For example, smart manufacturing with technologies such as 3D printing could become more widespread as the improved connectivity of IoT systems through 5G will be able to process production commands to the machines more effectively based on the customization data gathered from customers. Another example might be the deployment of connected self-driving vehicles, which could become more extensive in warehouses or for order deliveries thanks to 5G’s faster speed and reduced latency; this should make their operation safer in environments such as urbanized areas, in which autonomous vehicles will have to be able to avoid impacts with human-operated vehicles. As part of large IoT ecosystems, autonomous vehicles could
also communicate with warehouses and stores for stock replenishment or could deliver items to shoppers.
In brick-and-mortar stores, 5G could enable the implementation of enhanced IoT systems thanks to the faster data transmission and possibility of connecting a higher number of sensors and devices processing more data, given the greater connection density that the technology allows. For example, the resulting enhanced IoT systems would be able to detect more effectively when items are running out; data analytics powered by AI could process information faster and trigger commands to IoT devices to react to a given situation more effectively, for instance by prompting faster automated shelf replenishment.
In-store shopper engagement could become more intense, with greater customization of the shopping experience due to more effective use of data-heavy facial recognition technology and smart sensors that—with the support of 5G—detect, react and communicate faster with shoppers based on their behavior when browsing the store. Improved communication between connected devices such as AI-powered robots and the surrounding environment could make the deployment of robotics to assist shoppers in store common practice. For example, robots could bring items to the changing room for customers to try on upon shoppers’ request triggered by voice or touchscreen command through smart mirrors or smartphones. The improvement of the shopping experience resulting from the deployment of more effective
in-store technology should reflect positively on sales conversion.
Empowering Existing and New Use Cases for AI and Reality Technology in Retail
The enhanced mobile connectivity that 5G will provide should unleash the full potential of data-intense applications in retail, such as AI and machine learning, and of reality technologies including augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR). The applications of these technologies in retail is not new, but at present their use is restricted by limitations of the existing mobile communication systems, unable to process enough data at an adequate speed to provide a straightforward user experience.
With 5G, e-commerce apps could be able to leverage more data-intense AI and machine learning-powered functions to provide a more targeted and customized shopper experience. Chatbots and virtual personal assistants will become more effective thanks to the quantity and quality of shoppers’ information that AI and machine learning technology will be able to process at a faster speed due to 5G’s enhanced connectivity.
5G might enable a more widespread deployment of new-generation AR and VR that will make it possible for shoppers to virtually try on clothing or experience the use of products such as sports equipment or services such as holidays. The enhanced connectivity will improve the quality of the content in AR and VR, and will make it possible for shoppers in a dense space—such as a busy store outlet—to experience the technology simultaneously with other shoppers, without compromising the quality of the experience.
Thanks to its superior data processing capability, 5G could give way to brand new applications. One possible new use case in retail could be tactile Internet, the ability to emulate the sensation of touch through the interaction with connected devices. This could be used for online shopping, where the technology will make it possible to use connected devices such as wearables to feel the fabrics of the garment that the shopper is looking to buy, or to virtually try on clothing items.
Commercial Introduction Expected by 2020
The commercial introduction of 5G networks is expected to be completed between 2019 and 2020. Announcements of the upcoming commercialization of 5G mobile services have been made by South Korea’s telecommunication operator KT, which stated at the mobile industry exhibition MWC 2019 that it would introduce 5G mobile services in March 2019 (at the time of writing, press sources reported launch of commercial 5G services by KT in South Korea starting early April 2019, in collaboration with telecommunications firm Ericsson). The company showcased 5G trial services at the PyeongChang Winter Olympics Games in February 2018. In Japan, mobile phone operator NTT DoCoMo is planning to launch 5G mobile communication service in 2020, while telecommunications firm China Mobile will launch 5G smartphones in the first half of 2019, as part of the push for 5G precommercial trials in 2019 and commercialization by 2020, China Daily reported in November 2018.
In the US, telecommunications company Verizon will launch its 5G network in Chicago and Minneapolis on April 11, 2019; starting from March 14, 2019, the company made available to preorder an add-on device—the 5G Moto Mod—to turn Moto Z3 devices into 5G-enabled smartphones, the company announced on March 13, 2019. AT&T, T-Mobile, Sprint, US Cellular, C Spire and Charter are other operators in the US that are either planning a launch or testing the technology in 2019–20.
Below, we list selected Android smartphones manufacturers that have announced upcoming releases of 5G-enabled devices.
[caption id="attachment_82874" align="aligncenter" width="720"]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
For example, smart manufacturing with technologies such as 3D printing could become more widespread as the improved connectivity of IoT systems through 5G will be able to process production commands to the machines more effectively based on the customization data gathered from customers. Another example might be the deployment of connected self-driving vehicles, which could become more extensive in warehouses or for order deliveries thanks to 5G’s faster speed and reduced latency; this should make their operation safer in environments such as urbanized areas, in which autonomous vehicles will have to be able to avoid impacts with human-operated vehicles. As part of large IoT ecosystems, autonomous vehicles could
also communicate with warehouses and stores for stock replenishment or could deliver items to shoppers.
In brick-and-mortar stores, 5G could enable the implementation of enhanced IoT systems thanks to the faster data transmission and possibility of connecting a higher number of sensors and devices processing more data, given the greater connection density that the technology allows. For example, the resulting enhanced IoT systems would be able to detect more effectively when items are running out; data analytics powered by AI could process information faster and trigger commands to IoT devices to react to a given situation more effectively, for instance by prompting faster automated shelf replenishment.
In-store shopper engagement could become more intense, with greater customization of the shopping experience due to more effective use of data-heavy facial recognition technology and smart sensors that—with the support of 5G—detect, react and communicate faster with shoppers based on their behavior when browsing the store. Improved communication between connected devices such as AI-powered robots and the surrounding environment could make the deployment of robotics to assist shoppers in store common practice. For example, robots could bring items to the changing room for customers to try on upon shoppers’ request triggered by voice or touchscreen command through smart mirrors or smartphones. The improvement of the shopping experience resulting from the deployment of more effective
in-store technology should reflect positively on sales conversion.
Empowering Existing and New Use Cases for AI and Reality Technology in Retail
The enhanced mobile connectivity that 5G will provide should unleash the full potential of data-intense applications in retail, such as AI and machine learning, and of reality technologies including augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR). The applications of these technologies in retail is not new, but at present their use is restricted by limitations of the existing mobile communication systems, unable to process enough data at an adequate speed to provide a straightforward user experience.
With 5G, e-commerce apps could be able to leverage more data-intense AI and machine learning-powered functions to provide a more targeted and customized shopper experience. Chatbots and virtual personal assistants will become more effective thanks to the quantity and quality of shoppers’ information that AI and machine learning technology will be able to process at a faster speed due to 5G’s enhanced connectivity.
5G might enable a more widespread deployment of new-generation AR and VR that will make it possible for shoppers to virtually try on clothing or experience the use of products such as sports equipment or services such as holidays. The enhanced connectivity will improve the quality of the content in AR and VR, and will make it possible for shoppers in a dense space—such as a busy store outlet—to experience the technology simultaneously with other shoppers, without compromising the quality of the experience.
Thanks to its superior data processing capability, 5G could give way to brand new applications. One possible new use case in retail could be tactile Internet, the ability to emulate the sensation of touch through the interaction with connected devices. This could be used for online shopping, where the technology will make it possible to use connected devices such as wearables to feel the fabrics of the garment that the shopper is looking to buy, or to virtually try on clothing items.
Commercial Introduction Expected by 2020
The commercial introduction of 5G networks is expected to be completed between 2019 and 2020. Announcements of the upcoming commercialization of 5G mobile services have been made by South Korea’s telecommunication operator KT, which stated at the mobile industry exhibition MWC 2019 that it would introduce 5G mobile services in March 2019 (at the time of writing, press sources reported launch of commercial 5G services by KT in South Korea starting early April 2019, in collaboration with telecommunications firm Ericsson). The company showcased 5G trial services at the PyeongChang Winter Olympics Games in February 2018. In Japan, mobile phone operator NTT DoCoMo is planning to launch 5G mobile communication service in 2020, while telecommunications firm China Mobile will launch 5G smartphones in the first half of 2019, as part of the push for 5G precommercial trials in 2019 and commercialization by 2020, China Daily reported in November 2018.
In the US, telecommunications company Verizon will launch its 5G network in Chicago and Minneapolis on April 11, 2019; starting from March 14, 2019, the company made available to preorder an add-on device—the 5G Moto Mod—to turn Moto Z3 devices into 5G-enabled smartphones, the company announced on March 13, 2019. AT&T, T-Mobile, Sprint, US Cellular, C Spire and Charter are other operators in the US that are either planning a launch or testing the technology in 2019–20.
Below, we list selected Android smartphones manufacturers that have announced upcoming releases of 5G-enabled devices.
[caption id="attachment_82874" align="aligncenter" width="720"]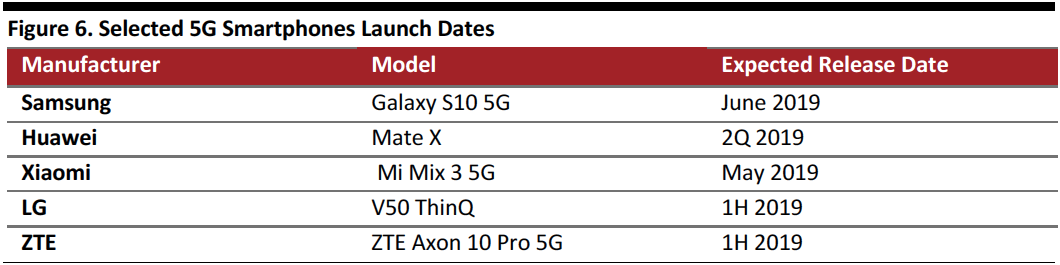 Sources: Tomsguide.com/Techadvisor.co.uk/Oled-info.com[/caption]
Strong Expansion Expected for the 5G Sector
The market for 5G is expected to expand rapidly in the next few years:
Sources: Tomsguide.com/Techadvisor.co.uk/Oled-info.com[/caption]
Strong Expansion Expected for the 5G Sector
The market for 5G is expected to expand rapidly in the next few years:
 Source: 5G Americas[/caption]
Key Insights
The introduction of 5G is promising to significantly advance the deployment of disruptive technologies in retail, providing the capability in terms of connection speed, responsiveness and density that is needed to enable operational effectiveness in existing applications—as well as the development of new use cases—which are expected to dramatically improve the consumer experience and to further the growth of the retail industry.
Source: 5G Americas[/caption]
Key Insights
The introduction of 5G is promising to significantly advance the deployment of disruptive technologies in retail, providing the capability in terms of connection speed, responsiveness and density that is needed to enable operational effectiveness in existing applications—as well as the development of new use cases—which are expected to dramatically improve the consumer experience and to further the growth of the retail industry.
 Source: Ofcom[/caption]
5G’s technical characteristics should make it extremely fast and reliable, improving dramatically the existing uses of mobile connectivity and enabling new applications. The increased efficiency also means that 5G will require less energy consumption than previous mobile technologies to run the same functions, resulting in cost reductions.
[caption id="attachment_82868" align="aligncenter" width="720"]
Source: Ofcom[/caption]
5G’s technical characteristics should make it extremely fast and reliable, improving dramatically the existing uses of mobile connectivity and enabling new applications. The increased efficiency also means that 5G will require less energy consumption than previous mobile technologies to run the same functions, resulting in cost reductions.
[caption id="attachment_82868" align="aligncenter" width="720"] Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Impact of 5G in Retail: Improved Operations and New Use Cases to Generate Additional Revenue
5G promises to have a significant impact on retail, improving and expanding existing applications and powering new use cases. The application of the technology to retail operations is expected to translate into additional revenue for the industry—particularly from e-commerce operations, in which the enhanced connectivity will lead to more straightforward online shopping journeys, but also from a more extensive and efficient use of in-store technology, which should also encourage sale conversion.
A Boost for E-Commerce
5G will make the Internet more accessible, making it easier, more efficient and convenient to shop online. More shoppers will be able to browse e-commerce websites faster. E-commerce portals will become more engaging and visual, with greater use of images and short videos. Mobile commerce will become particularly convenient as the improved speed, reduced latency and increased connection density delivered by the technology will enable consumers to shop on the go more easily.
Delivering an efficient and hassle-free mobile shopping experience is becoming increasingly important for retailers, as mobile commerce is gaining a growing share of e-commerce while browsing visits are becoming shorter: Retailers need to deliver information instantly to prompt a shopping decision and provide a straightforward checkout. In the US, online visits through smartphones grew 89% in the three-year period through 2017, compared to a decline of 17% and 30% in visits through desktop computers and tablets, respectively, according to technology firm Adobe. At the same time, smartphone visits are becoming shorter—by almost 10% in the US in the period 2015–17, according to Adobe—making it even more pressing to optimize the browsing experience.
Because of 5G’s improved access and connectivity, more shoppers are expected to be online and to complete purchases faster. Adobe notes that there is a proven relationship between online conversion and connection speed. Faster speed should translate into a boost of revenue for e-commerce. The tech firm estimates that 5G could bring US online retailers an additional
$12 billion per year by 2021.
[caption id="attachment_82870" align="aligncenter" width="720"]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
Impact of 5G in Retail: Improved Operations and New Use Cases to Generate Additional Revenue
5G promises to have a significant impact on retail, improving and expanding existing applications and powering new use cases. The application of the technology to retail operations is expected to translate into additional revenue for the industry—particularly from e-commerce operations, in which the enhanced connectivity will lead to more straightforward online shopping journeys, but also from a more extensive and efficient use of in-store technology, which should also encourage sale conversion.
A Boost for E-Commerce
5G will make the Internet more accessible, making it easier, more efficient and convenient to shop online. More shoppers will be able to browse e-commerce websites faster. E-commerce portals will become more engaging and visual, with greater use of images and short videos. Mobile commerce will become particularly convenient as the improved speed, reduced latency and increased connection density delivered by the technology will enable consumers to shop on the go more easily.
Delivering an efficient and hassle-free mobile shopping experience is becoming increasingly important for retailers, as mobile commerce is gaining a growing share of e-commerce while browsing visits are becoming shorter: Retailers need to deliver information instantly to prompt a shopping decision and provide a straightforward checkout. In the US, online visits through smartphones grew 89% in the three-year period through 2017, compared to a decline of 17% and 30% in visits through desktop computers and tablets, respectively, according to technology firm Adobe. At the same time, smartphone visits are becoming shorter—by almost 10% in the US in the period 2015–17, according to Adobe—making it even more pressing to optimize the browsing experience.
Because of 5G’s improved access and connectivity, more shoppers are expected to be online and to complete purchases faster. Adobe notes that there is a proven relationship between online conversion and connection speed. Faster speed should translate into a boost of revenue for e-commerce. The tech firm estimates that 5G could bring US online retailers an additional
$12 billion per year by 2021.
[caption id="attachment_82870" align="aligncenter" width="720"] Source: Adobe Analytics[/caption]
Unleashing IoT Capabilities
Source: Adobe Analytics[/caption]
Unleashing IoT Capabilities
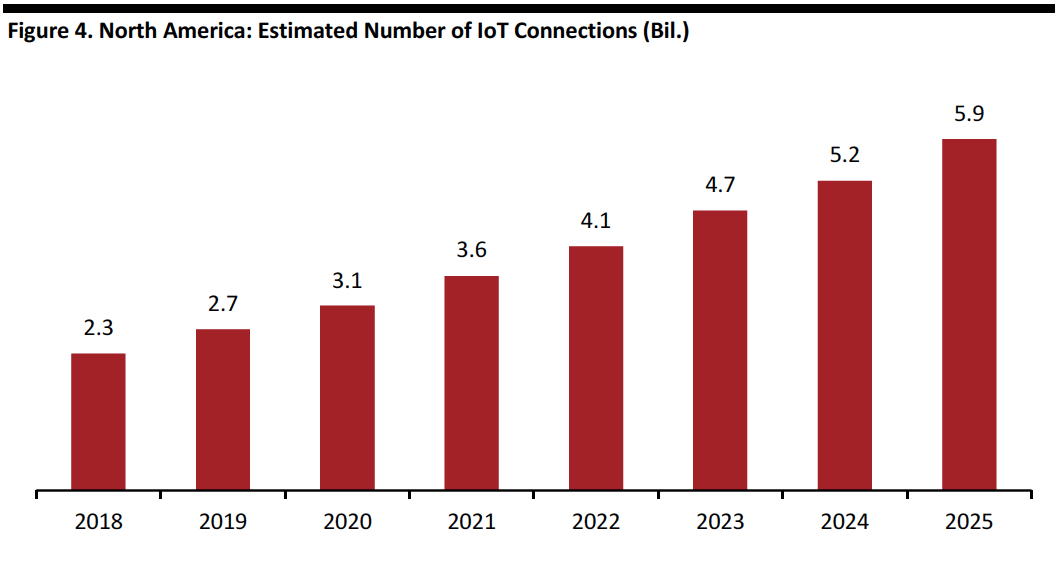
5G will contribute to the expansion of applications and the scalability of IoT systems, enabling more devices to be connected and interact as part of a network. It is expected that 3.6 billion more devices will be connected in IoT ecosystems in North America by 2025, as shown below.
[caption id="attachment_82871" align="aligncenter" width="720"] Source: GSMA[/caption]
The increased density promised by 5G technology will enable connectivity of larger IoT ecosystems. 5G’s faster speed and reduced latency will improve existing IoT systems and give rise to new use cases such as fully automated ecosystems in which self-driving vehicles will operate effectively.
5G is likely to support a new generation of IoT systems in which connected devices that communicate within the network will work together with intelligent IoT nodes that will use AI and machine learning to make autonomous decisions based on the information transmitted by other nodes within the system.
In retail, such 5G-powered IoT systems will be able to support operations including smart manufacturing, sourcing, supply chain, fulfillment, last-mile delivery and technology deployment in brick-and-mortar stores.
[caption id="attachment_82873" align="aligncenter" width="720"]
Source: GSMA[/caption]
The increased density promised by 5G technology will enable connectivity of larger IoT ecosystems. 5G’s faster speed and reduced latency will improve existing IoT systems and give rise to new use cases such as fully automated ecosystems in which self-driving vehicles will operate effectively.
5G is likely to support a new generation of IoT systems in which connected devices that communicate within the network will work together with intelligent IoT nodes that will use AI and machine learning to make autonomous decisions based on the information transmitted by other nodes within the system.
In retail, such 5G-powered IoT systems will be able to support operations including smart manufacturing, sourcing, supply chain, fulfillment, last-mile delivery and technology deployment in brick-and-mortar stores.
[caption id="attachment_82873" align="aligncenter" width="720"] Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
For example, smart manufacturing with technologies such as 3D printing could become more widespread as the improved connectivity of IoT systems through 5G will be able to process production commands to the machines more effectively based on the customization data gathered from customers. Another example might be the deployment of connected self-driving vehicles, which could become more extensive in warehouses or for order deliveries thanks to 5G’s faster speed and reduced latency; this should make their operation safer in environments such as urbanized areas, in which autonomous vehicles will have to be able to avoid impacts with human-operated vehicles. As part of large IoT ecosystems, autonomous vehicles could
also communicate with warehouses and stores for stock replenishment or could deliver items to shoppers.
In brick-and-mortar stores, 5G could enable the implementation of enhanced IoT systems thanks to the faster data transmission and possibility of connecting a higher number of sensors and devices processing more data, given the greater connection density that the technology allows. For example, the resulting enhanced IoT systems would be able to detect more effectively when items are running out; data analytics powered by AI could process information faster and trigger commands to IoT devices to react to a given situation more effectively, for instance by prompting faster automated shelf replenishment.
In-store shopper engagement could become more intense, with greater customization of the shopping experience due to more effective use of data-heavy facial recognition technology and smart sensors that—with the support of 5G—detect, react and communicate faster with shoppers based on their behavior when browsing the store. Improved communication between connected devices such as AI-powered robots and the surrounding environment could make the deployment of robotics to assist shoppers in store common practice. For example, robots could bring items to the changing room for customers to try on upon shoppers’ request triggered by voice or touchscreen command through smart mirrors or smartphones. The improvement of the shopping experience resulting from the deployment of more effective
in-store technology should reflect positively on sales conversion.
Empowering Existing and New Use Cases for AI and Reality Technology in Retail
The enhanced mobile connectivity that 5G will provide should unleash the full potential of data-intense applications in retail, such as AI and machine learning, and of reality technologies including augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR). The applications of these technologies in retail is not new, but at present their use is restricted by limitations of the existing mobile communication systems, unable to process enough data at an adequate speed to provide a straightforward user experience.
With 5G, e-commerce apps could be able to leverage more data-intense AI and machine learning-powered functions to provide a more targeted and customized shopper experience. Chatbots and virtual personal assistants will become more effective thanks to the quantity and quality of shoppers’ information that AI and machine learning technology will be able to process at a faster speed due to 5G’s enhanced connectivity.
5G might enable a more widespread deployment of new-generation AR and VR that will make it possible for shoppers to virtually try on clothing or experience the use of products such as sports equipment or services such as holidays. The enhanced connectivity will improve the quality of the content in AR and VR, and will make it possible for shoppers in a dense space—such as a busy store outlet—to experience the technology simultaneously with other shoppers, without compromising the quality of the experience.
Thanks to its superior data processing capability, 5G could give way to brand new applications. One possible new use case in retail could be tactile Internet, the ability to emulate the sensation of touch through the interaction with connected devices. This could be used for online shopping, where the technology will make it possible to use connected devices such as wearables to feel the fabrics of the garment that the shopper is looking to buy, or to virtually try on clothing items.
Commercial Introduction Expected by 2020
The commercial introduction of 5G networks is expected to be completed between 2019 and 2020. Announcements of the upcoming commercialization of 5G mobile services have been made by South Korea’s telecommunication operator KT, which stated at the mobile industry exhibition MWC 2019 that it would introduce 5G mobile services in March 2019 (at the time of writing, press sources reported launch of commercial 5G services by KT in South Korea starting early April 2019, in collaboration with telecommunications firm Ericsson). The company showcased 5G trial services at the PyeongChang Winter Olympics Games in February 2018. In Japan, mobile phone operator NTT DoCoMo is planning to launch 5G mobile communication service in 2020, while telecommunications firm China Mobile will launch 5G smartphones in the first half of 2019, as part of the push for 5G precommercial trials in 2019 and commercialization by 2020, China Daily reported in November 2018.
In the US, telecommunications company Verizon will launch its 5G network in Chicago and Minneapolis on April 11, 2019; starting from March 14, 2019, the company made available to preorder an add-on device—the 5G Moto Mod—to turn Moto Z3 devices into 5G-enabled smartphones, the company announced on March 13, 2019. AT&T, T-Mobile, Sprint, US Cellular, C Spire and Charter are other operators in the US that are either planning a launch or testing the technology in 2019–20.
Below, we list selected Android smartphones manufacturers that have announced upcoming releases of 5G-enabled devices.
[caption id="attachment_82874" align="aligncenter" width="720"]
Source: Coresight Research[/caption]
For example, smart manufacturing with technologies such as 3D printing could become more widespread as the improved connectivity of IoT systems through 5G will be able to process production commands to the machines more effectively based on the customization data gathered from customers. Another example might be the deployment of connected self-driving vehicles, which could become more extensive in warehouses or for order deliveries thanks to 5G’s faster speed and reduced latency; this should make their operation safer in environments such as urbanized areas, in which autonomous vehicles will have to be able to avoid impacts with human-operated vehicles. As part of large IoT ecosystems, autonomous vehicles could
also communicate with warehouses and stores for stock replenishment or could deliver items to shoppers.
In brick-and-mortar stores, 5G could enable the implementation of enhanced IoT systems thanks to the faster data transmission and possibility of connecting a higher number of sensors and devices processing more data, given the greater connection density that the technology allows. For example, the resulting enhanced IoT systems would be able to detect more effectively when items are running out; data analytics powered by AI could process information faster and trigger commands to IoT devices to react to a given situation more effectively, for instance by prompting faster automated shelf replenishment.
In-store shopper engagement could become more intense, with greater customization of the shopping experience due to more effective use of data-heavy facial recognition technology and smart sensors that—with the support of 5G—detect, react and communicate faster with shoppers based on their behavior when browsing the store. Improved communication between connected devices such as AI-powered robots and the surrounding environment could make the deployment of robotics to assist shoppers in store common practice. For example, robots could bring items to the changing room for customers to try on upon shoppers’ request triggered by voice or touchscreen command through smart mirrors or smartphones. The improvement of the shopping experience resulting from the deployment of more effective
in-store technology should reflect positively on sales conversion.
Empowering Existing and New Use Cases for AI and Reality Technology in Retail
The enhanced mobile connectivity that 5G will provide should unleash the full potential of data-intense applications in retail, such as AI and machine learning, and of reality technologies including augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR). The applications of these technologies in retail is not new, but at present their use is restricted by limitations of the existing mobile communication systems, unable to process enough data at an adequate speed to provide a straightforward user experience.
With 5G, e-commerce apps could be able to leverage more data-intense AI and machine learning-powered functions to provide a more targeted and customized shopper experience. Chatbots and virtual personal assistants will become more effective thanks to the quantity and quality of shoppers’ information that AI and machine learning technology will be able to process at a faster speed due to 5G’s enhanced connectivity.
5G might enable a more widespread deployment of new-generation AR and VR that will make it possible for shoppers to virtually try on clothing or experience the use of products such as sports equipment or services such as holidays. The enhanced connectivity will improve the quality of the content in AR and VR, and will make it possible for shoppers in a dense space—such as a busy store outlet—to experience the technology simultaneously with other shoppers, without compromising the quality of the experience.
Thanks to its superior data processing capability, 5G could give way to brand new applications. One possible new use case in retail could be tactile Internet, the ability to emulate the sensation of touch through the interaction with connected devices. This could be used for online shopping, where the technology will make it possible to use connected devices such as wearables to feel the fabrics of the garment that the shopper is looking to buy, or to virtually try on clothing items.
Commercial Introduction Expected by 2020
The commercial introduction of 5G networks is expected to be completed between 2019 and 2020. Announcements of the upcoming commercialization of 5G mobile services have been made by South Korea’s telecommunication operator KT, which stated at the mobile industry exhibition MWC 2019 that it would introduce 5G mobile services in March 2019 (at the time of writing, press sources reported launch of commercial 5G services by KT in South Korea starting early April 2019, in collaboration with telecommunications firm Ericsson). The company showcased 5G trial services at the PyeongChang Winter Olympics Games in February 2018. In Japan, mobile phone operator NTT DoCoMo is planning to launch 5G mobile communication service in 2020, while telecommunications firm China Mobile will launch 5G smartphones in the first half of 2019, as part of the push for 5G precommercial trials in 2019 and commercialization by 2020, China Daily reported in November 2018.
In the US, telecommunications company Verizon will launch its 5G network in Chicago and Minneapolis on April 11, 2019; starting from March 14, 2019, the company made available to preorder an add-on device—the 5G Moto Mod—to turn Moto Z3 devices into 5G-enabled smartphones, the company announced on March 13, 2019. AT&T, T-Mobile, Sprint, US Cellular, C Spire and Charter are other operators in the US that are either planning a launch or testing the technology in 2019–20.
Below, we list selected Android smartphones manufacturers that have announced upcoming releases of 5G-enabled devices.
[caption id="attachment_82874" align="aligncenter" width="720"] Sources: Tomsguide.com/Techadvisor.co.uk/Oled-info.com[/caption]
Strong Expansion Expected for the 5G Sector
The market for 5G is expected to expand rapidly in the next few years:
Sources: Tomsguide.com/Techadvisor.co.uk/Oled-info.com[/caption]
Strong Expansion Expected for the 5G Sector
The market for 5G is expected to expand rapidly in the next few years:
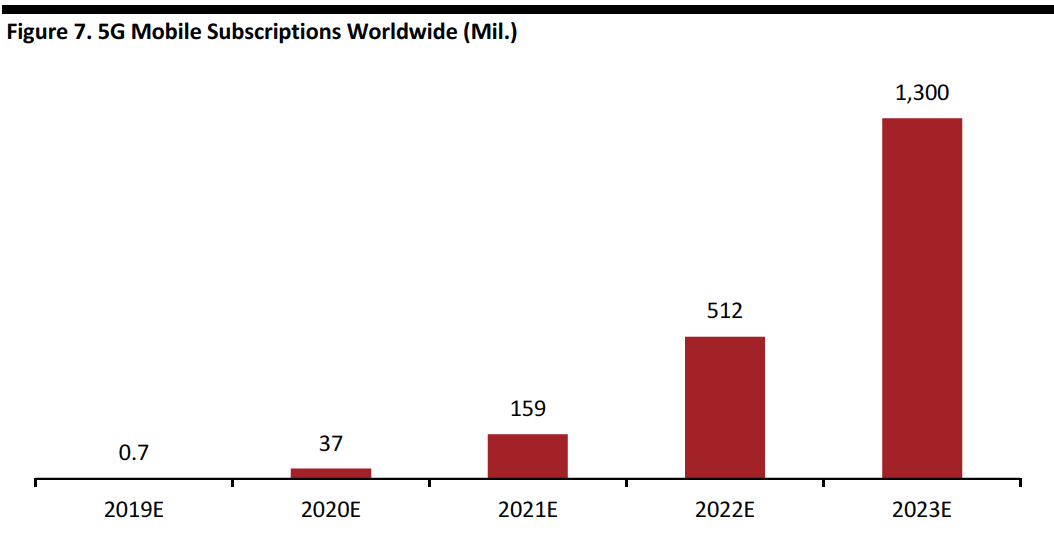
- The number of 5G mobile subscriptions worldwide should reach 1.3 billion units by 2023, according to estimates from trade organization 5G Americas.
- With 1.4 billion units, trade body GSMA forecasts 5G will account for 15% of all connections globally, excluding cellular IoT, by 2025.
- By 2025, there will be 401 million 5G connections in North America, according to specialist publication FierceWireless; and there will be 1.3 billion 5G users in China, according to market-research firm iResearch.
- Global spending on 5G mobile infrastructure is predicted to grow to $2.3 billion by 2021 from just $60 million in 2019, according to data firms IHS and Statista.
 Source: 5G Americas[/caption]
Key Insights
The introduction of 5G is promising to significantly advance the deployment of disruptive technologies in retail, providing the capability in terms of connection speed, responsiveness and density that is needed to enable operational effectiveness in existing applications—as well as the development of new use cases—which are expected to dramatically improve the consumer experience and to further the growth of the retail industry.
Source: 5G Americas[/caption]
Key Insights
The introduction of 5G is promising to significantly advance the deployment of disruptive technologies in retail, providing the capability in terms of connection speed, responsiveness and density that is needed to enable operational effectiveness in existing applications—as well as the development of new use cases—which are expected to dramatically improve the consumer experience and to further the growth of the retail industry.